Hi there!
I would like to set the CLK Frequency of my Arduino 2560 Mega to round about 50 kHz. I am aware that there are some predefined Clock dividers, which allow me to set the clock rate down to 125 kHz. Unfortunately this is still too much for my slave device I would like to communicate with due to R/C suppresors.
Another option I saw was to prescale the clock to 8 mHz by using this in the setup:
CLKPR = 0b10000000;
CLKPR = 0b00000001;
So the final CLK rate ended up at 62,5 kHz.
After testing my setup at this pace the result was that it was still too fast for the slave device I am using.
So the question is :
Is there a way I can adjust the speed of my CLK frquency to 50 kHZ or even individually to any desired freqency?
And if there´s a way, how?
Thank you in advance!
daandx:
Another option I saw was to prescale the clock to 8 mHz by using this in the setup:
CLKPR = 0b10000000;
CLKPR = 0b00000001;
So the final CLK rate ended up at 62,5 kHz.
After testing my setup at this pace the result was that it was still too fast
So use one of the other prescale values:
0b0000010 = 4 (4 MHz)
0b0000011 = 8 (2 MHz)
0b0000100 = 16 (1 MHz)
...
0b0001000 = 256 (62 kHz)
thank you for the quick answer @johnwasser!
As you might have misunderstood, 62,5 kHz is too fast for my purpose. I need something round about 50 kHz CLK frquency.
The prescaled values you mentioned offer a variety of higher frequency (from 62,5kHz up to 4mHz) am I right?
So if I´m not mistaken they dont work for me ![]()
You could write bit-banged SPI code to run at any (slow) speed you want.
@gfvalvo thanks for the hint. Unfortunately I haven´t got any experience in bit banging programming so far so if possible I would like to use the code which is already written. Writing an entirely new one would be the last option for me atm
here's an example code using timer2 here:
for OCR2A=31 you should get a clk freq close to 50kHz
hope that helps...
@sherzaad, thank you! it seems to work to scale the CLK with the proposed signal so far. I hope it´ll work with my setup. At the moment the polarity of the CLK is low at the beginning. Do you know how to adapt the moduled clock on a logic high at the beginning?
daandx:
@sherzaad, thank you! it seems to work to scale the CLK with the proposed signal so far. I hope it´ll work with my setup. At the moment the polarity of the CLK is low at the beginning. Do you know how to adapt the moduled clock on a logic high at the beginning?
You titled your thread "SPI CLK Frequency Settings" so I'm assuming this is all related to SPI.
If you have a timing diagram for the SPI comms or can at least tell us which clock mode your device should be using, it way very well turn out to be irrelevant that CLK start low.
If is was me I would simply use a transistor to logic NOT/AND it...
daandx:
thank you for the quick answer @johnwasser!
As you might have misunderstood, 62,5 kHz is too fast for my purpose. I need something round about 50 kHz CLK frquency.
If an 8 MHz system clock gets you 62.5 kHz SPI clock then a 4 MHz system clock should get you a 31.25 kHz SPI clock; well under 50 kHz.
@johnwasser thank you! seems like it was a long day yesterday for me ![]() the prescaling works that way pretty well.
the prescaling works that way pretty well.
However I do not understand why my MISO signal doesnt work correct.
I attached the picture of the analog signal, which shows from top to bottom following signals:
-MOSI (blue)
-CLK (pink)
-SS (yellow)
-MISO (green)
I do have 10,1 kO Pull Up Resistor on the MISO line.
Does anyone know why the signal is still not clear?
daandx:
however the upload of the image didnt work. I hope it does now...
Nope. ![]()
Hello guys, unfortuantely I had to quit yesterday. The attachment should work now. I do have a stable signal now (see attachment). The purpose of the SPI communication is to communicate with a slave device which measures cell voltages, using the Arduino as the Master.
Even though the timing looks correct to me, the meausured cell voltages are not.
I am using this library & adapted it to the pinout of the 2560 Mega:
However, the code does make sense to me there is one part which doesn´t:
void LTC6802::readValues(const byte cmd, const byte numOfRegisters, byte *const arr)
{
do
{
read(cmd, numOfRegisters, arr);
}
while (arr[0] == 0xff);
}
The .ino code looks like this:
#include <LTC6802.h>
/**
- Chip 1 SPI bus address.
*/
static const byte address1 = 0x04;/**
- Chip select pin.
