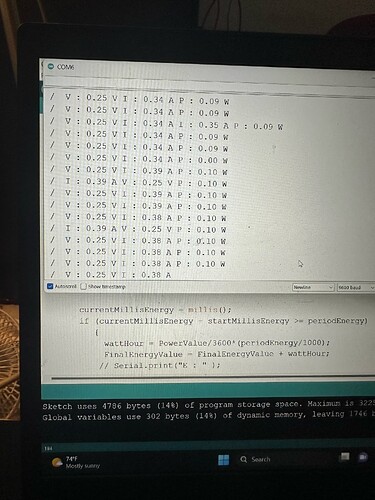
Hi all,
Beginner coder here. I'm working on a project to collect data off a 12V DC battery. I need to collect Voltage, Amps, and the code will calculate Power, Watt-Hours, etc. Everything is working correctly on the hardware side and with the code as well, I just need to know how I can best display my results on serial monitor for data collection. I was copying and pasting my data into Excel, and some lines of the serial monitor switched the positions of volts and amps, and with 3000+ data points I can't manually swap all of the faulty data points.
I need my serial monitor to be impeccable when displaying my results. I've attached a copy of my serial monitor and code below.
Thanks in advance, I'm sure this is simple but I am a new programmer. Would appreciate any advice!
/* 0- General */
int decimalPrecision = 2; // decimal places for all values shown in LED Display & Serial Monitor
/* 1- DC Voltage Measurement using Voltage Divider Method */
int VoltageAnalogInputPin = A1; // Which pin to measure Voltage Value (A0 is reserved for LCD Shield buttons function)
float voltageSampleRead = 0; /* to read the value of a sample*/
float voltageLastSample = 0; /* to count time for each sample. Technically 1 milli second 1 sample is taken */
float voltageSampleSum = 0; /* accumulation of sample readings */
float voltageSampleCount = 0; /* to count number of sample. */
float voltageMean ; /* to calculate the average value from all samples*/
float moduleSupplyVoltageV = 5; /* maximum measuring voltage , default 5V*/
float R1 = 47000; //30000.0; // Input resistance value for R1 (in ohm) based on Voltage Divider Method
float R2 = 2200; //7500.0; // Input resistance value for R2 (in ohm) based on Voltage Divider Method
float finalVoltage =0; /*shows the final voltage reading*/
/* 2- DC Current Measurement */
int CurrentAnalogInputPin = A2; // Which pin to measure Current Value (A0 is reserved for LCD Shield buttons function)
float mVperAmpValue = 100; // If using ACS712 current module : for 5A module key in 185, for 20A module key in 100, for 30A module key in 66
// If using "Hall-Effect" Current Transformer, key in value using this formula: mVperAmp = maximum voltage range (in milli volt) / current rating of CT
/* For example, a 20A Hall-Effect Current Transformer rated at 20A, 2.5V +/- 0.625V, mVperAmp will be 625 mV / 20A = 31.25mV/A */
float moduleMiddleVoltage = 2500; /* when there is no reading, the voltage is at middle Vcc. For 5V power supply, the middle voltage is 2500mV;*/
float moduleSupplyVoltage = 5000; /* supply voltage to current sensor module, default 5000mV*/
float currentSampleRead = 0; /* to read the value of a sample*/
float currentLastSample = 0; /* to count time for each sample. Technically 1 milli second 1 sample is taken */
float currentSampleSum = 0; /* accumulation of sample readings */
float currentSampleCount = 0; /* to count number of sample. */
float currentMean ; /* to calculate the average value from all samples*/
float finalCurrent ; /* the final current reading without adding offset value*/
float finalCurrent2 ; /* the final current reading*/
/* 2.1- DC Current Offset */
int OffsetRead = 0; /* To switch between functions for auto callibation purpose */
float currentOffset =-.29 ; // to Offset deviation and accuracy. Offset any fake current when no current operates.
// Look into serial monitor to add or minus the value.
// 0.26 means add 0.26A to all current measured value.
