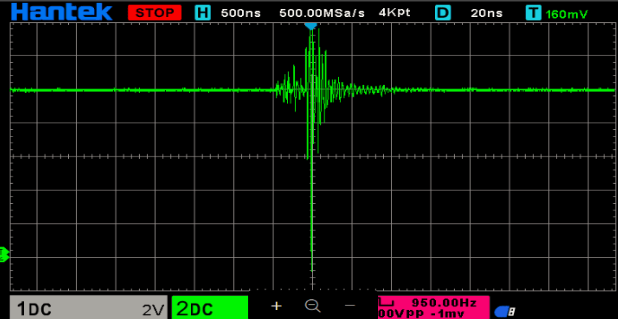
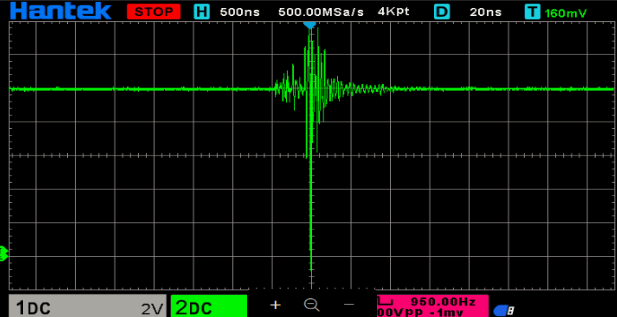
Hello everyone,
I'm working on a data logger project using an ESP32 microcontroller. I have successfully interfaced the following components:
- Temperature Sensor(NTC)
- Current Sensor
- Voltage Sensor
- RTC Module (DS1307)-->I2c
- SD Card Module--->SPI
- Bluetooth Module
Observations:
- The SD card works fine when interfaced with the temperature, voltage, current sensors, and Bluetooth module.
- The RTC module (DS1307) also works correctly when used with the temperature, voltage, current sensors, and Bluetooth module.
Issue:
When I use the RTC and SD card together, I encounter the following problems:
- The SD card gets corrupted after some time.
- The RTC shows incorrect date and time during operation.
Additional Details:
- Both the SD card and RTC modules work perfectly in standalone tests.
- The issue only arises when both components are used simultaneously.
#include <esp_task_wdt.h>
#include "Measurements.h"
#include "SDcard.h"
#include "RTClib.h"
#include "Wire.h"
#include <string.h>
DS1307 rtc;
String Date = " ";
String Time = " ";
//Pin
#define currentSensor 33
#define voltageSensor 32
#define temperatureSensor 35
#define WDT_TIMEOUT 3
#define LED 26
#define LED2 10
#define BUILTIN_LED 2
#define timeIntervalForBT 1000
#define interrupt_pin 34
int sensorPin = 13;
// Time specific
#define timeIntervalForBT 1000
unsigned long startTime;
unsigned long lastTime;
uint64_t lastTick = 0;
uint64_t diff = 0;
// Flags
bool SDCAvailable = false;
bool logging = false;
// Global Vars
File file;
String filename = "/datalog.csv";
int kmph =0;
// debug
bool stateL = false;
//SWS
int td=0;
float a=0;
int present =1;
int prev =1;
int present_Time = 0;
int prev_Time=0;
//Speed
volatile uint16_t call_counter = 0;
volatile uint16_t counter = 0;
uint32_t last_interrupt_time = 0;
uint32_t last_rising_time = 0;
uint32_t rising_diff = 0;
DateTime rtc_get_time() {
return rtc.now();
}
// Function to check RTC connection by attempting communication
bool checkRTCConnection() {
Wire.beginTransmission(0x68); // DS1307 RTC I2C address is 0x68
uint8_t error = Wire.endTransmission();
// If there is no error, the RTC is connected
return (error == 0);
}
// Function to initialize the RTC
void initializeRTC() {
if (!rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("RTC initialization failed! Check connections.");
return; // Don't halt execution; allow reconnection attempts
}
if (!rtc.isrunning()) {
Serial.println("RTC is not running. Setting current time...");
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__))); // Set RTC to compile time
Serial.println("RTC time has been set.");
}
}
void IRAM_ATTR isr(){
//interrupt function for speed
// delayMicroseconds(10);
// digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
call_counter++;
uint32_t current_time = millis();
uint32_t interrupt_diff = current_time - last_interrupt_time;
last_interrupt_time = millis();
if (interrupt_diff < 10){
return;
}
delayMicroseconds(10);
if (digitalRead(interrupt_pin) == 0){
return;
}
// digitalWrite(onboard_led, !(digitalRead(onboard_led)));
rising_diff = millis() - last_rising_time;
counter++;
last_rising_time = millis();
}
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
esp_task_wdt_init(WDT_TIMEOUT, true);
