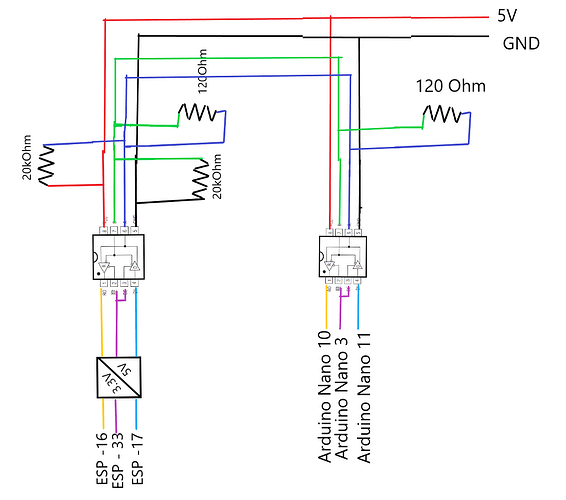
At the moment the master Max485 chip and slave Max485 are with following connections
I don't understand how should I change?
I see 2 new resistors, not in original diagram nor in the pic of breadboard which is what I have been referring too..
new pic please of current hookup..
~q
I'm sorry, I introduced them this morning at dawn after having better read the TTL Max485 scheme which inserted pull up and pull down resistors on the master side to stabilize the signal ... and after reading this attached document on fail safe ... however the current situation is as follows as in the picture
AN-960 Analog Devices RS485.pdf (245,9 KB)
and this is serial monitor on slave sketch
Pretty sure you're gonna need them ceramics..
real close to vcc on both max chips..
red and blue wires that connect busses between boards..
try moving those to the chip not using the + and - busses as connection points..
go back to just terminators and probably would work without them too..
you should be able to omit the max chips and use the level converter for rs232 and see if you can send data that way, then you will now, it's in the max circuit..
you're getting something, so i don't think it's software, definitely garbled..
still, caps..
~q
Forgive me for taking more time, but I didn't understand very well what you are saying, let me summarize:
- Sketchmaster; should be OK
- Sketch Slaves; since it receives the signal from the master and he doesn't respond, you think it's a hardware issue...
- You ask me to swap the bus wires, A and B to try and to insert two 20 kOhm resistors also on the Max485 of the slave
....it's correct? Did I understand correctly what you are saying?
- Sketchmaster is sending now, that much I know.
- Sketch Slave appears to be receiving gibberish (slave not responding see below).
- No you misunderstood me, sorry.
If the slave receives the query, but detects a communication error (parity, LRC,
or CRC), no response is returned. The master program will eventually process
a timeout condition for the query
Page 94 Exception Responses
Sorry.. ~q
Master Sketch:
#include "SPI.h"
#include "TFT_eSPI.h"
#include <PNGdec.h>
#include "logo.h"
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
PNG png; // PNG decoder inatance
#define MAX_IMAGE_WDITH 240 // Adjust for your images
// Use hardware SPI
TFT_eSPI tft = TFT_eSPI();
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
#define PinRicezione 16 // collegare l'RO della RS485
#define PinTrasmissione 17 //collegare il DI della RS485
#define PinControllo 33 //collegare il DE e l'RE della RS485
#define MODBUS_SERIAL_BAUD 9600 // Baud rate for esp32 and max485 communication
ModbusMaster node; //Creo l'oggetto node
int16_t xpos = 80;
int16_t ypos = 10;
//variabili dove memorizzo le letture provenienti dagli slave
int S1_dato1 =0; int S1_dato2 =0; int S1_dato3 =0; int S1_dato4 =0; int S1_dato5 =0; int S1_dato6 =0;
int S2_dato1 =0; int S2_dato2 =0; int S2_dato3 =0; int S2_dato4 =0; int S2_dato5 =0; int S2_dato6 =0;
int S3_dato1 =0; int S3_dato2 =0; int S3_dato3 =0; int S3_dato4 =0; int S3_dato5 =0; int S3_dato6 =0;
int S4_dato1 =0; int S4_dato2 =0; int S4_dato3 =0; int S4_dato4 =0; int S4_dato5 =0; int S4_dato6 =0;
//variabili di servizio
int result = 0; //variabile di lettura del buffer
int p = 0; //contatore
void preTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 1); //abilito il DE/RE della RS485 alla trasmissione
}
void postTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 0); //disabilito il DE/RE della RS485 alla trasmissione
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
tft.begin(); //Inizializzazione schermo
tft.setRotation(0); //Rotazione schermo 0=verticale 1=orizzontale
tft.fillScreen(TFT_BLUE); //cancella lo schermo e lo colora di blu
tft.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW); //setta il colore del testo
tft.setTextSize(3); //setta la dimensione del carattere
tft.setCursor(50, 80); //posiziona il cursore alle coordinate indicate
tft.println("BE MAKER"); //scrive il testo nella posizione del cursore
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE);
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.setCursor(20, 110);
tft.println("INIZIALIZZAZIONE");
tft.drawLine(5, 130, 235, 130, TFT_WHITE); //disegna una linea con parametri: coordinate di inizio e di fine e colore
pinMode(PinControllo, OUTPUT); //settaggio pin di abilitazione della trasmissione e ricezione
// Init in receive mode
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 0); //setto il pin inizialmente in ricezione
//Serial2.begin(baud-rate, protocol, RX pin, TX pin);.
