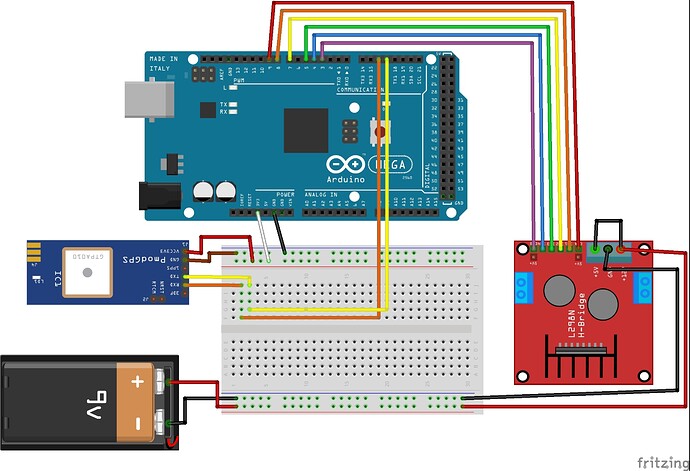
Hi
My apologies if this isn't the right subforum to ask this question, but I do think its a programming problem, not anything else - I might be wrong. If I should have posted this somewhere else, please let me know where and I will delete this thread and start new one in that subforum.
I'm working on a project where we have to make a trolley follow the user.
I'm using:
2 Xbee 802.15.4
2 Arduino Mega
2 PmodGPS
2 DC Motors
1 L298N Dual H-Bridge Motor Controller - power by external 9V battery
I've got the GPS data being transferred between the two arduinos, I've worked out the distance and I have worked out the bearing as well, all thanks to users from this forum.
Now that I'm getting this working, I tried to program it so that it runs the motor when its more than 5m apart. I've tried to make it work but due to my novice programming skills, it didn't. ![]()
My thought process was that if the distance is more than 5m, the arduino should put the motor controller pin HIGH. If its not then all the pin would be set to LOW.
I tried creating a separate void declaration for controlling the pins. That didn't work. The last thing I tried was to just put the HIGH LOW code in the ShowParsedData loop. That obviously didn't work either.
Could anyone tell me what I'm doing wrong and how I could achieve this?
Please let me know if I've missed something, or if anyone wants more details.
N.B. If the some parts of the Rx code look out of place and/or stupid, I've been doing a trial and error to get it to work, so I've moved some stuff here and there, just to see what happens.
High Regards
Here's the transmitter code (getting GPS from the user - Working):
#include <NMEAGPS.h>
NMEAGPS gps;
gps_fix fix;
#define gpsPort Serial1
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsPort.begin( 9600 );
// Might be needed:
//
// #define RSTpin 37 //pin 37, JE-08
// pinMode(RST, OUTPUT);
// digitalWrite(RST, LOW);
}
void loop()
{
if (gps.available( gpsPort ))
{
fix = gps.read();
if (fix.valid.satellites)
{
Serial.print( fix.satellites );
}
Serial.print(',');
if (fix.valid.location)
Serial.print( fix.latitude(), 6 );
Serial.print(',');
if (fix.valid.location)
Serial.print( fix.longitude(), 6 );
Serial.println();
}
}
Here's the receiver (gets GPS data from user, compares it with its own, calculates distance and bearing, and should send signal to the motor controller which should run the two motors):
/* 16-03-2018
* Rx Motor move with GPS
* Untested
*
*/
//Include libraries
#include <NMEAGPS.h> //Library to print in NMEA format i.e. XX.YYZZZZ or DD.MMSSSS
//Define serial ports
#define gpsPort Serial2 //GPS port using Tx/Rx port 2
#define fobPort Serial //Incoming data from fob on port 0
//Define variables
NMEAGPS gps;
gps_fix trolley;
//Define parameters for receiving array
const size_t NUM_CHARS = 64; //Size of array
char receivedChars[ NUM_CHARS ]; //Array to store received characteristics
boolean newData = false;
// variables to hold the parsed data
int fobSat;
NeoGPS::Location_t fobLoc;
float fobAlt;
//Define motor variables and connections
// Motor A
int enA = 9;
int in1 = 8; //forward
int in2 = 7; //backwards
// Motor B
int enB = 3;
int in3 = 5; //left
int in4 = 4; //right
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsPort.begin( 9600 );
Serial.println("Start");
//Set motor control pins to output
pinMode(enA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in4, OUTPUT);
// Start with motors disabled and direction forward
// Motor A
digitalWrite(enA, LOW);
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
// Motor B
digitalWrite(enB, LOW);
digitalWrite(in3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
// Check for data from the Fob
recvWithEndMarkers();
if (newData)
{
parseFobData();
showParsedData();
newData = false;
}
// Check for data from the GPS
if (gps.available( gpsPort ))
{
trolley = gps.read(); //Stores GPSR data as trolley
}
}
//Defines parsing parameters, such as when to start and when to stop parsing
void recvWithEndMarkers()
{
static size_t index = 0;
const char endMarker = '\n';
while (fobPort.available() && !newData)
{
char rc = fobPort.read();
//Serial.print(rc); // for debugging
if (rc != endMarker)
{
if (index < NUM_CHARS - 1)
{
receivedChars[ index++ ] = rc;
}
}
else
{
receivedChars[index] = '\0'; // terminate the string
index = 0; // reset for next time
newData = true;
}
}
}
//============
void parseFobData() // split the data into its parts
{
//Incoming data from fob
char *field;
field = strtok( receivedChars, "," ); //Starts from beginning, splits when sees comma
fobSat = atoi( field ); //Number of satellites the fob is connected to
field = strtok( nullptr, "," ); //Continues where left off i.e first comma then stops at the next
fobLoc.latF( atof( field ) ); //Fob's current latitude
field = strtok( nullptr, "," );
fobLoc.lonF( atof( field ) ); //Fob's current longitude
}
void showParsedData() //Shows all parsed data collected above and stores as different variables.
{
Serial.print("Fob Sats: ");
Serial.println( fobSat );
Serial.print("Fob Lat: ");
Serial.println( fobLoc.latF(), 6 );
Serial.print("Fob Lon: ");
Serial.println( fobLoc.lonF(), 6 );
Serial.print("Trolley Sats: ");
if (trolley.valid.satellites)
{
Serial.print( trolley.satellites ); //Number of satellites the trolley is connected to
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Trolley Lat: "); //trolley's current latitude
if (trolley.valid.location)
{
Serial.print( trolley.location.latF(), 6 );
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Trolley Lon: ");
if (trolley.valid.location)
{
Serial.print( trolley.location.lonF(), 6 ); //Trolley's current longitude
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Distance: ");
if (trolley.valid.location) {
float distance = trolley.location.DistanceKm( fobLoc ); //measures the distance as a float of 6 decimal points
distance = distance*1000;
Serial.print( distance, 6 );
if (distance > 5.000000)
{
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
digitalWrite(in3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
}
if ( distance < 5.000000)
{
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
}
} else {
Serial.print( '?' );
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Bearing: ");
if (trolley.valid.location)
{
float bearing = trolley.location.BearingToDegrees( fobLoc ); //measures direction
Serial.print( bearing, 6 );
}
else {
Serial.println( '?' );
}
Serial.println(); // extra blank line
Serial.println(); // extra blank line
}
Here's my serial monitor display:
Fob Sats: 4
Fob Lat: 43.383045
Fob Lon: -2.478903
Trolley Sats: 5
Trolley Lat: 43.383033
Trolley Lon: -2.478810
Distance: 6.252509
Bearing: 278.768463