esp_task_wdt_add(NULL);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial2.begin(9600);
pinMode(temperatureSensor,INPUT);
pinMode(voltageSensor,INPUT);
pinMode(currentSensor,INPUT);
pinMode(interrupt_pin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(BUILTIN_LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED2, OUTPUT);
attachInterrupt(interrupt_pin, isr, FALLING);
initializeRTC();
startSD();
// initial values
startTime = millis();
startLogging();
}
void startSD(){
int e = SD_init();
// int e = 0;
if (e == 0) {
SDCAvailable = true;
} else {
showError(e);
}
getFileName();
}
void loop() {
// Serial2.print("Current");
// Serial2.println(calculate_Current());
// Serial2.print("Voltage");
// Serial2.println(calculate_Voltage());
// Serial.print("ADC");
// Serial2.println(analogRead(33));
// Serial2.print("Temperature");
// Serial2.println(calculate_temperature());
Serial2.print("SWS");
Serial2.println(calculate_speed(rising_diff));
if (!checkRTCConnection()) {
Date = "NA";
Time = "NA";
// Serial.println("RTC lost connection! Displaying NA...");
} else {
// If RTC is connected, fetch the current time
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Format the date and time as strings
Date = String(now.year()) + "/" + String(now.month()) + "/" + String(now.day());
Time = String(now.hour()) + ":" + String(now.minute()) + ":" + String(now.second());
}
Serial2.println(Date);
Serial2.println(Time);
if(logging){
unsigned long curTime = millis() - startTime;
unsigned long displayCurTime = curTime / 1000;
if(SD_openWrite(filename, calculate_Voltage(), calculate_Current(), calculate_temperature(), calculate_speed(rising_diff),Date,Time, curTime)){
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
digitalWrite(BUILTIN_LED, HIGH);
esp_task_wdt_reset();
} else {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BUILTIN_LED, LOW);
SD_init();
}
if (curTime > (lastTime + timeIntervalForBT)) {
// bluetooth
// Serial2.printf("#data,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%lu,%lu\n", calculate_Voltage(), calculate_Current(), calculate_temperature(), SWS(), displayCurTime);
lastTime = curTime;
}
esp_task_wdt_reset();
}
}
void showError(int i) {
Serial.println(i);
}
bool setFileName(String _fn){
Serial.println("Saving file as: " + _fn);
if (SD_setFileName(_fn)){
filename = "/" + _fn + ".csv";
}
}
void getFileName(){
String filenameFromSD = SD_getFileName();
filename = (filenameFromSD == " ")? "/datalog.csv" : filenameFromSD;
}
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
void startLogging(){
Serial.println("Starting logging");
if(SD_writeFirstLine(filename)){
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BUILTIN_LED, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
digitalWrite(BUILTIN_LED, LOW);
}
logging = true;
// if (SDCAvailable) { file = SD_openFile(filename); }
startTime = millis();
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
}
void stopLogging(){
Serial.println("Stopped logging");
logging = false;
digitalWrite(BUILTIN_LED, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
// if (SD_closeFile(file)){ Serial.println("file closed"); }
// else { Serial.println("unable to close file");}
}
void countPulse(){
uint64_t tdiff = millis() - lastTick;
if (tdiff > 100){
diff = tdiff;
}
lastTick = millis();
}