/* if you have LCD Display Shield, this offset can be automatically adjusted by pressing SELECT button */
float offsetLastSample = 0; /* to count time for each sample. Technically 1 milli second 1 sample is taken */
float offsetSampleCount = 0; /* to count number of sample. */
/* 3- DC Power Wattage calculation */
float PowerValue =0; /* Initial calculation Power Value */
unsigned long startMillisPower; /* start counting time for power */
unsigned long currentMillisPower; /* current counting time for power */
const unsigned long periodPower = 1000; // refresh every X seconds (in seconds) Default 1 = 1 second
/* 4- DC Watt-hour calculation */
float wattHour = 0; /* Initial calculation Energy Value */
unsigned long startMillisEnergy; /* start counting time for Energy */
unsigned long currentMillisEnergy; /* current counting time for Energy */
const unsigned long periodEnergy = 1000; // refresh every X seconds (in seconds) Default 1000 = 1 second
float FinalEnergyValue = 0; /*shows the final Energy reading*/
/* 5 - LCD Display */
// #include<LiquidCrystal.h> /*Load the liquid Crystal Library (by default already built-it with arduino solftware)*/
// LiquidCrystal LCD(8,9,4,5,6,7); /*Creating the LiquidCrystal object named LCD */
// unsigned long startMillisLCD; /* start counting time for LCD Display */
// unsigned long currentMillisLCD; /* current counting time for LCD Display */
// const unsigned long periodLCD = 1000; // refresh every X seconds (in seconds) in LED Display. Default 1000 = 1 second
void setup() /* The Codes only run 1 time only when Arduino started.*/
{
/* 0- General */
Serial.begin(9600); /* In order to see value in serial monitor */
/* 3- DC Power Wattage calculation */
startMillisPower = millis();
/* 4- DC Watt-hour calculation */
startMillisEnergy = millis();
/* 5 - LCD Display */
// LCD.begin(16,2); /*Tell Arduino that our LCD has 16 columns and 2 rows*/
// LCD.setCursor(0,0); /*Set LCD to upper left corner of display*/
//startMillisLCD = millis();
}
void loop() /* The Codes run repeatly over and over again.*/
{
/* 0- General */
/* 0.1- Button Function */
// int buttonRead;
// buttonRead = analogRead (0); // Read analog pin A0. Analog pin A0 automatically reserved for button function in LCD Display Shield
/*Right button is pressed */
//if (buttonRead < 60)
// { LCD.setCursor(0,0); LCD.print ("PRESS <SELECT> "); }
/* Up button is pressed */
//else if (buttonRead < 200)
//{ LCD.setCursor(0,0); LCD.print ("PRESS <SELECT> "); }
/* Down button is pressed */
//else if (buttonRead < 400)
//{ LCD.setCursor(0,0); LCD.print ("PRESS <SELECT> "); }
/* Left button is pressed */
//else if (buttonRead < 600)
//{ LCD.setCursor(0,0); LCD.print ("PRESS <SELECT> "); }
/* Select button is pressed */
//else if (buttonRead < 800)
//{
//OffsetRead = 1; // to activate offset
// LCD.setCursor(0,0);
//LCD.print ("INITIALIZING..... ");
//LCD.setCursor(0,1);
//LCD.print ("WAIT 5 SEC ..... ");
//}
/* 1- DC Voltage Measurement using Voltage Divider Method */
if(millis() >= voltageLastSample + 1 ) /* every 1 milli second taking 1 reading */
{
voltageSampleRead = analogRead(VoltageAnalogInputPin); /* read the sample value */
voltageSampleSum = voltageSampleSum + voltageSampleRead ; /* accumulate value with older sample readings*/
voltageSampleCount = voltageSampleCount + 1; /* to move on to the next following count */
voltageLastSample = millis(); /* to reset the time again so that next cycle can start again*/
}
if(voltageSampleCount == 1000) /* after 1000 count or 1000 milli seconds (1 second), do the codes below*/
{
voltageMean = voltageSampleSum/voltageSampleCount; /* calculate average value of all sample readings taken*/
finalVoltage = .25+((voltageMean*moduleSupplyVoltageV)/1024) / (R2/(R1+R2)); /* Calculate the expected monitoring votlage */
Serial.print("V : ");
Serial.print( finalVoltage,decimalPrecision);
Serial.print(" V ");
// Serial.println();
