Hello,
I'm trying to write a test sketch to practice working with the PmodRTCC module found here. I am able to get the program to compile (but not upload) when I select one of the Digilent boards within the Arduino IDE, however I get a rather long collection of errors when I try compiling it with my Arduino Uno as the selected board.
I am using the RTCCI2C library found on their webiste (automatic download).
Does anyone have any insight on what the issue might be?
The error is quite lengthy so I'll post it below.
For reference, this is my code that I am working with:
#include <RTCCI2C.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
RTCCI2C myRTCC;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
myRTCC.begin();
myRTCC.setSec(RTCC_RTCC, 0x00);
myRTCC.setMin(RTCC_RTCC, 0x01);
myRTCC.setHour(RTCC_RTCC, 0x21);
myRTCC.setDay(RTCC_RTCC, 0x05);
myRTCC.setDate(RTCC_RTCC, 0x09);
myRTCC.setMonth(RTCC_RTCC, 0x04);
myRTCC.setYear(0x14);
myRTCC.startClock();
Serial.print("The date is: ");
Serial.print(myRTCC.getDate(RTCC_RTCC));
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(myRTCC.getMonth(RTCC_RTCC));
Serial.print("/");
Serial.println(myRTCC.getYear());
}
void loop() {
}
It would appear that the error exceeds the character limit, so I've attached it as a .txt file to this post instead.
Full Compling Error.txt (18.5 KB)
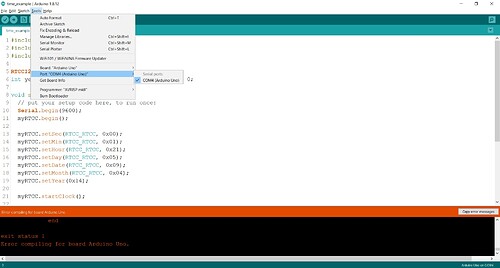
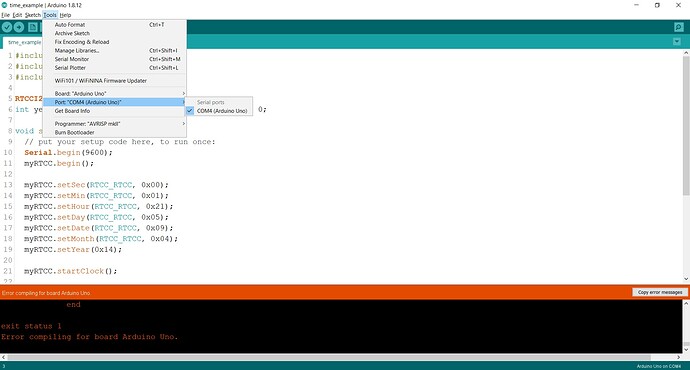
Use "Tools" in the IDE monitor and check "Port".
I'm only able to select COM4 (Arduino Uno)
Good. That's not the issue. My mistake.
What about including "wire.h" before RTCCI2C.h? A wild guess.
The error report tells something wrong with wire.h. One more guess, if the above doesn't work, is to omit the include of wire.h. Maybe the RTSSI2C fixes that by itself.
Hmm... that didn't solve it either. I'm still getting the same error.
It's saying that it's not liking how Wire.[whatever] is working? This is leading me to think that it may be an issue with how the library is coded maybe?
I was reding the error report as certain members of wire.h is abcent. Maybe another library contains a Wire of some kind but withound the functions being needed. This is way beyond my knowledge. Let the night pass and wait for more knowing helpers to step in.
I've been tinkering around with the code some more and it would appear that the problem is indeed the way the RTCCI2C library was written. For example, in the library they use code such as Wire.send(), while the corresponding function in Arduino is Wire.write().
I managed to change some of the code around and rather than use the library, I've had to use the Wire library to read/write over the SCL/SDA pins. It's kind of lengthy so I've only gotten the startup and seconds figured out so far, but here is a code that I have that is working great counting from 0-59.
