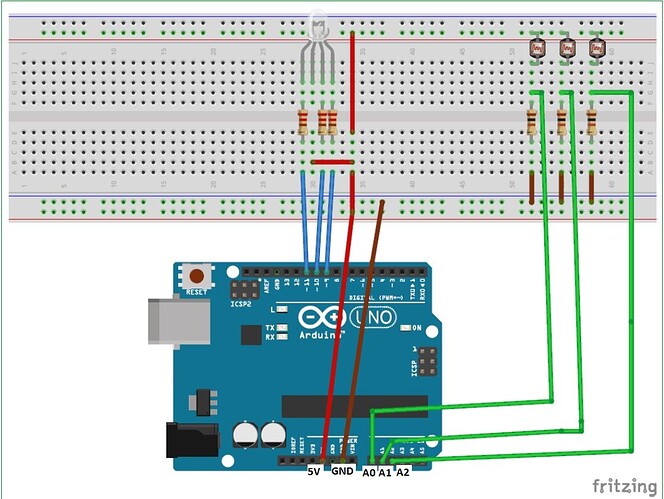
I am doing a project with an arduino board and c++ coding. My group and I are trying to change the color of an rgb led by covering different photo-resistors. I have attatched an image showing almost the wiring we are using, the only difference is that we are using a cathode led, so it is grounded instead. Does anyone have tips that might help us?
code:
//similar project: Arduino Color Mixing Lamp using RGB LED and LDR
//photoresistor project: https://create.arduino.cc/projecthub/Ayeon0122/reading-a-photoresistor-1e705e
const byte outputValue1 = A0; //this one when covered will make red on it's own
const byte outputValue2 = A1; //this one when covered will make green on it's own
const byte outputValue3 = A2; //this one when covered will make blue on it's own
const byte red_light_pin= 11; //these three singnify where the power for the red, green, and blue will be for the rgb led
const byte green_light_pin = 10;
const byte blue_light_pin = 9;
unsigned int lightCal1 = 0; //these help collect the light value from the photoresistors
unsigned int lightVal1 = 0; //red
unsigned int lightCal2 = 0;
unsigned int lightVal2 = 0; //green
unsigned int lightCal3 = 0;
unsigned int lightVal3 = 0; //blue
void setup() {
pinMode(red_light_pin, OUTPUT); //these three set up the led pins to be an output, telling the arduino to send info out to the led
pinMode(green_light_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(blue_light_pin, OUTPUT);
lightCal1 = analogRead(outputValue1); //these three take an initial reading of the light from the photoresistors
lightCal2 = analogRead(outputValue2);
lightCal3 = analogRead(outputValue3);
}
void loop()
{
lightVal1 = analogRead(outputValue1); //these three take readings from the photoresistors
lightVal2 = analogRead(outputValue2);
lightVal3 = analogRead(outputValue3);
Serial.println("Raw Sensor Values:"); // these print the values from the photoresistors onto the serial monitor
Serial.print("\t red: ");
Serial.print(lightVal1);
Serial.print("\t green: ");
Serial.print(lightVal2);
Serial.print("\t blue: ");
Serial.println(lightVal3);
//if the light value (lightVal) is less than initial reading (the lightCal) it is dark (covered)
if ((lightVal1 < lightCal1 - 50) and (lightVal2 < lightCal2 - 50) and (lightVal3 < lightCal3 - 50))
{RGB_color(255, 255 ,255);
}//if all photoresistors are covered, the led will be white
else if (lightVal1 < lightCal1 - 50)
{RGB_color(255, 0, 0);
}//if first photoresistor is covered, the led will be red
else if (lightVal2 < lightCal2 - 50)
{RGB_color(0, 255, 0);
}//if second photoresistor is covered, the led will be green
else if (lightVal3 < lightCal3 - 50)
{RGB_color(0, 0, 255);
}//if second and third photoresistors are covered, the led will be cyan
else {RGB_color(0, 0, 0);
}//if no photoresistors are covered the led will not light up, no power to red, green, or blue
}
void RGB_color(int red_light_value, int green_light_value, int blue_light_value) //this defines RGB_color, so the led will actually light up the colors and send electricity to the led
{
analogWrite(red_light_pin, red_light_value);
analogWrite(green_light_pin, green_light_value);
analogWrite(blue_light_pin, blue_light_value);
}