//Serial2.begin(MODBUS_SERIAL_BAUD, SERIAL_8E1, PinRicezione, PinTrasmissione);
//Serial2.setTimeout(200);
//RS485Serial.begin(9600);
Serial2.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, PinRicezione, PinTrasmissione);
// Modbus slave ID 1
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.setCursor(5, 140);
tft.print("Iniz.RS485...");
tft.setCursor(5, 160);
tft.print("Iniz.Slave 1...");
node.setSlave(1);
node.begin(1, Serial2);
delay(100);
// Modbus slave ID 2
tft.setCursor(5, 180);
tft.println("Iniz.Slave 2...");
node.setSlave(2);
node.begin(2, Serial2);
delay(100);
// Modbus slave ID 3
tft.setCursor(5, 200);
tft.println("Iniz.Slave 3...");
node.setSlave(3);
node.begin(3, Serial2);
delay(100);
//Modbus slave ID 4
tft.setCursor(5, 220);
tft.println("Iniz.Slave 4...");
node.setSlave(4);
node.begin(4, Serial2);
delay(1000);
// Callbacks allow us to configure the RS485 transceiver correctly
tft.setCursor(5, 240);
tft.println("Iniz.Master...");
node.preTransmission(preTransmission);
node.postTransmission(postTransmission);
delay(2000);
maschera();
}
void maschera() {
tft.fillScreen(TFT_BLUE); //cancella lo schermo e lo colora di blu
tft.setRotation(0); //Rotazione schermo 0=verticale 1=orizzontale
tft.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW); //setta il colore del testo
tft.setTextSize(3); //setta la dimensione del carattere
tft.setCursor(50, 80); //posiziona il cursore alle coordinate indicate
tft.println("BE MAKER"); //scrive il testo nella posizione del cursore
//Inserimento maschera dati
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE);
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.setCursor(5, 110);
tft.println("STATO SENSORI S");
tft.drawLine(5, 130, 235, 130, TFT_WHITE); //disegna una linea con parametri: coordinate di inizio e di fine e colore
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.setCursor(5, 140);
tft.println("TEMP. STG [C]:");
tft.setCursor(5, 160);
tft.println("TEMP. EXT [C]:");
tft.setCursor(5, 180);
tft.println("SENS. ACQUA 1:");
tft.setCursor(5, 200);
tft.println("SENS. ACQUA 2:");
tft.setCursor(5, 220);
tft.println("SENS. ACQUA 3:");
tft.setCursor(5, 240);
tft.println("SENS. ACQUA 4:");
tft.drawLine(5, 260, 235, 260, TFT_WHITE);
}
int soglia_acqua_min = 470;
int soglia_acqua_max = 512;
float lungh = 1.0;
void loop() {
//inserimento logo
int16_t rc = png.openFLASH((uint8_t *)logo, sizeof(logo), pngDraw);
if (rc == PNG_SUCCESS) {
tft.startWrite();
rc = png.decode(NULL, 0);
tft.endWrite();
}
int t = 0;
t = p % 1; //Calcola il resto della divisione per il numero di slave e sarà un valore circolare 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1,...
