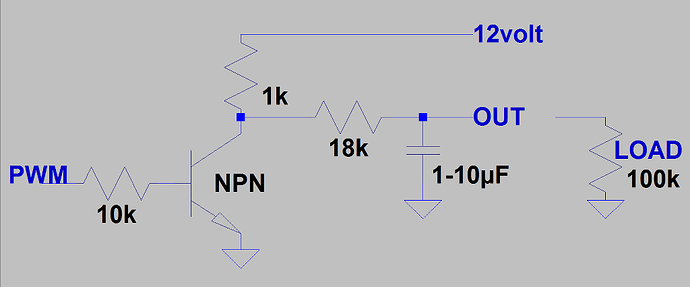
I have a project where I am controlling a pump using the Arduino. The pump has a serial interface and can be direct wired so that an input voltage from 0-10V controls the output pump speed (the pump is not actually running on the voltage, it is simply using it as an input).
When the project started I used the Arduino onboard power to use the PWM output to control the voltage from 0-5V without issue. But the full pump range requires 0-10V. To that end I followed the instructions I found at Instructables to put together a setup using a transistor and an external power supply. The sketch from that site is:
// Define which pin to be used to communicate with Base pin of TIP120 transistor
int TIP120pin = 11; //for this project, I pick Arduino's PMW pin 11
void setup()
{
pinMode(TIP120pin, OUTPUT); // Set pin for output to control TIP120 Base pin
analogWrite(TIP120pin, 255); // By changing values from 0 to 255 you can control motor speed
}
void loop()
{
}
The wiring was done on a breadboard and the setup, as far as I can tell is wired identical to the example at the website. I will update this with a wiring diagram once I get a chance to draw one out. Anyway, by changing the analogWrite value I could successfully adjust the output voltage of the system from 5V to 10V, but even at a analogWrite value of 0 I still had 5V at the output (measured with a multimeter). So now I am wondering if I am seeing the voltage from the board (and if so how do I stop that) or is one of the specs from the transistor giving me problems, some sort of minimum voltage, or do I just have the thing wired wrong? I am hopeful that someone more experienced could give their guidance on this.
I have the spec sheet for the transistor attached.
TIP120.pdf (45.2 KB)