In the original code, I can set the threshold to any value between 1 and 255 and I get this output :
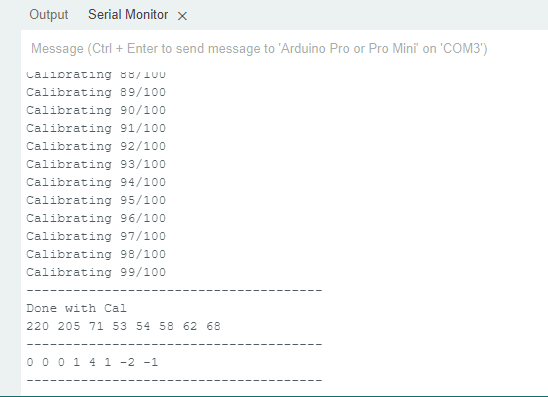
and if I change it to 100, I get...
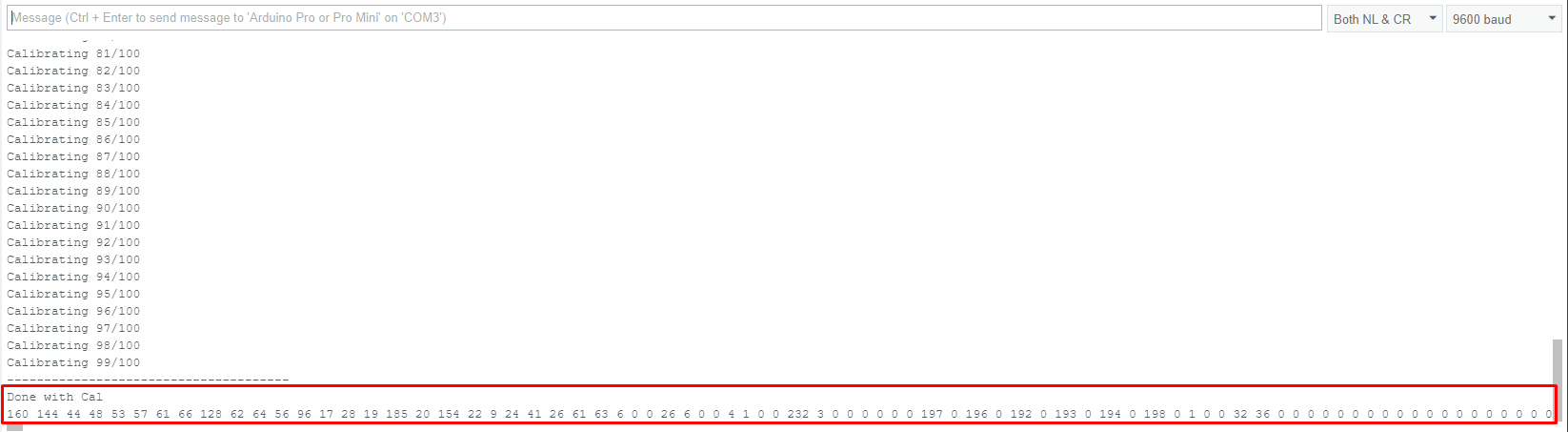
In the original code, If I set the threshold to zero (0) and I get this output - everything circled in red should be new lines below and I don't get any posts regarding the threshold value like above:
That seems funny to me that it behaves this way - doesn't it?
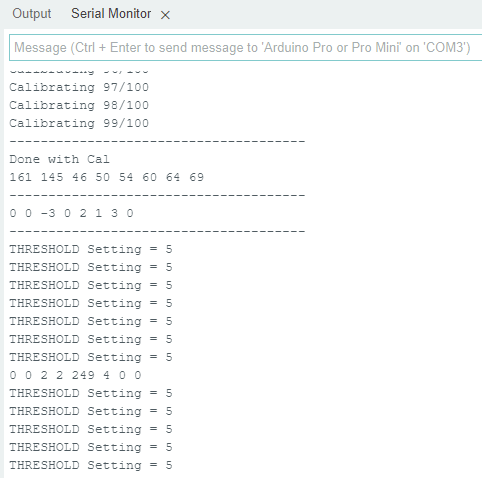
So, when I attempt to replace Threshold value with the pot setting, the code gets all jacked.
In this latest attempt. The serial Monitor pauses after the calibration routine and doesn't post and pin A0 outputs nor any A2 outputs (for the threshold/potSet).
/*
* Christmas Light Controller & Real Time Frequency Analyzer based on FHT code by Open Music Labs at http://openmusiclabs.com
*
* Then modified by PK from : https://dqydj.com/build-your-own-real-time-frequency-analyzer-and-christmas-light-controller/
*
* Modified by dimecoin: https://github.com/dimecoin/XmasFHT
*
* Requires FHT library, from here:
* http://wiki.openmusiclabs.com/wiki/ArduinoFHT
*/
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Easy Customizations
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Adjust the Treshold - what volume should make it light up?
#define THRESHOLD A2
int potSet = 35;
// Old way if you want to statically set this.
// Attempt to 'zero out' noise when line in is 'quiet'. You can change this to make some segments more sensitive.
// defaults:
// { 100, 81, 54, 47, 56, 58, 60, 67 };
//int oct_bias[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// New Auto calibration.
uint8_t oct_bias[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
uint16_t cal_bias[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
/* Number of times to sample the "natural noise" on wires to get average.
* This average is used to cancel out noise while running.
* Don't call to many times or will be slow to startup.
