Hi, this is a MY COMPLETE CODE in which my two motors need to align themself to a fixed limit switcher.
Inside the do...while the absolute positioning is increased step by step each iteration (i am using a tmc2209 driverwith a 1/8 of a step resolution) and then stopped by the if when the limit switcher is pressed.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Stepper.h>
#include <ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
#include <std_msgs/Int32.h>
#include <rosserial_arduino/Test.h>
#include <AccelStepper.h>
#include <MultiStepper.h>
ros::NodeHandle nh;
using rosserial_arduino::Test;
//rosrun rosserial_python serial_node.py /dev/ttyUSB0
long positions[2]; // Array of desired stepper absolute positions
const int dirPinR = 5;
const int stepPinR = 6;
const int enPinR = 7;
const int dirPinL = 11;
const int stepPinL = 10;
const int enPinL = 2;
const int sensor0degL = 9;
const int sensor0degR = 4;
int homedL = 0;
int homedR = 0;
int pos=0; //actual position
int destination = 999;
AccelStepper myRStepper(AccelStepper::DRIVER, stepPinR, dirPinR);
AccelStepper myLStepper(AccelStepper::DRIVER, stepPinL, dirPinL);
MultiStepper motors;
void callback(const Test::Request & req, Test::Response & res){
String temp = req.input;
nh.logerror(req.input);
destination = atoi(req.input);
}
ros::ServiceServer<Test::Request, Test::Response> server("Test",&callback);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
myRStepper.setMaxSpeed(300);
myLStepper.setMaxSpeed(300);
pinMode(stepPinR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPinR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enPinR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor0degR, INPUT);
pinMode(stepPinL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPinL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enPinL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensor0degL, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(sensor0degR, INPUT_PULLUP);
nh.initNode();
nh.advertiseService(server);
motors.addStepper(myRStepper);
motors.addStepper(myLStepper);
positions[0] = 0;
positions[1] = 0;
homedL = 0;
homedR = 0;
digitalWrite(enPinR, LOW);//activate R motor
digitalWrite(enPinL, LOW);//activate L motor
}
void loop() {
delay(500);
if (destination == 1)/*GOAL UP*/{
nh.loginfo("dentro up");
if (pos == 0){/*currently zero*/
positions[0] = positions[0]+96;
positions[1] = positions[1]+96;
motors.moveTo(positions);
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED UP positions");
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
else if (pos == 2){/*currently down*/
positions[0] = positions[0]+192;
positions[1] = positions[1]+192;
motors.moveTo(positions);
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED UP positions");
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
pos = destination;/*update the actual postion*/
destination = 9;/*reset the request*/
}
else if (destination == 0)/*GOAL ZERO*/{
nh.loginfo("dentro zero");
if (pos == 2){ /*currently down*/
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED ZERO positions");
positions[0] = positions[0]+96;
positions[1] = positions[1]+96;
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
else if (pos == 1){/*currently up*/
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED ZERO positions");
positions[0] = positions[0]-96;
positions[1] = positions[1]-96;
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
pos = destination;/*update the actual postion*/
destination = 9;/*reset the request*/
}
else if (destination == 2)/*GOAL DOWN*/{
if (pos == 0){/*currently zero*/
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED DOWN positions");
positions[0] = positions[0]-96;
positions[1] = positions[1]-96;
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
else if (pos == 1){/*currently up*/
nh.loginfo("REQUESTED DOWN positions");
positions[0] = positions[0]-192;
positions[1] = positions[1]-192;
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.runSpeedToPosition();
}
pos = destination;/*update the actual postion*/
destination = 9;/*reset the request*/
}
else if (destination == 3)/*HOMING*/{
nh.loginfo("STARTING HOMING PROCEDURE");
homedL = 0;
homedR = 0;
do {
if (homedR == 0) positions[0]=positions[0] + 8;
if (homedL == 0) positions[1]=positions[1] + 8;
if(digitalRead(sensor0degR) == LOW)/*R limit switcher pressed*/{
nh.loginfo("R HOMED");
digitalWrite(enPinR, HIGH);//deactivate R motor
myRStepper.stop();
homedR = 1;
}
if (digitalRead(sensor0degL) == LOW)/*L limit switcher pressed*/{
nh.loginfo("L HOMED");
digitalWrite(enPinL, HIGH);//deactivate L motor
myLStepper.stop();
homedL = 1;
}
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.run();
} while (homedR == 0 || homedL == 0);
pos = 0; /*the homing procedure was completed*/
destination = 9;/*reset the request*/
nh.loginfo("HOMING PROCEDURE COMPLETED");
digitalWrite(enPinR, LOW);//activate R motor
digitalWrite(enPinL, LOW);//activate L motor
}
else if (destination == 999) nh.logwarn ("HOMING REQUIRED");
else if (pos == destination) nh.loginfo("THE ACTUAL POSITION WAS REQUESTED");/*No movement required*/
else if (destination == 9) nh.loginfo("CORRECT MOVEMENT, READY FOR NEW");
else nh.loginfo("WRONG REQUEST");
nh.spinOnce();
}
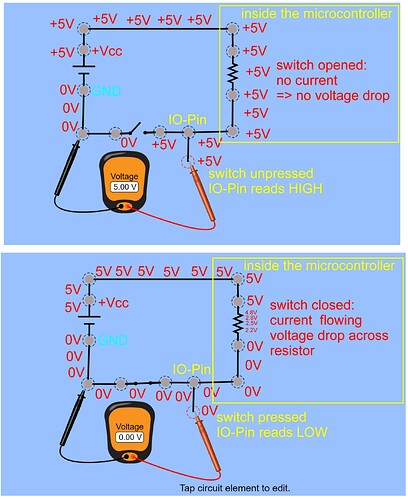
The problem is that the changing in value of the limit switchers are not always seen by my arduino nano approx. once every dozen time(in setup the pins are declared with pinMode () correctly) while if I remove the
motors.moveTo(positions);
motors.run();
commands, the changing of states are visible by my code.
I am a novice to .ino coding and i would appreciate any help.
Thanks in advance.