//Serial.print("Contatore ");
//Serial.print(p);
//Serial.print(" Resto ");
//Serial.println(t);
//Lettura dati dagli Slave
//Lettura valori sensori S1
if(t == 0){
Serial.println("Interrogo Slave 1...");
node.setSlave(1); //Seleziono Slave 1
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x7531, 16); //0x7531 in hex significa 30001 in decimale, il 16 indica che il buffer ha 16 posizioni
Serial.print("result is...");Serial.println(result);
Serial.print("check is...");Serial.println(node.ku8MBSuccess);
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
S1_dato1 = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
S1_dato2 = node.getResponseBuffer(1);
S1_dato3 = node.getResponseBuffer(2);
S1_dato4 = node.getResponseBuffer(3);
S1_dato5 = node.getResponseBuffer(4);
S1_dato6 = node.getResponseBuffer(5);
Serial.println("Dati ricevuti...");
}
pagina(1, S1_dato1, S1_dato2, S1_dato3, S1_dato4, S1_dato5, S1_dato6);
delay(2000);
}
//Lettura valori sensori S2
if(t == 1){
node.setSlave(2); //Seleziono Slave 2
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x7919, 16); //0x7919 in hex significa 31001 in decimale, il 16 indica che il buffer ha 16 posizioni
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
S2_dato1 = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
S2_dato2 = node.getResponseBuffer(1);
S2_dato3 = node.getResponseBuffer(2);
S2_dato4 = node.getResponseBuffer(3);
S2_dato5 = node.getResponseBuffer(4);
S2_dato6 = node.getResponseBuffer(5);
}
pagina(2, S2_dato1, S2_dato2, S2_dato3, S2_dato4, S2_dato5, S2_dato6);
delay(2000);
}
//Lettura valori sensori S3
if(t == 2){
node.setSlave(3); //Seleziono Slave 3
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x7D01, 16); //0x7D01 in hex significa 32001 in decimale, il 16 indica che il buffer ha 16 posizioni
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
S3_dato1 = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
S3_dato2 = node.getResponseBuffer(1);
S3_dato3 = node.getResponseBuffer(2);
S3_dato4 = node.getResponseBuffer(3);
S3_dato5 = node.getResponseBuffer(4);
S3_dato6 = node.getResponseBuffer(5);
}
pagina(3, S3_dato1, S3_dato2, S3_dato3, S3_dato4, S3_dato5, S3_dato6);
delay(2000);
}
//Lettura valori sensori S4
if(t == 3){
node.setSlave(4); //Seleziono Slave 3
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x80E9, 16); //0x80E9 in hex significa 33001 in decimale, il 16 indica che il buffer ha 16 posizioni
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
S4_dato1 = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
S4_dato2 = node.getResponseBuffer(1);
S4_dato3 = node.getResponseBuffer(2);
S4_dato4 = node.getResponseBuffer(3);
S4_dato5 = node.getResponseBuffer(4);
S4_dato6 = node.getResponseBuffer(5);
}
pagina(4, S4_dato1, S4_dato2, S4_dato3, S4_dato4, S4_dato5, S4_dato6);
delay(2000);
}
p++;
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.setTextSize(3);
tft.setCursor(40, 285);
tft.print(" ");
}
void pagina (int pg, int s1, int s2, int s3, int s4, int s5, int s6){
//Serial.print("pagina ");
//Serial.println(pg);
tft.setTextSize(2); //setta la dimensione del carattere
tft.setCursor(200, 110);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE); //setta il colore del testo
tft.print(pg); // Indica il sensore a cui la pagina fa riferimento
if (s1 > 5000) {
tft.setCursor(180, 140);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 140);
tft.println(float (s1/100.0));
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 140);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 140);
tft.println(float (s1/100.0));
}
if (s2 > 5000) {
tft.setCursor(180, 160);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 160);
tft.println(float (s2/100.0));
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 160);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 160);
tft.println(float (s2/100.0));
}
if (s3 > soglia_acqua_min) {
tft.setCursor(180, 180);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 180);
float dist_1 = lungh - ((s3*1.0)/(soglia_acqua_max*1.0));
tft.println(dist_1);
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 180);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 180);
tft.println(s3);
}
if (s4 > soglia_acqua_min) {
tft.setCursor(180, 200);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 200);
float dist_2 = lungh - ((s4*1.0)/(soglia_acqua_max*1.0));
tft.println(dist_2);
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 200);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 200);
tft.println(s4);
}
if (s5 > soglia_acqua_min) {
tft.setCursor(180, 220);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 220);
float dist_3 = lungh - ((s5*1.0)/(soglia_acqua_max*1.0));
tft.println(dist_3);
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 220);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 220);