// Serial.print('\t');
// Serial.print(" / ");
voltageSampleSum =0; /* to reset accumulate sample values for the next cycle */
voltageSampleCount=0; /* to reset number of sample for the next cycle */
}
/* 2- DC Current Measurement */
if(millis() >= currentLastSample + 1 ) /* every 1 milli second taking 1 reading */
{
currentSampleRead = analogRead(CurrentAnalogInputPin)-((moduleMiddleVoltage/moduleSupplyVoltage)*1024); /* read the sample value */
currentSampleSum = (currentSampleSum + currentSampleRead) ; /* accumulate value with older sample readings*/
currentSampleCount = currentSampleCount + 1; /* to move on to the next following count */
currentLastSample = millis(); /* to reset the time again so that next cycle can start again*/
}
if(currentSampleCount == 1000) /* after 1000 count or 1000 milli seconds (1 second), do the calculation and display value*/
{
currentMean = currentSampleSum/currentSampleCount; /* calculate average value of all sample readings taken*/
finalCurrent = (((currentMean /1024) *5000) /mVperAmpValue); /* calculate the final RMS current*/
finalCurrent2 = -(finalCurrent + currentOffset);
// Serial.print('\t');
// Serial.print('\t');
Serial.print("I : ");
Serial.print(finalCurrent2,decimalPrecision);
Serial.print(" A ");
//Serial.print('\t');
//Serial.println();
//Serial.print(" / ");
currentSampleSum =0; /* to reset accumulate sample values for the next cycle */
currentSampleCount=0; /* to reset number of sample for the next cycle */
}
/* 2.1 - Offset DC Current */
if(OffsetRead == 1)
{
currentOffset = 0; /* set back currentOffset as default*/
if(millis() >= offsetLastSample + 1) /* offset 1 - to centralise analogRead waveform*/
{
offsetSampleCount = offsetSampleCount + 1;
offsetLastSample = millis();
}
if(offsetSampleCount == 2500) /* need to wait first offset take into effect. Delay 2.5 seconds */
{ /* So this code is to delay 2.5 seconds after button pressed */
currentOffset = - finalCurrent; /* to offset values */
OffsetRead = 0; /* until next offset button is pressed*/
offsetSampleCount = 0; /* to reset the time again so that next cycle can start again */
}
}
/* 3- DC Power Wattage calculation */
currentMillisPower = millis(); /* Count the time for power */
if (currentMillisPower - startMillisPower >= periodPower)
{
PowerValue = finalCurrent2 * finalVoltage;
// Serial.print('\t');
Serial.print("P : " );
Serial.print(PowerValue,decimalPrecision);
Serial.print(" W ");
Serial.println();
Serial.print(" / ");
startMillisPower = currentMillisPower ; /* Set the starting point again for next counting time */
}
/* 4- DC Watt-hour calculation */
currentMillisEnergy = millis(); /* Count the time for current */
if (currentMillisEnergy - startMillisEnergy >= periodEnergy)
{
wattHour = PowerValue/3600*(periodEnergy/1000); /* for smoothing calculation*/
FinalEnergyValue = FinalEnergyValue + wattHour;
// Serial.print("E : " );
//Serial.print(FinalEnergyValue,decimalPrecision);
//Serial.print(" Wh ");
//Serial.println(" / ");
startMillisEnergy = currentMillisEnergy ; /* Set the starting point again for next counting time */
}
/* 5 - LCD Display */
//currentMillisLCD = millis();
//if (currentMillisLCD - startMillisLCD >= periodLCD)
// {
// LCD.setCursor(0,0); /* Set cursor to first colum 0 and second row 1 */
//LCD.print(finalVoltage,decimalPrecision); /* display voltage value in LCD in first row */
//LCD.print("V ");
//LCD.setCursor(8,0);
//LCD.print(PowerValue,decimalPrecision-1); /* display power value in LCD */
//LCD.print("W ");
//LCD.setCursor(0,1); /* set display starts at second row */
//LCD.print(finalCurrent2,decimalPrecision); /* display current value in LCD in first row */
//LCD.print("A ");
//LCD.setCursor(8,1);
//LCD.print(FinalEnergyValue/1000,decimalPrecision-1); /* display energy value in LCD */
//LCD.print("kWh ");
//startMillisLCD = currentMillisLCD ; /* Set the starting point again for next counting time */
//}
}