*/
static const byte csPin1 = 53;/**
- Chip 1 LTC6802 object.
*/
static LTC6802 chip1 = LTC6802(address1, csPin1);/**
- Arduino setup.
*/
void setup()
{Serial.begin(9600);
LTC6802::initSPI(); // Init SPI bus
chip1.cfgRead(); // Read configuration from chip
chip1.cfgSetLVLPL(true); //true=1=LVLPL an, false=0 togglepl(default)
chip1.cfgSetGPIO1(false); // default setup is 0
chip1.cfgSetGPIO2(false); // default setup is 0
chip1.cfgSetCDC(1); // Measure mode 13ms (war auf 1)
chip1.cfgSetMCI(0x0fff); // Disable interrupts
chip1.cfgWrite(false); // Write configuration back to chip
Serial.println("Initialized chip");
delay(2000);
}/**
- Arduino main loop.
*/
void loop()
{chip1.cfgWrite(false); // Write configuration back to chip, because chip resets these every 2.5s when nothing happens on SPI
chip1.temperatureMeasure(); // Measure temperatures on chip
chip1.temperatureRead(); // Read temperatures from chip
chip1.temperatureDebugOutput(); // Send temperatures to serial
chip1.cellsMeasure(); // Measure cell voltages on chip
chip1.cellsRead(); // Read cell voltages from chip
chip1.cellsDebugOutput(); // Send cell voltages to serial
chip1.cfgDebugOutput();
delay(3000);
}
daandx:
....
I am using this library & adapted it to the pinout of the 2560 Mega:
GitHub - PowerStat/LTC6802: Arduino library for the LTC6802 multicell battery stack monitor ic from analog devices.....
However, the code does make sense to me there is one part which doesn´t:The .ino code looks like this:
I had a look at the library and there is more thing that dont make sense!
for example this routine "LTC6802::initSPI()", if you look at the code within the library,
void LTC6802::initSPI(const byte pinMOSI, const byte pinMISO, const byte pinCLK)
{
// TODO parameters for different arduinos (pins, clock)
pinMode(pinMOSI, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinMISO, INPUT);
pinMode(pinCLK, OUTPUT);
// SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST);
// SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3);
// SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16);
// SPI.begin();
// SPI.begin(ETHERNET_SHIELD_SPI_CS);
// SPI.setClockDivider(ETHERNET_SHIELD_SPI_CS, SPI_CLOCK_DIV16);
// SPI.setDataMode(ETHERNET_SHIELD_SPI_CS, SPI_MODE3);
}
the SPI port is not EVEN initialised in it!!!!!
if you are willing to give it a go I would modify the about routine with the .cpp file to the following and try again:
void LTC6802::initSPI()
{
SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3);
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16);
SPI.begin();
}
Of course I assuming you are correctly connected the MOSI, MISO and SCLK from your MEGA to the LTC6802! ![]()
hope the helps....
@sherzaad thanks for the reply! I forgot to mention that I already checked that point and initialised it that way:
void LTC6802::initSPI(const byte pinMOSI, const byte pinMISO, const byte pinCLK)
{
// TODO parameters for different arduinos (pins, clock)
pinMode(pinMOSI, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinMISO, INPUT);
pinMode(pinCLK, OUTPUT);SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3);
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV128);
CLKPR = 0b10000000;
CLKPR = 0b00000010;
SPI.begin();}
So as you can see the preset of the CLK is set.
If this would have been done as well as putting the right pin connections, I assume the code would not get me to the physical signals attached before ![]()
Apart from that I´m curious what other parts do not make sense to you
I don't know why you are doing that though... :o
If I read the data sheet the chip SCLK can go up to 1MHz...
meaning the change to the routine in replay #12 should be sufficient...
Well I need to clock down due to the RC suppressors on the PCB which cannot handle 1MHz even though the chip could as i posted in #1. So I had to slow down at least 50kHz. But that works fine so far with the initialisation.
The thing I wonder about if there is another key figure I missed in the .cpp or .h file which is not working correctly or has to be adjusted. It seems to me that the chip is missing some instruction, which could mean there is a logic mistake in the code I do not see at the moment.
Apart from the readValue condition i posted before I dont see the problem. Do you think this could be the issue?
daandx:
Well I need to clock down due to the RC suppressors on the PCB which cannot handle 1MHz even though the chip could as i posted in #1. So I had to slow down at least 50kHz. But that works fine so far with the initialisation.
