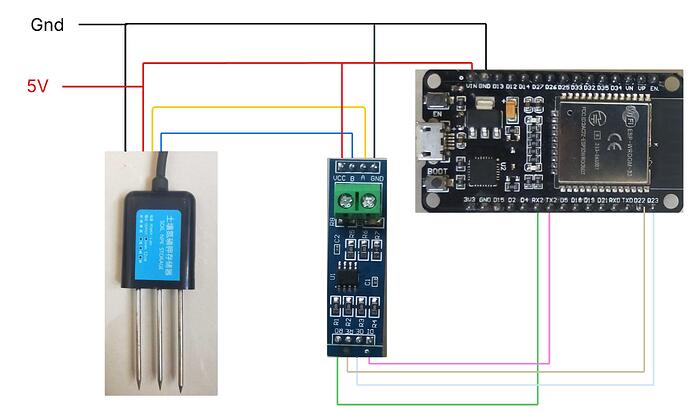
ok I'll share the connection
Initially, i had an issue with the baudrate as i set it to 9600 and was getting raw data, i later changed it to 4800 and got meaningful values
I'd appreciate it
![]() Thank you
Thank you
I also faced this issue before and then I changed my TTL to RS485.
Requesting Nitrogen...
Timeout! No response.
Requesting Phosphorous...
Timeout! No response.
Requesting Potassium...
Timeout! No response.
Nitrogen: 255 mg/kg
Phosphorous: 255 mg/kg
Potassium: 255 mg/kg
Requesting Nitrogen...
This is the response that i was getting , could it be because i was using the wrong addresses and registers ?
At first i used the code as is but i was getting raw data which i couldn't understand, then after i changed the line of code :
Serial.begin(115200) to Serial.begin(4800) and i started getting data i could understand
NPK Sensor Manual 6-1.pdf (357.8 KB)
I have the manual and its in chinese and i can't seem to figure out the inquiry frame hexadecimal values
ok, I'll help you as much as possible.
You can use some other manual for these sensors
If you use Google translate on that document, you get this one:
NPK Sensor Manual 6-1 - Translated.pdf (606.4 KB)
It's not pretty but its better than learning Chinese.
Definitely way better than learning chinese ![]()
I asked deepseek to extract the inquiry frame for me and used the above code but i'm still facing the same problem ![]()
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#define RE 22
#define DE 23
// Modbus RTU requests for reading NPK values
const byte nitro[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x1E, 0x00, 0x01, 0xE4, 0x0C};
const byte phos[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x1F, 0x00, 0x01, 0xB5, 0xCC};
const byte pota[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x20, 0x00, 0x01, 0x85, 0xC0};
byte values[11];
HardwareSerial mod(2); // Use HardwareSerial on UART2 (TX2 = 17, RX2 = 16)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(4800);
mod.begin(4800, SERIAL_8N1, 16, 17); // Try 9600 first, if not working try 4800
pinMode(RE, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DE, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RE, LOW);
digitalWrite(DE, LOW);
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
byte val1 = nitrogen();
delay(250);
byte val2 = phosphorous();
delay(250);
byte val3 = potassium();
delay(250);
Serial.print("Nitrogen: ");
Serial.print(val1);
Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Phosphorous: ");
Serial.print(val2);
Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Potassium: ");
Serial.print(val3);
Serial.println(" mg/kg");
delay(2000);
}
byte nitrogen(){
Serial.println("Requesting Nitrogen...");
digitalWrite(DE, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RE, HIGH);
delay(10);
mod.write(nitro, sizeof(nitro));
mod.flush();
digitalWrite(DE, LOW);
digitalWrite(RE, LOW);
long timeout = millis();
while (mod.available() < 7) {
if (millis() - timeout > 2000) {
Serial.println("Timeout! No response.");
return 255;
}
delay(10);
}
Serial.print("Response: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
values[i] = mod.read();
Serial.print(values[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
return values[4];
}
byte phosphorous(){
Serial.println("Requesting Phosphorous...");
digitalWrite(DE, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RE, HIGH);
delay(10);
mod.write(phos, sizeof(phos));
mod.flush();
digitalWrite(DE, LOW);
digitalWrite(RE, LOW);
long timeout = millis();
while (mod.available() < 7) {
if (millis() - timeout > 2000) {
Serial.println("Timeout! No response.");
return 255;
}
delay(10);
}
Serial.print("Response: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
values[i] = mod.read();
Serial.print(values[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
return values[4];
}
byte potassium(){
Serial.println("Requesting Potassium...");
digitalWrite(DE, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RE, HIGH);
delay(10);
mod.write(pota, sizeof(pota));
mod.flush();
digitalWrite(DE, LOW);
digitalWrite(RE, LOW);
long timeout = millis();
while (mod.available() < 7) {
if (millis() - timeout > 2000) {
Serial.println("Timeout! No response.");
return 255;
}
delay(10);
}
Serial.print("Response: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
values[i] = mod.read();
Serial.print(values[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
return values[4];
}
Really appreciate it
I have sent you a program along with some information regarding your sensor. You may also try it.
Those canned modbus messages are quite common and they are querying the wrong registers according to the Chinese user manual you provided.
The user manual says that Nitrogen is in register 04h, Phosphorous in 05h and Potassium in 06h. Assuming that you have been given the correct user manual for your NPK sensor, then the three canned modbus messages would be:
const byte nitro[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x01, 0xC5, 0xCB};
const byte phos[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x05, 0x00, 0x01, 0x94, 0x0B};
const byte pota[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x06, 0x00, 0x01, 0x64, 0x0B};
But those values you get back could be anything and you wouldn't know if they were correct or not.