#include <Wire.h>
#define eepromRead 0xAF // Binary value is 10101111
#define eepromWrite 0xAE // Binary value is 10101110
#define sramRead 0xDF // Binary value is 11011111
#define sramWrite 0xDE // Binary value is 11011110
/* The Bits for the seconds registers on RTCC memory works like this:
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0
Bit 7 controls the crystal, a 1 is on and a 0 is off
bits 6 - 4 control the 10 seconds place
bits 3 - 0 control the 1 seconds place */
uint8_t rgbSec [2] = {0x00, 0x00}; // {Address, Value to be written}
int seconds;
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start clock
//The 7th bit of the RTCC_RTCC second register controls the oscillator
//Set address to the RTCC_RTCC second register
uint8_t temp;
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(0x00);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
// Get second
while (Wire.available()) {
temp = Wire.read();
}
//set the 7th bit to stop the clock
temp = (temp | 0x80);
//start clock
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(0x00);
Wire.write(temp);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Write seconds
rgbSec[0] = 0x00;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbSec[0]);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(sramRead);
Wire.write(rgbSec[0]);
Wire.write(rgbSec[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
temp = Wire.read();
if ((temp & 0x80) == 0x80) { //preserve configuration bits
rgbSec[1] = (rgbSec[1] | 0x80);
}
}
void loop() {
//get seconds
uint8_t bSec;
uint8_t bSecBuffer = 0;
bSec = 0x00;
// Set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bSec);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Read address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bSecBuffer = Wire.read();
}
// Return valid bits
seconds = bSecBuffer & 0x7F; // this returns a Decimil value for seconds
Serial.println(seconds, HEX); // The decimal value for seconds needs to be converted to Hex to make sense.
delay(500); // wait a half second before printing another number to the serial monitor
}
And... Here is a more completed code containing the month, day, year, and time, but not the battery backup.
#include <Wire.h>
#define eepromRead 0xAF // Binary value is 10101111
#define eepromWrite 0xAE // Binary value is 10101110
#define sramRead 0xDF // Binary value is 11011111
#define sramWrite 0xDE // Binary value is 11011110
/* The Bits for the seconds registers on RTCC memory works like this:
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0
Bit 7 controls the crystal, a 1 is on and a 0 is off
bits 6 - 4 control the 10 seconds place
bits 3 - 0 control the 1 seconds place */
uint8_t rgbSec [2] = {0x00, 0x00}; // {Address, Value to be written}, this is for seconds
uint8_t rgbMin [2] = {0x01, 0x00}; // {Address, Value to be written}, this is for minutes
uint8_t rgbHour [2] = {0x02, 0x00}; // {Address, Value to be written}, this is for Hours
uint8_t rgbDay [2] = {0x03, 0x00}; // Days of the week
uint8_t rgbDate [2] = {0x04, 0x00}; // Calander date (1-31)
uint8_t rgbMonth [2] = {0x05, 0x00}; // calander month (1-12)
uint8_t rgbYear [2] = {0x06, 0x00}; // year (0-99)
int seconds;
int minutes;
int hours;
int days;
char writtenDays;
int date;
int month;
int year;
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start clock
//The 7th bit of the RTCC_RTCC second register controls the oscillator
//Set address to the RTCC_RTCC second register
uint8_t temp;
rgbSec[0] = 0x00;
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbSec[0]);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
// Get second
while (Wire.available()) {
temp = Wire.read();
}
//set the 7th bit to stop the clock
temp = (temp | 0x80);
//start clock
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(0x00);
Wire.write(temp);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Write seconds
rgbSec[0] = 0x00;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbSec[0]);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Set Seconds
Wire.beginTransmission(sramRead);
Wire.write(rgbSec[0]);
Wire.write(rgbSec[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
temp = Wire.read();
if ((temp & 0x80) == 0x80) { //preserve configuration bits
rgbSec[1] = (rgbSec[1] | 0x80);
}
//set minute
rgbMin[1] = 57; // this is the decimal number (57) that coorsponds to the hex number (39)
Wire.beginTransmission(sramRead); // was 0x6F
Wire.write(rgbMin[0]);
Wire.write(rgbMin[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
//Set Hour
rgbHour[0] = 0x02;
rgbHour[1] = 34; // 33 is the Decimal number that coorsponds to the Hex number 21 (9PM);
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F); // was 0x6F
Wire.write(rgbHour[0]);
Wire.write(rgbHour[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
//Set Day of the week (days)
rgbDay[0] = 0x03;
rgbDay[1] = 0x06;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbDay[0]);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
temp = Wire.read(); // 0x06 = 6 = Friday
}
//reserve the control bits
rgbDay[1] = ((rgbDay[1] & 0x07) | (temp & 0xF8));
//set day
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbDay[0]);
Wire.write(rgbDay[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
// set calander date (1-31
rgbDate[1] = 0x0A; // enter the value for the date here
//Set address of the date register
rgbDate[0] = 0x04;
//set date
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbDate[0]);
Wire.write(rgbDate[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
//set month
rgbMonth[1] = 0x04; // sets the current month
//Set address of the month register
rgbMonth[0] = 0x05;
//set month
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbMonth[0]);
Wire.write(rgbMonth[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
//Set Year
rgbYear[0] = 0x06;
rgbYear[1] = 0x14; // 14 in Hex is 20 in decimal.
