I would like to use a digital I2S microphone to record audio and store it as wav on a PC, preferably over serial connection. I have tried this with the boards ESP32 dev kit v1, MKR Wifi 1010 and Adafruit Feather M0 in combination with the microphones SPH0645 or INMP441, but never succeeded.
Here are the exemplary codes for the use of the ESP32 dev kit v1 with the SPH0645 from Adafruit (Overview | Adafruit I2S MEMS Microphone Breakout | Adafruit Learning System).
Arduino:
const i2s_port_t I2S_PORT = I2S_NUM_0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Configuring I2S...");
const i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
.mode = i2s_mode_t(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX),
.sample_rate = 16000,
.bits_per_sample = I2S_BITS_PER_SAMPLE_32BIT,
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_RIGHT,
.communication_format = i2s_comm_format_t(I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S | I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S_MSB),
.intr_alloc_flags = ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1,
.dma_buf_count = 8, // Increased buffer count
.dma_buf_len = 64 // Increased buffer length
};
const i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
.bck_io_num = 33, // BCKL
.ws_io_num = 25, // LRCL
.data_out_num = -1, // not used (only for speakers)
.data_in_num = 32 // DOUT
};
esp_err_t err = i2s_driver_install(I2S_PORT, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("Failed installing driver: %d\n", err);
while (true);
}
err = i2s_set_pin(I2S_PORT, &pin_config);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("Failed setting pin: %d\n", err);
while (true);
}
Serial.println("I2S driver installed.");
}
void loop() {
// Wait for the start command from the Python script
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char command = Serial.read();
if (command == 's') { // Start command received
int duration = 10; // Recording duration in seconds
int sample_rate = 16000; // Same as the ESP32 sample rate
int samples_to_send = duration * sample_rate;
for (int i = 0; i < samples_to_send; i++) {
int32_t sample = 0;
size_t bytes_read;
i2s_read(I2S_PORT, &sample, 4, &bytes_read, portMAX_DELAY); // no timeout
if (bytes_read > 0) {
sample >>= 14;
int16_t out = sample;
Serial.println(out);
}
}
Serial.write('e'); // Send an end signal to the Python script
}
}
}
Python code:
import datetime
import wave
# open a serial connection to the Arduino
ser = serial.Serial('COM16', 115200)
# ask the user for the length of the audio in seconds
length = int(input("Enter the length of the recording in seconds: "))
# get the current date and time
now = datetime.datetime.now()
# create a filename with a datetimestamp
filename = "recording_{}.wav".format(now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S"))
# set the WAV file parameters
channels = 1
sample_width = 2 # 2 bytes per sample
sample_rate = 16000
# open a file for writing the audio data
with wave.open(filename, 'wb') as f:
# set the WAV file parameters
f.setnchannels(channels)
f.setsampwidth(sample_width)
f.setframerate(sample_rate)
# read audio data from the serial port and write it to the file
for i in range(length*sample_rate):
data = ser.read(2)
if data:
f.writeframes(data)
# close the serial connection
ser.close()
print("Recording saved as {}".format(filename))
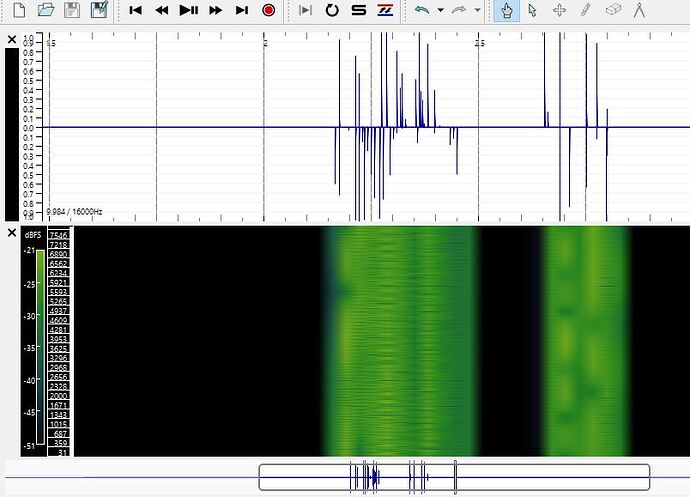
The above setup with the ESP32 dev kit v1 and the SPH0645 results in a wav file with the correct file structure (44 byte header etc.) but a signal that doesn't show the expected amplitudes and spectrogram features. It rather looks interrupted and distorted (see image).
Has anyone tried this and could help me figure out the correct hardware and code setup to achieve a successful recording?
Cheers!