tft.println(s5);
}
if (s6 > soglia_acqua_min) {
tft.setCursor(180, 240);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 240);
float dist_4 = lungh - ((s6*1.0)/(soglia_acqua_max*1.0));
tft.println(dist_4);
allarme(pg);
} else {
tft.setCursor(180, 240);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.println(" ");
tft.setCursor(180, 240);
tft.println(s6);
}
}
int g = 0;
void allarme(int f){
int j=0;
j = g % 2;
//Serial.print("Contatore allarme ");
//Serial.print(f);
//Serial.print(" Resto ");
//Serial.println(j);
if (j==0) {
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_RED);
tft.setTextSize(3);
tft.setCursor(40, 285);
tft.println("ALLARME !");
tft.setTextSize(2);
} else {
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE,TFT_BLUE);
tft.setTextSize(3);
tft.setCursor(40, 285);
tft.println("ALLARME !");
tft.setTextSize(2);
}
g++;
}
//=========================================v==========================================
// pngDraw
//====================================================================================
// This next function will be called during decoding of the png file to
// render each image line to the TFT. If you use a different TFT library
// you will need to adapt this function to suit.
// Callback function to draw pixels to the display
void pngDraw(PNGDRAW *pDraw) {
uint16_t lineBuffer[MAX_IMAGE_WDITH];
png.getLineAsRGB565(pDraw, lineBuffer, PNG_RGB565_BIG_ENDIAN, 0xffffffff);
tft.pushImage(xpos, ypos + pDraw->y, pDraw->iWidth, 1, lineBuffer);
}
Slave Sketch
#include <ModbusSlave.h> //libreria da caricaricare da https://github.com/yaacov/ArduinoModbusSlave
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> //libreria standard dell'IDE di Arduino
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#define PinRicezione 10 // collegare l'RO della RS485
#define PinTrasmissione 11 //collegare il DI della RS485
#define PinControllo 3 //collegare il DE e l'RE della RS485
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 2
SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(PinRicezione, PinTrasmissione); // RX, TX
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);
int NomeSlave = 1; //indirizzo dello slave
Modbus slave(RS485Serial, NomeSlave, PinControllo); //Creo l'oggetto slave
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(PinControllo, OUTPUT); // RS485 control pin must be output
sensors.begin();
slave.cbVector[CB_READ_INPUT_REGISTERS] = readAnalogIn; //funzione che legge su un pin analogico dello slave comandato dal master
// set Serial and slave at baud 9600.
RS485Serial.begin( 9600 );
slave.begin( 9600 );
}
void loop() {
slave.poll();
}
int tempC_int;
uint16_t readAnalogIn(uint8_t fc, uint16_t address, uint16_t length) {
Serial.println("Slave 1 chiamato da Master");
sensors.requestTemperatures(); // Send the command to get temperatures
float tempC = sensors.getTempCByIndex(0);
if(tempC != DEVICE_DISCONNECTED_C)
{
tempC_int=tempC*100;
}
else
{
tempC_int=0;
}
// write uint16_t value to the response buffer.
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(0, 500);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(1, 601);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(2, 702);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(3, analogRead(A3));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(4, 804);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(5, 905);
Serial.println("Dati inviati...");
/*
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(0, tempC_int);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(1, analogRead(A2));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(2, analogRead(A4));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(3, analogRead(A5));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(4, analogRead(A6));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(5, analogRead(A7));
/*
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(0, analogRead(A0));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(1, analogRead(A1));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(2, analogRead(A2));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(3, analogRead(A3));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(4, analogRead(A4));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(5, analogRead(A5));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(6, analogRead(A6));
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(7, analogRead(A7));
*/
for (int i = 6; i < length; i++) {
// scrivo i restanti valori del buffer a zero
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(i, 0);
}
return STATUS_OK;
}
if you want I can clean it of the instructions for the management of the TFT
put all that aside for a bit and try getting hello received on the slave..
master..