* Dont' call over 16777215 or so times or it might overflow (plus would take forever to startup).
ie. 256 (max reading) * CAL_TIME needs to be <= (2^32)-1 (size in bits of unint16_t)
*/
#define CAL_TIME 100
// Divide Threshold by 2 for top octave? 1 - yes 2 - no. Makes highest frequency blink more.
#define TOP_OCTAVE_DIVIDE false //was false - SPJ
// This is for ACTIVE HIGH relays (works with LEDS for testing), switch values if you have ACTIVE LOW relays.
#define ACTIVE_ON HIGH //was HIGH - SPJ
#define ACTIVE_OFF LOW //was LOW - SPJ
// enable for serial mode output, comment out to speed up lights
#define DEBUG //was Uncommented - SPJ
// Timer/delay for self test on startup.
#define SELFTESTTIME 100
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Hard Customizations - know what you are doing, please.
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// FHT defaults - don't change without reading the Open Music Labs documentation at openmusiclabs.com
#define LOG_OUT 1 // use the log output function
#define FHT_N 256 // set to 256 point fht
#define OCTAVE 1
#define OCT_NORM 0
// include the library, must be done after some of the aboves are defined.. (required by FHT, won't work if included in wrong order)
#include <FHT.h>
// Delay - defines how many cycles before the lights will update. OML's algorithm at 256 samples (needed for our 8 octaves) takes
// 3.18 ms per cycle, so we essentially throw out 14 cycles (I used mechanical relays, you can lower this for solid state relays).
// 15 cycles = 47.7 ms update rate. Be careful here and don't change it too quickly! I warned you!
// Default is 15
#define DELAY 5 //was 15 - SPJ
// Don't change NUM_PINS. FHT outputs 8 octs.
#define NUM_PINS 8
// Pin configuration, there is only 8 channels here. Add duplicate entries if you don't have 8 lights, must be 8!
int relayPins[] = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
uint8_t x[NUM_PINS];
void frequencyGraph(uint8_t x[], int size);
void setup() {
// pin setup
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; i++) {
pinMode(relayPins[i], OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], ACTIVE_OFF);
}
// quick self test
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < NUM_PINS; j++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[j], ACTIVE_ON);
delay(SELFTESTTIME);
digitalWrite(relayPins[j], ACTIVE_OFF);
}
}
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
};
#endif
TIMSK0 = 0; // turn off timer0 for lower jitter
ADCSRA = 0xe5; // set the adc to free running mode
// This is setting up A0 - dime
ADMUX = 0x40; // use adc0
DIDR0 = 0x01; // turn off the digital input for adc0
}
/**********************************************************************************
Loop - includes initialization function and the full loop
**********************************************************************************/
void loop() {
//int data = analogRead(A2);
//int potSet = map(data, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// True full loop
int q = 0;
int cal = 0;
while (1) { // reduces jitter
cli(); // UDRE interrupt slows this way down on arduino1.0
for (int i = 0; i < FHT_N; i++) { // save 256 samples
while (!(ADCSRA & 0x10)) ; // wait for adc to be ready
ADCSRA = 0xf5; // restart adc
// This is his way of reading Analog 0 (A0). It pulls in L[ow] and H[igh] bit. - dimecoin
byte m = ADCL; // fetch adc data
byte j = ADCH;
int k = (j << 8) | m; // form into an int
k -= 0x0200; // form into a signed int
k <<= 6; // form into a 16b signed int
fht_input[i] = k; // put real data into bins
}
fht_window(); // window the data for better frequency response
fht_reorder(); // reorder the data before doing the fht
fht_run(); // process the data in the fht
fht_mag_octave(); // take the output of the fht
sei();
// We are in calibration mode.
if (cal < CAL_TIME) {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; ++i) {
cal_bias[i] += fht_oct_out[i];
}
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print(F("Calibrating "));
Serial.print(cal);
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.println(CAL_TIME);
#endif
cal++;
continue;
}
// Calibration mode has just ended, crunch data collected.
if (cal == CAL_TIME) {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; ++i) {
oct_bias[i] = (uint8_t) (cal_bias[i] / CAL_TIME);
}
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println(F("--------------------------------------"));
Serial.println(F("Done with Cal"));
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; ++i) {
Serial.print(oct_bias[i]);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println(F(""));
Serial.println(F("--------------------------------------"));
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; ++i) {
Serial.print(fht_oct_out[i] - oct_bias[i]);
Serial.print(F(" "));
}
Serial.println(F(""));
Serial.println(F("--------------------------------------"));
Serial.flush();
#endif
// Ready signal.
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], ACTIVE_ON);
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], ACTIVE_OFF);
}
cal++;
continue;
}
// Normal play mode
if (q % DELAY == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; i++) {
x[i] = fht_oct_out[i] - oct_bias[i];
}
frequencyGraph(x, NUM_PINS);
#ifdef DEBUG
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_PINS; ++i) {
Serial.print(x[i]);
Serial.print(F(" "));
}
Serial.println(F(""));
#endif
}
++q;
}
}
void frequencyGraph(uint8_t x[], int size) {
int data = analogRead(A2);
int potSet = map(data, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
int top_threshold = potSet;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
x[i] = max(x[i], 0);
// Special logic for last pin
if (TOP_OCTAVE_DIVIDE && i == (size - 1)) {
top_threshold /= 2;
}
if (x[i] >= top_threshold) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], ACTIVE_ON);
} else if (x[i] < top_threshold) {
// && digitalRead(relayPins[i]) == ACTIVE_ON ) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], ACTIVE_OFF);
}
Serial.print("Potentiometer Setting = ");
Serial.println(potSet);
}
}