The thing I wonder about if there is another key figure I missed in the .cpp or .h file which is not working correctly or has to be adjusted. It seems to me that the chip is missing some instruction, which could mean there is a logic mistake in the code I do not see at the moment.
Apart from the readValue condition i posted before I dont see the problem. Do you think this could be the issue?
ok fair enough....
anyhow, since now you have SPI.begin() in 'init' routine and give the added mod you've included for the CLK, IMHO all the "SPI.beginTransaction(spiSettings);" and "SPI.endTransaction();" in the other routine should be commented out as they are unnecessary and could be the issue.
also donno if that matters but this I would take out of the 'initSPI' routine:
//update system clock prescaler
CLKPR = 0b10000000;
CLKPR = 0b00000010;
and put as the very first lines of code in 'setup' as IMHO it affects SPI as well as Serial comms
hope that helps....
Hi there! Sorry for the late response, I hadnt had the chance to work on this the last days.
Unfortunately the Code before didnt work out after several more tries that´s why I decided to write this Code which keeps it pretty simple:
#include "SPI.h"
//Definiere Chip Commands
#define WRCFG 0x01 // Write Configuration Register Group
#define RDCFG 0x02 // Read Configuration Register Group
#define RDCV 0x04 // Read Cell Voltage Register Group
#define RDFLG 0x06 // Read Flag Register Group
#define RDTMP 0x08 // Read Temperature Register Group
#define STCVAD 0x10 // (ALL)Start Cell Voltage A/D Conversions and Poll Status
#define STOWAD 0x20 // (ALL)Start Open - Wire A/D Conversions and Poll Status
#define STTMPAWD 0x30 // (ALL)Start Temperature A/D Conversions and Poll Status
#define PLADC 0x40 // Poll A/D Converter Status
#define PLINT 0x50 // Poll Interrupt Status
#define STCVDC 0x60 // (ALL)Start Cell Voltage A/D Conversions and Poll Status, with Discharge Permitted
#define STOWDC 0x70 // (ALL)Start Opne-Wire A/D Conversions and Poll Status, with Discharge Permitted
// OWN SETUP SETTINGS
#define address 0x01 // Put the AddressCode of the DEVICE IN HERE
#define CSPIN 53
// CHIP SETTINGS
#define CFGR0 B00001001 //WDT,GPIO2 (1=pin pull down off(default);GPIO1 (1=pin pull down off(default);LVLPL (default=0=off);CELL10 (default =0=12CellMode);CDC[2];CDC[1];CDC[0]
#define CFGR1 0x00
#define CFGR2 0x00
#define CFGR3 0x00
#define CFGR4 0x00
#define CFGR5 0x00
byte cellRegisters=18; // CV[0-17]
byte cellvolts[12];
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
SPIINIT();
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
WriteConfigurationRegister() ;
//READCELLVLVL ();
READCELLVT ();
delay(200);
}
//
void SPIINIT()
{
pinMode(53, OUTPUT); // SS
pinMode(52, OUTPUT); //SCK
pinMode(51, OUTPUT); //MOSI (from CHIP SIDE: SDI)
pinMode(50, INPUT); //MISO (from CHIP SIDE: SDO)
//SPIMODUS
CLKPR = 0b10000000; //CLK von 125kHZ auf 62,5 kHz
CLKPR = 0b00000010;
SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST); //Most Significant Bit
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3); //111
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV128); // default=16 MHz;
//Start the SPI Communication
SPI.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void WriteConfigurationRegister()
{
digitalWrite(CSPIN, LOW); //Start Communication
SPI.transfer(WRCFG);
SPI.transfer(CFGR0);
SPI.transfer(CFGR1);
SPI.transfer(CFGR2);
SPI.transfer(CFGR3);
SPI.transfer(CFGR4);
SPI.transfer(CFGR5);
digitalWrite(CSPIN, HIGH); //End Communication
//delay(20); //"Sicherheitshalber" wenn Auskommentiert MOSI im ersten Block zu sehen
}
void READCELLVT () //VARiANTE BROADCAST COMMAND WITH TOGGLEPOLLING
{
digitalWrite(CSPIN,LOW);
SPI.transfer(address);
SPI.transfer(RDCV);
byte CV[cellRegisters];
for (int i = 0; i < cellRegisters; ++i)
{
CV[i] = SPI.transfer(RDCV);
}
digitalWrite(CSPIN,HIGH);
delay(20);
digitalWrite(CSPIN,LOW);
SPI.transfer(STCVAD); // All Devices Start Conversion
delay(20); // mindestens 12ms laut Datenblatt
digitalWrite(CSPIN,HIGH); //
cellvolts[0] = CV[0] | ((CV[1] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[1] = ((CV[1] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[2] << 4);