//set year
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(rgbYear[0]);
Wire.write(rgbYear[1]);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void loop() {
//get seconds
uint8_t bSec;
uint8_t bSecBuffer = 0;
bSec = 0x00;
// Set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bSec);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Read address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bSecBuffer = Wire.read();
}
// Return valid bits
seconds = bSecBuffer & 0x7F; // this returns a Decimil value for seconds
// Get minutes
uint8_t bMinBuffer = 0;
uint8_t bMin;
// RTCC_RTCC
bMin = 0x01;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bMin);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bMinBuffer = Wire.read();
}
minutes = bMinBuffer & 0x7F; // returns the decimal value for mintues
// Get hours
uint8_t bHourBuffer = 0;
uint8_t bHour;
//Set address of the hour register
bHour = 0x02;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bHour);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bHourBuffer = Wire.read();
}
hours = bHourBuffer & 0x3F;
// Get Day
uint8_t bDayBuffer = 0;
uint8_t bDay;
//Set address of the day register
bDay = 0x03;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bDay);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bDayBuffer = Wire.read();
}
// return valid bits
days = (bDayBuffer & 0x07);
//Get date
uint8_t bDateBuffer = 0;
uint8_t bDate;
bDate = 0x04; //calendar date
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bDate);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bDateBuffer = Wire.read();
}
date = bDateBuffer & 0x3F;
//Get Month
uint8_t bMonthBuffer = 0;
uint8_t bMonth;
bMonth = 0x05;
//set address
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(bMonth);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bMonthBuffer = Wire.read();
}
month = bMonthBuffer & 0x1F;
//Get Year
uint8_t bYearBuffer = 0;
//set address
// only RTCC_RTCC has the year register
Wire.beginTransmission(0x6F);
Wire.write(0x06);
Wire.endTransmission();
//read from address
Wire.requestFrom(0x6F, 1);
while (Wire.available()) {
bYearBuffer = Wire.read();
}
year = bYearBuffer & 0xFF;
Serial.print("20");
Serial.print(year);
Serial.print("/");
switch (month) {
case 0x01:
Serial.print("Jan");
break;
case 0x02:
Serial.print("Feb");
break;
case 0x03:
Serial.print("Mar");
break;
case 0x04:
Serial.print("Apr");
break;
case 0x05:
Serial.print("May");
break;
case 0x06:
Serial.print("Jun");
break;
case 0x07:
Serial.print("Jul");
break;
case 0x08:
Serial.print("Aug");
break;
case 0x09:
Serial.print("Sep");
break;
case 0x10:
Serial.print("Oct");
case 0x11:
Serial.print("Nov");
case 0x12:
Serial.print("Dec");
break;
default:
Serial.print("Error");
break;
}
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(date, HEX);
Serial.print("/");
switch (days) {
case 1:
Serial.print("Sunday");
break;
case 2:
Serial.print("Monday");
break;
case 3:
Serial.print("Tuesday");
break;
case 4:
Serial.print("Wednesday");
break;
case 5:
Serial.print("Thrusday");
break;
case 6:
Serial.print("Friday");
break;
case 7:
Serial.print("Saturday");
break;
default:
Serial.print("Error");
break;
}
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(hours, HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minutes, HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(seconds, HEX); // The decimal value for seconds needs to be converted to Hex to make sense.
delay(1000); // wait one second before printing another number to the serial monitor
}