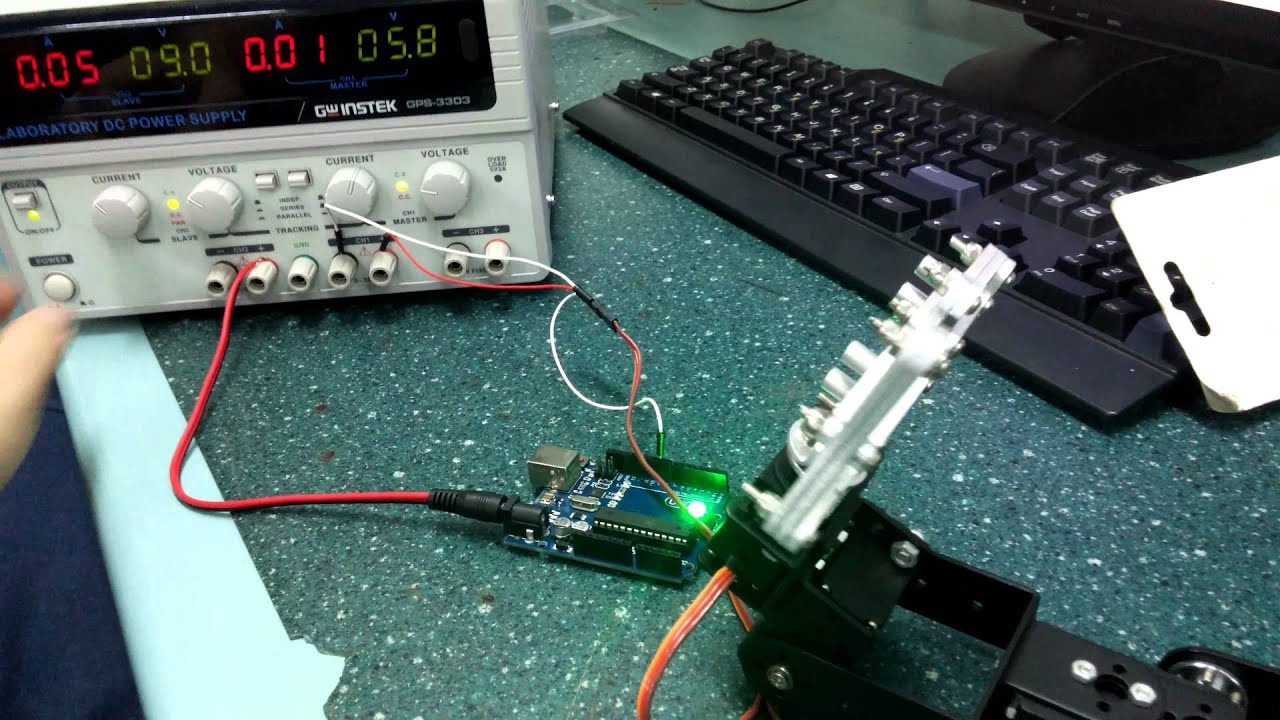
Hello. For my college project my friend and I decided we will build a robotic arm controlled wirelessly by a glove, built to imitate our movements. Since the beginning we had problems understanding how to properly contol the servos through C language. Wev'e got a stock code from the internet, but we are not sure if it fits the servo. It's my first time working with Arudino devices, and using C language ( I'm working with C++ ), but we are determined to make a good project from what we got and what we will learn in the journey.
We have tried the knob servo stock program but the servo ignores the program and tries to keep spinning, griding its gears, even when we tweaked the code to make it turn 180 degrees back and forth. Is there a different library for that servo?
Here is the example code:
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo;
int potpin = 0;
int val;
void setup()
{
myservo.attach(9);
}
void loop()
{
val = analogRead(potpin);
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180);
myservo.write(val);
delay(15);
}
We have tried out own program to try and move the servos but encountered these problems listed below:
As seen at the first seconds, the servo is at is limit/edge. When power is turned on, it bounces to life and goes around until it hits the end, then tries to move more, buzzing and possibly forcing the gears. Note that the generator shows a short circuit. I don't really understand where's the problem and why it's short. We kept all cables seperated and clear. From what I've seen it's the case with all the servos. What's going on?
Next thing we tried to do is to figure out how to work with an MPU6050. We have used an internet code, connected to MPU6050 to the board, and got odd results. Extreme constant acceleration, degrees of MPU ( allegedly ) that always move but balance in the end to around -200. Is this how the MPU is suposed to work?
Code used on MPU:
#include<Wire.h>
const int MPU=0x68; // I2C address of the MPU-6050
int16_t AcX,AcY,AcZ,Tmp,GyX,GyY,GyZ;
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU);
Wire.write(0x6B); // PWR_MGMT_1 register
Wire.write(0); // set to zero (wakes up the MPU-6050)
Wire.endTransmission(true);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU);
Wire.write(0x3B); // starting with register 0x3B (ACCEL_XOUT_H)
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(MPU,14,true); // request a total of 14 registers
AcX=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x3B (ACCEL_XOUT_H) & 0x3C (ACCEL_XOUT_L)
AcY=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x3D (ACCEL_YOUT_H) & 0x3E (ACCEL_YOUT_L)
AcZ=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x3F (ACCEL_ZOUT_H) & 0x40 (ACCEL_ZOUT_L)
Tmp=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x41 (TEMP_OUT_H) & 0x42 (TEMP_OUT_L)
GyX=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x43 (GYRO_XOUT_H) & 0x44 (GYRO_XOUT_L)
GyY=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x45 (GYRO_YOUT_H) & 0x46 (GYRO_YOUT_L)
GyZ=Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); // 0x47 (GYRO_ZOUT_H) & 0x48 (GYRO_ZOUT_L)
Serial.print("Accelerometer: ");
Serial.print("X = "); Serial.print(AcX);
Serial.print(" | Y = "); Serial.print(AcY);
Serial.print(" | Z = "); Serial.println(AcZ);
//equation for temperature in degrees C from datasheet
Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(Tmp/340.00+36.53); Serial.println(" C ");
Serial.print("Gyroscope: ");
Serial.print("X = "); Serial.print(GyX);
Serial.print(" | Y = "); Serial.print(GyY);
Serial.print(" | Z = "); Serial.println(GyZ);
Serial.println(" ");
delay(333);
}
All information and help would be much appreciated. We are stuck, and so is our director.
Thanks.