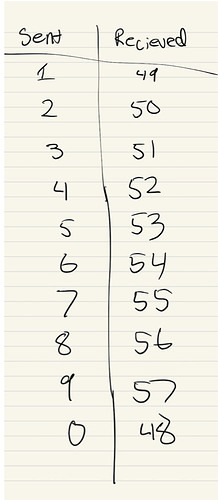
I am trying to send a String, one character at a time, from one Arduino to another. The String contained a list of numbers. It appears that for each char sent (one digit of the number), the other Arduino receives a value that is 48 greater than the number sent (See the image below).
I know I can just subtract 48 but I want to know why this is happening.
The code for the master Arduino is as follows:
//Master
#include <Wire.h>
#include <util/atomic.h>
String i2c_rcv; //data received from I2C bus
unsigned long time_start; //start time in milliseconds
//Encoder Lists
String posList_uno;
int numSteps_uno = 0;
String posList_server;
int numSteps_server = 0;
void setup() {
//Connect to Computer
Serial.begin(9600);
// join I2C bus as Slave with address 0x08
Wire.begin(8);
Serial.println("Arduino Connected");
// initialize global variables
i2c_rcv = "";
time_start = millis();
Serial.println("Time Started");
Wire.onReceive(dataRcv);
signalArduino(5);
getPathFromArduino();
Serial.println("posList_uno");
Serial.println(posList_uno);
}
void loop() {
}
//Send val to other Arduino
void signalArduino(int val) {
Wire.beginTransmission(8);
Serial.println("began transmission");
Wire.write(val);
Serial.println("Value Written");
Wire.endTransmission();
//Serial.println(val + " sent to Arduino");
}
void getPathFromArduino() {
posList_uno = "";
while(posList_uno.length() == 0){
ATOMIC_BLOCK(ATOMIC_RESTORESTATE) {
posList_uno = i2c_rcv;
i2c_rcv = "";
}
}
}
void sendArduinoPath() {
Wire.beginTransmission(8);
for (int i = 0; i < posList_server.length(); i++) {
Wire.write(posList_server[i]);
}
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("lists sent to arduino");
}
void dataRcv(int numBytes) {
Serial.println("RCV Triggerred");
while (Wire.available()) { // read all bytes received
i2c_rcv += Wire.read();
Serial.print("Recieved Data: ");
Serial.println(i2c_rcv);
}
}
The code for the slave Arduino is as follows:
//Slave
#include <Wire.h>
String i2c_rcv; // data received from I2C bus
unsigned long time_start; // start time in milliseconds
int message;
int prevMessage;
//Encoder Lists
String posList;
int numSteps = 0;
int posAList_rcv[20];
int posBList_rcv[20];
int numSteps_rcv = 0;
void setup() {
//Connect to Computer
Serial.begin(9600);
// join I2C bus as Slave with address 0x08
Wire.begin(8);
Serial.println("Arduino Connected");
// initialize global variables
i2c_rcv = "";
time_start = millis();
Serial.println("Time Started");
message = 0;
prevMessage = 0;
// event handler initializations
Wire.onReceive(dataRcv); // register an event handler for received data
Serial.println("Create List");
posList = "1234567890";
numSteps = 5;
Serial.println("List Created");
Serial.println(posList);
Serial.print("numSteps: ");
Serial.println(numSteps);
}
void loop() {
message = i2c_rcv.toInt();
if (message == 5) {
Serial.println("Entered Loop");
sendEncoderList();
message = 0;
i2c_rcv = "";
}
}
//received data handler function
void dataRcv(int numBytes) {
while (Wire.available()) { // read all bytes received
i2c_rcv += Wire.read();
Serial.print("Recieved Data");
Serial.println(i2c_rcv);
}
}
void sendEncoderList() {
Wire.beginTransmission(8);
for (int i = 0; i < posList.length(); i++) {
Wire.write(posList[i]);
Serial.print(posList[i]);
}
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("lists sent");
}
void getPath() {
String result = i2c_rcv;
int nextComma = 0;
Serial.println(result);
nextComma = result.indexOf(",");
if (nextComma > 0) {
numSteps_rcv = result.substring(0, nextComma).toInt();
} else {
Serial.println("error");
}
for (int i = 0; i < numSteps; i++) {
result = result.substring(nextComma);
nextComma = result.indexOf(",");
posAList_rcv[i] = result.substring(0, nextComma).toInt();
result = result.substring(nextComma);
nextComma = result.indexOf(",");
posBList_rcv[i] = result.substring(0, nextComma).toInt();
}
}```
Thank you