cellvolts[2] = CV[3] | ((CV[4] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[3] = ((CV[4] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[5] << 4);
cellvolts[4] = CV[6] | ((CV[7] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[5] = ((CV[7] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[8] << 4);
cellvolts[6] = CV[9] | ((CV[10] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[7] = ((CV[10] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[11] << 4);
cellvolts[8] = CV[12] | ((CV[13] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[9] = ((CV[13] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[14] << 4);
cellvolts[10] = CV[15] | ((CV[16] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[11] = ((CV[16] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[17] << 4);
Serial.print(CV[0] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[1] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[2] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[3] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[4] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[5] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[6] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[7] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[8] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[9] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[10] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(CV[11] * 1.5 / 1000);
}
void READCELLVLVL () //VARiANTE LEVEL POLLING
{
digitalWrite(CSPIN,LOW);
SPI.transfer(address);
SPI.transfer(RDCV);
byte CV[cellRegisters];
for (int i = 0; i < cellRegisters; ++i)
{
CV[i] = SPI.transfer(RDCV);
}
digitalWrite(CSPIN,HIGH);
delay(20);
digitalWrite(CSPIN,LOW);
SPI.transfer(address);
SPI.transfer(PLINT);
delay(20); // mindestens 12ms laut Datenblatt
digitalWrite(CSPIN,HIGH); //
cellvolts[0] = CV[0] | ((CV[1] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[1] = ((CV[1] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[2] << 4);
cellvolts[2] = CV[3] | ((CV[4] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[3] = ((CV[4] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[5] << 4);
cellvolts[4] = CV[6] | ((CV[7] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[5] = ((CV[7] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[8] << 4);
cellvolts[6] = CV[9] | ((CV[10] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[7] = ((CV[10] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[11] << 4);
cellvolts[8] = CV[12] | ((CV[13] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[9] = ((CV[13] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[14] << 4);
cellvolts[10] = CV[15] | ((CV[16] & 0x0F) << 8);
cellvolts[11] = ((CV[16] & 0xf0) >> 4) | (CV[17] << 4);
Serial.print(CV[0] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[1] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[2] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[3] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[4] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[5] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[6] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[7] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[8] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[9] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(CV[10] * 1.5 / 1000);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(CV[11] * 1.5 / 1000);
}
I tried out the togglepolling modus as well as the Levelpolling modus.
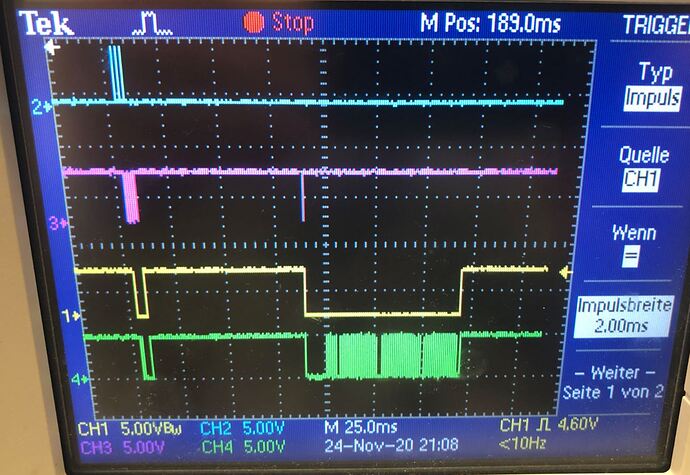
Implementing the toggle polling modus I saw this physical signal and wonder, why there is no clock on the second Slave Select Part. (blue-MOSI; pink-CLK, yellow- CS/SS, green- MISO)
In the datasheet of the chip it is written: "SDO output toggles at 1kHz rate, indicating conversions complete for all devices"
So thats what its doing in this case.
If in LVLPL it´s "SDO output from bottom device pulled low if any device has an interrupt condition; otherwise, SDO high"
I´m not sure if this is case applies.
Apart from that in both cases there is no CLK Signal. As far as I know, CLK is obligatory to read any bits on the MISO line. Therefore does anyone know why the Master doesnt clock?