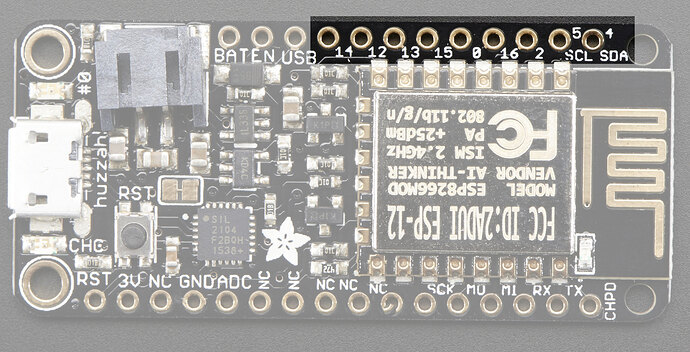
I am testing this simple sketch that drives 2, DC Motors.
For the life of me I cannot figure out, nor find a reference that explains/defines what the proper pin numbers are. I.E.
board-pin = sketch-pin
I said GPIO in the subject but I could have that all wrong as well.
So, here is the sketch and here are the simple lines that defines what pins are to be used.
// Motor A
int enA = 9;
int in1 = 8;
int in2 = 7;
// Motor B
int enB = 3;
int in3 = 5;
int in4 = 4;
I have been struggling for at least a week to equate the sketch pin numbers to a board pin number.
The board that I am using is a Feather Huzzah.
Additionally, it seems that perhaps depending on the manufacturer and/or rev and/or ???, the stupid pin numbers may be different.
Also it seems that what I thought to be a GPIO pin, and under control of the sketch, was always on, even though it was not used in the sketch. That was pin 2, TX.
/*
L298N Motor Demonstration
L298N-Motor-Demo.ino
Demonstrates functions of L298N Motor Controller
DroneBot Workshop 2017
http://dronebotworkshop.com
*/
// Motor A
int enA = 9;
int in1 = 8;
int in2 = 7;
// Motor B
int enB = 3;
int in3 = 5;
int in4 = 4;
void setup()
{
// Set all the motor control pins to outputs
pinMode(enA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in4, OUTPUT);
}
void demoOne()
{
// This function will run the motors in both directions at a fixed speed
// Turn on motor A
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
// Set speed to 200 out of possible range 0~255
analogWrite(enA, 200);
// Turn on motor B
digitalWrite(in3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
// Set speed to 200 out of possible range 0~255
analogWrite(enB, 200);
delay(2000);
// Now change motor directions
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, HIGH);
delay(2000);
// Now turn off motors
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
}
void demoTwo()
{
// This function will run the motors across the range of possible speeds
// Note that maximum speed is determined by the motor itself and the operating voltage
// Turn on motors
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, HIGH);
// Accelerate from zero to maximum speed
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
analogWrite(enA, i);
analogWrite(enB, i);
delay(20);
}
// Decelerate from maximum speed to zero
for (int i = 255; i >= 0; --i)
{
analogWrite(enA, i);
analogWrite(enB, i);
delay(20);
}
// Now turn off motors
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
}
void loop()
{
demoOne();
delay(1000);
demoTwo();
delay(1000);
}