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#define PinRicezione 16 // collegare l'RO della RS485
#define PinTrasmissione 17 //collegare il DI della RS485
#define PinControllo 33 //collegare il DE e l'RE della RS485
#define MODBUS_SERIAL_BAUD 9600 // Baud rate for esp32 and max485 communication
void preTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 1); //abilito il DE/RE della RS485 alla trasmissione
}
void postTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 0); //disabilito il DE/RE della RS485 alla trasmissione
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(PinControllo, OUTPUT); //settaggio pin di abilitazione della trasmissione e ricezione
// Init in receive mode
digitalWrite(PinControllo, 0); //setto il pin inizialmente in ricezione
Serial2.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, PinRicezione, PinTrasmissione);
}
void loop() {
preTransmission();
Serial2.println("Hello");
postTransmission();
delay(10000);
}
use the 1st slave sketch that just writes what it gets and you should see a hello every 10 seconds..
let's see some hellos..
~q
HI qubits-us,
First of all I want to thank you for your time and know that if you come to Monza (in Italy) you have a paid cappuccino and croissant...
I'm following your suggestion, to figure out what's wrong you need to focus on the only part that's wrong and leave the rest alone. So I rebuilt the Master Slave circuits without the mess of the TFT and I also inserted a new component that I received this morning from Amazon instead of the breadboard power supply: a voltage regulator module with Vin (4.75V-12V) and 3.3V output. The detailed features are as follows
Fasizi 3.3 DC Voltage Regulator Step Down Power Supply Module 4.75V-12V to 3.3V 800mA
Output current: 0.8A
Line adjustment rate: 0.2% (maximum)
Load regulation: 0.4% (max.)
Packing type: SOT-223
Operating junction temperature range: - 40 to 125°C
Welding temperature (25 seconds): 265°C
Storage temperature: - 65~150°C
Output voltage: 3.267 to 3.333V (IOUT: 0 to 1A, VIN: 4.75V to 12V)
Line regulation (maximum): 10 mV (VIN: 4.75V to 12V)
Load regulation (maximum): 15 mV (VIN = 5V, IOUT: 0 to 1A)
Voltage difference (maximum): 1.3V
Current Limit: 900~1500mA
Quiescent Current (Maximum): 10mA
Ripple suppression (minimum): 60dB
Dimensions: 8.6mm x 12.33mm
As you can see in the post I reinserted the pattern and I also took a picture of you.
Now let's move on to the software part. I proceeded to load the sketches you indicated on the Master and on the slave (I had to add a few serial.print lines for debugging. Unfortunately, the result is not the expected one, instead of the Hello message appearing on the serial monitor of the slave, a 0 comes out first and immediately after another 0, and this every 3 seconds (I reduced the time compared to the 10 seconds you indicated because it was a very long time to wait).
But something new happened that had never happened before and that is that this time both the leds on the ESP32 and on the Arduino nano flash in synchrony every 3 seconds.
FYI, I tried removing the 20K pull-up resistor and the slave output went from 0 0 to 255 as photo. your opinion: what can it mean to pass from 0 to 255, it seems from a low value to a high value...
Sorry for the late reply..
beautiful..
New power supply, ok..
Wasn't leaning that direction..
A couple of 485 boards and we wouldn't be here now, but what ever..
Been thinking about what else to try..
Still don't like how the A and B on the max chips plug into the breadboard busses..
Try this, remove resistors, connect the 2 max chips A B directly..
Try first at 9600, if no go reduce baud rate really low, like 300 on both sender and receiver and test again..
I also didn't like the level converter either, but I have seen they do make high speed ones so, I've ignored it..
The output of the level convert should be compatible with the nano, so you should hypothetically be able to omit the max chips and test level converter using 232, send to recv, recv to send, no changes needed to sketch should get hellos..
max chips could be going a bit crazy, they switch fast, the ceramic caps real close to each vcc to grnd might be necessary not optional..
or just order a couple of 485 adapter boards and move on..
good luck.. ~q
PROBLEMS SOLVED
I'm not going to explain everything I had to do....it would be too long in a language I don't know very well, but I'll give you the final solution.
Scheme to run like the one shown in my previous post by eliminating the 20k resistors.
