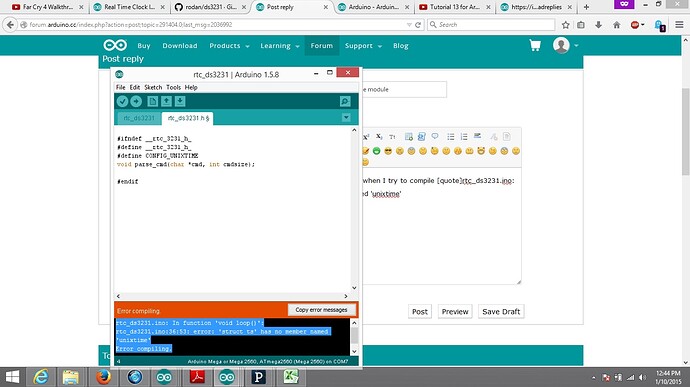
I am using the example given in the 3231 library below is the code
#include <Wire.h>
#include "ds3231.h"
#include "rtc_ds3231.h"
#define BUFF_MAX 128
uint8_t time[8];
char recv[BUFF_MAX];
unsigned int recv_size = 0;
unsigned long prev, interval = 5000;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
DS3231_init(DS3231_INTCN);
memset(recv, 0, BUFF_MAX);
Serial.println("GET time");
}
void loop()
{
char in;
char buff[BUFF_MAX];
unsigned long now = millis();
struct ts t;
// show time once in a while
if ((now - prev > interval) && (Serial.available() <= 0)) {
DS3231_get(&t);
// there is a compile time option in the library to include unixtime support
#ifdef CONFIG_UNIXTIME
snprintf(buff, BUFF_MAX, "%d.%02d.%02d %02d:%02d:%02d %ld", t.year,
t.mon, t.mday, t.hour, t.min, t.sec, t.unixtime);
#else
snprintf(buff, BUFF_MAX, "%d.%02d.%02d %02d:%02d:%02d", t.year,
t.mon, t.mday, t.hour, t.min, t.sec);
#endif
Serial.println(buff);
prev = now;
}
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
in = Serial.read();
if ((in == 10 || in == 13) && (recv_size > 0)) {
parse_cmd(recv, recv_size);
recv_size = 0;
recv[0] = 0;
} else if (in < 48 || in > 122) {; // ignore ~[0-9A-Za-z]
} else if (recv_size > BUFF_MAX - 2) { // drop lines that are too long
// drop
recv_size = 0;
recv[0] = 0;
} else if (recv_size < BUFF_MAX - 2) {
recv[recv_size] = in;
recv[recv_size + 1] = 0;
recv_size += 1;
}
}
}
void parse_cmd(char *cmd, int cmdsize)
{
uint8_t i;
uint8_t reg_val;
char buff[BUFF_MAX];
struct ts t;
//snprintf(buff, BUFF_MAX, "cmd was '%s' %d\n", cmd, cmdsize);
//Serial.print(buff);
// TssmmhhWDDMMYYYY aka set time
if (cmd[0] == 84 && cmdsize == 16) {
//T355720619112011
t.sec = inp2toi(cmd, 1);
t.min = inp2toi(cmd, 3);
t.hour = inp2toi(cmd, 5);
t.wday = inp2toi(cmd, 7);
t.mday = inp2toi(cmd, 8);
t.mon = inp2toi(cmd, 10);
t.year = inp2toi(cmd, 12) * 100 + inp2toi(cmd, 14);
DS3231_set(t);
Serial.println("OK");
} else if (cmd[0] == 49 && cmdsize == 1) { // "1" get alarm 1
DS3231_get_a1(&buff[0], 59);
Serial.println(buff);
} else if (cmd[0] == 50 && cmdsize == 1) { // "2" get alarm 1
DS3231_get_a2(&buff[0], 59);
Serial.println(buff);
} else if (cmd[0] == 51 && cmdsize == 1) { // "3" get aging register
Serial.print("aging reg is ");
Serial.println(DS3231_get_aging(), DEC);
} else if (cmd[0] == 65 && cmdsize == 9) { // "A" set alarm 1
DS3231_set_creg(DS3231_INTCN | DS3231_A1IE);
//ASSMMHHDD
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
time[i] = (cmd[2 * i + 1] - 48) * 10 + cmd[2 * i + 2] - 48; // ss, mm, hh, dd
}
boolean flags[5] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
DS3231_set_a1(time[0], time[1], time[2], time[3], flags);
DS3231_get_a1(&buff[0], 59);
Serial.println(buff);
} else if (cmd[0] == 66 && cmdsize == 7) { // "B" Set Alarm 2
DS3231_set_creg(DS3231_INTCN | DS3231_A2IE);
//BMMHHDD
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
time[i] = (cmd[2 * i + 1] - 48) * 10 + cmd[2 * i + 2] - 48; // mm, hh, dd
}
boolean flags[5] = { 0, 0, 0, 0 };
DS3231_set_a2(time[0], time[1], time[2], flags);
DS3231_get_a2(&buff[0], 59);
Serial.println(buff);
} else if (cmd[0] == 67 && cmdsize == 1) { // "C" - get temperature register
Serial.print("temperature reg is ");
Serial.println(DS3231_get_treg(), DEC);
} else if (cmd[0] == 68 && cmdsize == 1) { // "D" - reset status register alarm flags
reg_val = DS3231_get_sreg();
reg_val &= B11111100;
DS3231_set_sreg(reg_val);
} else if (cmd[0] == 70 && cmdsize == 1) { // "F" - custom fct
reg_val = DS3231_get_addr(0x5);
Serial.print("orig ");
Serial.print(reg_val,DEC);
Serial.print("month is ");
Serial.println(bcdtodec(reg_val & 0x1F),DEC);
} else if (cmd[0] == 71 && cmdsize == 1) { // "G" - set aging status register
DS3231_set_aging(0);
} else if (cmd[0] == 83 && cmdsize == 1) { // "S" - get status register
Serial.print("status reg is ");
Serial.println(DS3231_get_sreg(), DEC);
} else {
Serial.print("unknown command prefix ");
Serial.println(cmd[0]);
Serial.println(cmd[0], DEC);
}
}
I have a question about this particular section
// there is a compile time option in the library to include unixtime support
#ifdef CONFIG_UNIXTIME
snprintf(buff, BUFF_MAX, "%d.%02d.%02d %02d:%02d:%02d %ld", t.year,
t.mon, t.mday, t.hour, t.min, t.sec, t.unixtime);
#else
snprintf(buff, BUFF_MAX, "%d.%02d.%02d %02d:%02d:%02d", t.year,
t.mon, t.mday, t.hour, t.min, t.sec);
#endif
My question is, it says there is a compile time option in the library to include unixtime support... Does anyone know how to do this though? Do I need to include the WiFiUdpNtpClient code and write t.unixtime = unixtime from that the Ntp code or is there a different way to do this?
My second question about the DS3231 chip is about the alarm option. I am under the impression you can set two alarms, and it works by triggering the interrupt. What has me confused is that for two alarms you would set the interrupt on pins two and three on the arduino presumably. However, do the interrupts initiate from two different pins on the DS3231?
The third and final question for now is how to work this line of code to set the alarm
} else if (cmd[0] == 65 && cmdsize == 9) { // "A" set alarm 1
DS3231_set_creg(DS3231_INTCN | DS3231_A1IE);
//ASSMMHHDD
I tried typing A in the serial monitor display but that didn't seem to work. Do I need to write A in one of the flag functions in the code instead?