As a test I would send out this canned modbus message:
const byte temp[] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x01, 0xD5, 0xCA};
If you get a response to that message, then it should be the temperature. Note that a decimal value of 275 needs to be divided by 10 to get 27.5C.
I disagree, even if they are anything, I still know if they are correct or not. ![]()
How should the sample code for temp look like ?
Because i tried adding temp and i got 255 degrees
1.Technical Specifications:
- Power Supply: DC 4.5-30V
- Communication: RS485 (ModBus-RTU)
- Measurable Parameters:
- Electrical Conductivity (EC): 0-20000 μS/cm
- Soil Moisture: 0-100%
- Temperature: -40 to 80°C
- pH: 3-9
- Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium (NPK): 0-2999 mg/kg
- Protection: IP68 (Waterproof, can be submerged)
2.Wiring & Connection:
- Brown: VCC (4.5-30V)
- Black: GND
- Yellow: RS485-A
- Blue: RS485-B
3.Communication (ModBus-RTU Protocol):
- Default Baud Rate: 4800 bps (Can be set to 2400 or 9600)
- Data Structure: 8-bit, No Parity, 1 Stop Bit, CRC Checksum
- Uses Function Codes: 0x03, 0x06, 0x10
- Example Readings (Hexadecimal Values Provided in the Manual):
- Moisture (0x0292) → 65.8% (after conversion)
- Temperature (0xFF9B) → -10.1°C
- Electrical Conductivity (0x03E8) → 1000 μS/cm
- pH (0x38) → 5.6
4.Common Issues & Solutions:
- Incorrect COM Port selection.
- Wrong baud rate.
- Incorrect wiring (A/B lines reversed).
- Signal interference or weak power supply.
-
To use the hexadecimal values in your ESP32 program, follow these steps:
-
Send the Modbus request (
01 03 00 00 00 07 04 08). -
Receive the Modbus response (
01 03 0E 02 92 FF 9B 03 E8 00 38 00 96 00 78 00 AA 57 B6). -
Extract and convert the hex values into real-world data (Moisture, Temperature, EC, pH, NPK).
You can try this program.
Are you using ESP32?
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#define RX2 16 // ESP32 RX pin for RS485
#define TX2 17 // ESP32 TX pin for RS485
#define MAX485_RE 22
#define MAX485_DE 23
HardwareSerial rs485Serial(2); // UART2 for RS485 communication
// Function to calculate CRC16 checksum for Modbus
uint16_t calculateCRC(uint8_t *buffer, uint8_t length) {
uint16_t crc = 0xFFFF;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < length; i++) {
crc ^= buffer[i];
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if (crc & 0x0001) {
crc >>= 1;
crc ^= 0xA001;
} else {
crc >>= 1;
}
}
}
return crc;
}
// Function to send Modbus request
void sendModbusRequest(uint8_t *request, uint8_t length) {
digitalWrite(MAX485_DE, HIGH);
digitalWrite(MAX485_RE, HIGH);
delay(10);
rs485Serial.write(request, length);
rs485Serial.flush();
digitalWrite(MAX485_DE, LOW);
digitalWrite(MAX485_RE, LOW);
}
// Function to receive Modbus response
bool receiveModbusResponse(uint8_t *response, uint8_t length) {
unsigned long startTime = millis();
uint8_t index = 0;
while (millis() - startTime < 1000) { // 1-second timeout
if (rs485Serial.available()) {
response[index++] = rs485Serial.read();
if (index >= length) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Serial Monitor
rs485Serial.begin(4800, SERIAL_8N1, RX2, TX2); // Modbus-RTU 4800 baud rate
pinMode(MAX485_DE, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MAX485_RE, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(MAX485_DE, LOW);
digitalWrite(MAX485_RE, LOW);
}
// Function to read sensor data
void readSensor() {
uint8_t request[] = { 0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x07, 0x00, 0x00 }; // Read 7 registers
uint16_t crc = calculateCRC(request, 6);
request[6] = crc & 0xFF;
request[7] = (crc >> 8) & 0xFF;
sendModbusRequest(request, sizeof(request));
uint8_t response[19]; // Expecting 19 bytes response
if (receiveModbusResponse(response, 19)) {
if (response[1] == 0x03) { // Check if response is valid
uint16_t moisture = (response[3] << 8) | response[4];
int16_t temp = (response[5] << 8) | response[6];
uint16_t ec = (response[7] << 8) | response[8];
uint16_t ph = (response[9] << 8) | response[10];
uint16_t nitrogen = (response[11] << 8) | response[12];
uint16_t phosphorus = (response[13] << 8) | response[14];
uint16_t potassium = (response[15] << 8) | response[16];
float moistureValue = moisture / 10.0;
float temperatureValue = (temp > 32767) ? (temp - 65536) / 10.0 : temp / 10.0;
float ecValue = ec;
float phValue = ph / 10.0;
float nitrogenValue = nitrogen;
float phosphorusValue = phosphorus;
float potassiumValue = potassium;
Serial.print("Moisture: "); Serial.print(moistureValue); Serial.println("%");
Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(temperatureValue); Serial.println("°C");
Serial.print("EC: "); Serial.print(ecValue); Serial.println(" μS/cm");
Serial.print("pH: "); Serial.print(phValue); Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Nitrogen (N): "); Serial.print(nitrogenValue); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Phosphorus (P): "); Serial.print(phosphorusValue); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Potassium (K): "); Serial.print(potassiumValue); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.println("-----------------------------");
} else {
Serial.println("Invalid response from sensor!");
}
} else {
Serial.println("No response from sensor!");
}
}
void loop() {
readSensor();
delay(2000);
}