The Arduino is doing both the sending and the receiving. I have tried powering the Arduino both with a USB cable from the computer and a wall charger and a 12V power supply.
Here the schematics can be seen (sorry for the rough drawings - I hope they make sense)
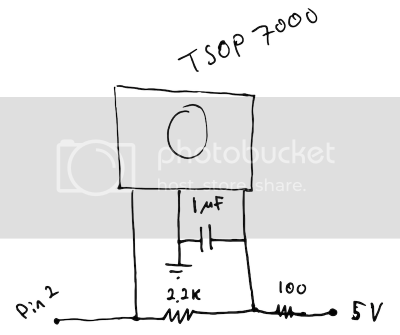

I am using a TSOP7000 because i use it with a Beo4 remote that sends 455 kHz signals instead of the usual 38 kHz.
As for the code here is a shortened version. Everything that is left is just a bunch of else if's
// This version is all the codes in an order based on the Beo4 remote layoyt
// We need to use the 'raw' pin reading methods
// because timing is very important here and the digitalRead()
// procedure is slower!
// uint8_t IRpin = 2;
// Digital pin #2 is the same as Pin D2 see
// http://arduino.cc/en/Hacking/PinMapping168 for the 'raw' pin mapping
#define IRpin_PIN PIND
#define IRpin 2
// the maximum pulse we'll listen for - 65 milliseconds is a long time
#define MAXPULSE 15000
#define NUMPULSES 22
// what our timing resolution should be, larger is better
// as its more 'precise' - but too large and you wont get
// accurate timing
#define RESOLUTION 20
// What percent we will allow in variation to match the same code
#define FUZZINESS 20
// we will store up to 100 pulse pairs (this is -a lot-)
uint16_t pulses[NUMPULSES][2]; // pair is high and low pulse
uint8_t currentpulse = 0; // index for pulses we're storing
#include <IRremote.h>
#include "IRreceivecodes_progmem.h"
#include "IRsendcodes.h"
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
//#include <avr/wdt.h> // For watchdog!
int ledstripPin = 10;
int delayTime = 1; // The delay time between each IR command in miliseconds
IRsend irsend; // IRSendPin fixed to 3 (PWM, output)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
//irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Begin the receiving process. This will enable the timer interrupt which consumes a small amount of CPU every 50 µs
//pinMode(IRsensor, INPUT);
analogWrite(ledstripPin, 0);
}
void loop(void) {
int numberpulses;
numberpulses = listenForIR();
// Top part
// TV button
if (IRcompare(numberpulses, TV, sizeof(TV))) {
for (int i=0; i <= 1; i++){
irsend.sendPanasonic(PanasonicAddress, PanasonicTV); // Panasonic TV input
delay(delayTime);
}
irsend.sendNEC(YamahaDTV, 32); // Yahama D-TV input. Used for TV
//Serial.println("TV");
}
// Light button not in use!
// Radio button
else if (IRcompare(numberpulses, Radio, sizeof(Radio))) {
for (int i=0; i <= 2; i++){
irsend.sendNEC(YamahaPowerOn, 32); // Yamaha power on
delay(delayTime);
}
irsend.sendNEC(YamahaMD, 32); // Yahama MD input. Used for iMac
//Serial.println("Radio");
}
// SAT button not in use!
// DVD button not in use!
// CD button
else if (IRcompare(numberpulses, CD,sizeof(CD))) {
irsend.sendNEC(YamahaPhono, 32); // Phono input. Used for record player
delay(delayTime);
//Serial.println("CD");
}
// VTape button
else if (IRcompare(numberpulses, VTape,sizeof(VTape))) {
for (int i=0; i <= 1; i++){
irsend.sendPanasonic(PanasonicAddress, PanasonicAV); // Change to AV
delay(delayTime);
}
irsend.sendNEC(YamahaDVD, 32); // Yahama DVD input. Used for Apple TV
//Serial.println("DVD");
}
// Record
else if (IRcompare(numberpulses, Record,sizeof(Record))) {
irsend.sendNEC(Yamaha6ch, 32); // 6ch input. Used for BD player, 6ch input
delay(delayTime);
//Serial.println("Record");
}
// AND SO ON
// The end
}
// ALL THE DEFINITIONS!
//KGO: added size of compare sample. Only compare the minimum of the two
boolean IRcompare(int numpulses, uint16_t Signal[], int refsize) {
int count = min(numpulses,refsize);
for (int i=0; i< count-1; i++) {
int oncode = pulses[i][1] * RESOLUTION / 10;
int offcode = pulses[i+1][0] * RESOLUTION / 10;
int onState = pgm_read_word_near(&(Signal[i*2 + 0]));
int offState = pgm_read_word_near(&(Signal[i*2 + 1]));
#ifdef DEBUG
//Serial.print(oncode); // the ON signal we heard
//Serial.print(" - ");
//Serial.print(Signal[i*2 + 0]); // the ON signal we want
#endif
// check to make sure the error is less than FUZZINESS percent
if ( abs(oncode - onState) <= (onState * FUZZINESS / 100)) {
#ifdef DEBUG
//Serial.print(" (ok)");
#endif
} else {
#ifdef DEBUG
//Serial.print(" (x)");
#endif
// we didn't match perfectly, return a false match
return false;
}
#ifdef DEBUG
// Serial.print(" \t"); // tab
// Serial.print(offcode); // the OFF signal we heard
// Serial.print(" - ");
// Serial.print(Signal[i*2 + 1]); // the OFF signal we want
#endif
if ( abs(offcode - offState) <= (offState * FUZZINESS / 100)) {
#ifdef DEBUG
// Serial.print(" (ok)");
#endif
} else {
#ifdef DEBUG
// Serial.print(" (x)");
#endif
// we didn't match perfectly, return a false match
return false;
}
#ifdef DEBUG
// Serial.println();
#endif
}
// Everything matched!
return true;
}
int listenForIR(void) {
currentpulse = 0;
while (1) {
uint16_t highpulse, lowpulse; // temporary storage timing
highpulse = lowpulse = 0; // start out with no pulse length
// while (digitalRead(IRpin)) { // this is too slow!
while (IRpin_PIN & (1 << IRpin)) {
// pin is still HIGH
// count off another few microseconds
highpulse++;
delayMicroseconds(RESOLUTION);
// If the pulse is too long, we 'timed out' - either nothing
// was received or the code is finished, so print what
// we've grabbed so far, and then reset
// KGO: Added check for end of receive buffer
if (((highpulse >= MAXPULSE) && (currentpulse != 0))|| currentpulse == NUMPULSES) {
return currentpulse;
}
}
// we didn't time out so lets stash the reading
pulses[currentpulse][0] = highpulse;
// same as above
while (! (IRpin_PIN & _BV(IRpin))) {
// pin is still LOW
lowpulse++;
delayMicroseconds(RESOLUTION);
// KGO: Added check for end of receive buffer
if (((lowpulse >= MAXPULSE) && (currentpulse != 0))|| currentpulse == NUMPULSES) {
return currentpulse;
}
}
pulses[currentpulse][1] = lowpulse;
// we read one high-low pulse successfully, continue!
currentpulse++;
}
}
Yeah, I didn't quite know how else to describe it  I am on pretty new ground working with this stuff and I just can't seem to get my head around the problem.
I am on pretty new ground working with this stuff and I just can't seem to get my head around the problem.

