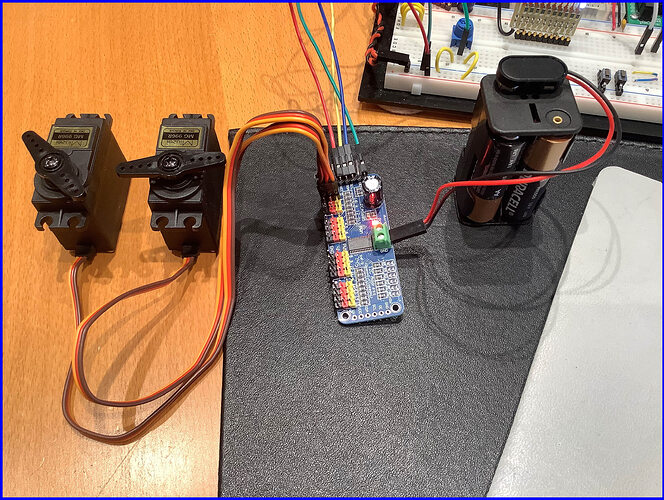
The Arduino can be powered by USB.
VCC on the PCA9865 powered by the Arduino 5V pin.
The PCA9865 servo power terminals, powered by four AA batteries.
This is confirmed to work for the first two servo positions:
/***************************************************
This is an example for our Adafruit 16-channel PWM & Servo driver
Servo test - this will drive 8 servos, one after the other on the
first 8 pins of the PCA9685
Pick one up today in the adafruit shop!
------> http://www.adafruit.com/products/815
These drivers use I2C to communicate, 2 pins are required to
interface.
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
please support Adafruit and open-source hardware by purchasing
products from Adafruit!
Written by Limor Fried/Ladyada for Adafruit Industries.
BSD license, all text above must be included in any redistribution
****************************************************/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_PWMServoDriver.h>
// called this way, it uses the default address 0x40
Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver();
// you can also call it with a different address you want
//Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver(0x41);
// you can also call it with a different address and I2C interface
//Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver(0x40, Wire);
// Depending on your servo make, the pulse width min and max may vary, you
// want these to be as small/large as possible without hitting the hard stop
// for max range. You'll have to tweak them as necessary to match the servos you
// have!
#define SERVOMIN 150 // This is the 'minimum' pulse length count (out of 4096)
#define SERVOMAX 600 // This is the 'maximum' pulse length count (out of 4096)
#define USMIN 600 // This is the rounded 'minimum' microsecond length based on the minimum pulse of 150
#define USMAX 2400 // This is the rounded 'maximum' microsecond length based on the maximum pulse of 600
#define SERVO_FREQ 50 // Analog servos run at ~50 Hz updates
// our servo # counter
uint8_t servonum = 0;
uint8_t servonumMax = 1;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("First 2 channels, Servo test!");
pwm.begin();
/*
* In theory the internal oscillator (clock) is 25MHz but it really isn't
* that precise. You can 'calibrate' this by tweaking this number until
* you get the PWM update frequency you're expecting!
* The int.osc. for the PCA9685 chip is a range between about 23-27MHz and
* is used for calculating things like writeMicroseconds()
* Analog servos run at ~50 Hz updates, It is importaint to use an
* oscilloscope in setting the int.osc frequency for the I2C PCA9685 chip.
* 1) Attach the oscilloscope to one of the PWM signal pins and ground on
* the I2C PCA9685 chip you are setting the value for.
* 2) Adjust setOscillatorFrequency() until the PWM update frequency is the
* expected value (50Hz for most ESCs)
* Setting the value here is specific to each individual I2C PCA9685 chip and
* affects the calculations for the PWM update frequency.
* Failure to correctly set the int.osc value will cause unexpected PWM results
*/
pwm.setOscillatorFrequency(27000000);
pwm.setPWMFreq(SERVO_FREQ); // Analog servos run at ~50 Hz updates
delay(10);
}
// You can use this function if you'd like to set the pulse length in seconds
// e.g. setServoPulse(0, 0.001) is a ~1 millisecond pulse width. It's not precise!
void setServoPulse(uint8_t n, double pulse) {
double pulselength;
pulselength = 1000000; // 1,000,000 us per second
pulselength /= SERVO_FREQ; // Analog servos run at ~60 Hz updates
Serial.print(pulselength); Serial.println(" us per period");
pulselength /= 4096; // 12 bits of resolution
Serial.print(pulselength); Serial.println(" us per bit");
pulse *= 1000000; // convert input seconds to us
pulse /= pulselength;
Serial.println(pulse);
pwm.setPWM(n, 0, pulse);
}
void loop() {
// Drive each servo one at a time using setPWM()
Serial.println(servonum);
for (uint16_t pulselen = SERVOMIN; pulselen < SERVOMAX; pulselen++) {
pwm.setPWM(servonum, 0, pulselen);
}
delay(500);
for (uint16_t pulselen = SERVOMAX; pulselen > SERVOMIN; pulselen--) {
pwm.setPWM(servonum, 0, pulselen);
}
delay(500);
// Drive each servo one at a time using writeMicroseconds(), it's not precise due to calculation rounding!
// The writeMicroseconds() function is used to mimic the Arduino Servo library writeMicroseconds() behavior.
for (uint16_t microsec = USMIN; microsec < USMAX; microsec++) {
pwm.writeMicroseconds(servonum, microsec);
}
delay(500);
for (uint16_t microsec = USMAX; microsec > USMIN; microsec--) {
pwm.writeMicroseconds(servonum, microsec);
}
delay(500);
servonum++;
if (servonum > servonumMax) servonum = 0; // Testing the first 8 servo channels
}