Sketch for the master to read 6 numbers of 2 bytes each (from 0 to 65k...) from slave 1 starting from register position 0x7531 (ie from position 30001).
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
#define MODBUS_DIR_PIN 33 // connect DE, RE pin of MAX485 to gpio 33
#define MODBUS_RX_PIN 16 // Rx pin
#define MODBUS_TX_PIN 17 // Tx pin
#define MODBUS_SERIAL_BAUD 9600 // Baud rate for esp32 and max485 communication
//Initialize the ModbusMaster object as node
ModbusMaster node;
//variabili dove memorizzo le letture provenienti dagli slave
int S1_dato1 =0; int S1_dato2 =0; int S1_dato3 =0; int S1_dato4 =0; int S1_dato5 =0; int S1_dato6 =0;
// Definisco le funzioni di comunicazioni pre e post trasmissione
void modbusPreTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(MODBUS_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
}
void modbusPostTransmission()
{
digitalWrite(MODBUS_DIR_PIN, LOW);
}
void setup() {
// esp serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(MODBUS_DIR_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(MODBUS_DIR_PIN, LOW); // Init in receive mode
//Serial2.begin(baud-rate, protocol, RX pin, TX pin);.
Serial2.begin(MODBUS_SERIAL_BAUD, SERIAL_8N1, MODBUS_RX_PIN, MODBUS_TX_PIN);
//Serial2.setTimeout(300);
Serial.println("Ho inizializzato la com. MODBUS Master...");
//modbus slave ID 1
node.begin(1, Serial2); //Un solo slave collegato
delay(50);
// callbacks allow us to configure the RS485 transceiver correctly
node.preTransmission(modbusPreTransmission);
node.postTransmission(modbusPostTransmission);
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result; //definisce la variabile result
node.setSlave(1); //Seleziono Slave 1
//Modbus function that Read Input Registers
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x7531, 6); //0x7531 in hex significa 30001 in decimale, il 6 indica che il buffer ha 6 posizioni
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
Serial.println("Success, Received data: ");
S1_dato1 = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
S1_dato2 = node.getResponseBuffer(1);
S1_dato3 = node.getResponseBuffer(2);
S1_dato4 = node.getResponseBuffer(3);
S1_dato5 = node.getResponseBuffer(4);
S1_dato6 = node.getResponseBuffer(5);
Serial.print(S1_dato1);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(S1_dato2);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(S1_dato3);Serial.println("---");
Serial.print(S1_dato4);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(S1_dato5);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(S1_dato6);Serial.println("---");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, Response Code: ");
Serial.println(result, DEC);
delay(3000);
}
delay(3000);
}
Sketch for Slave with Id 1
#include <ModbusSlave.h> //libreria da caricaricare da https://github.com/yaacov/ArduinoModbusSlave
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> //libreria standard dell'IDE di Arduino
#define PinRicezione 10 // collegare l'RO della RS485
#define PinTrasmissione 11 //collegare il DI della RS485
#define PinControllo 3 //collegare il DE e l'RE della RS485
SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(PinRicezione, PinTrasmissione); // RX, TX
int NomeSlave = 1; //indirizzo dello slave
Modbus slave(RS485Serial, NomeSlave, PinControllo); //Creo l'oggetto slave
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(PinControllo, OUTPUT); // RS485 control pin must be output
RS485Serial.begin(9600);
slave.begin(9600);
slave.cbVector[CB_READ_INPUT_REGISTERS] = readAnalogIn; //funzione che legge su un pin analogico dello slave comandato dal master
// set Serial and slave at baud 9600.
}
void loop() {
slave.poll();
}
uint16_t readAnalogIn(uint8_t fc, uint16_t address, uint16_t length) {
Serial.println("Slave 1 chiamato da Master");
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(0, 500);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(1, 601);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(2, 702);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(3, 1200);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(4, 804);
slave.writeRegisterToBuffer(5, 905);
Serial.println("Dati inviati...");
Serial.print(500);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(601);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(702);Serial.println("---");
Serial.print(1200);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(804);Serial.print("---");Serial.print(905);Serial.println("---");
return STATUS_OK;
}
qubits don't forget, when you come to Monza the cappuccino and croissant is offered by me...
This topic was automatically closed 180 days after the last reply. New replies are no longer allowed.