Hi,
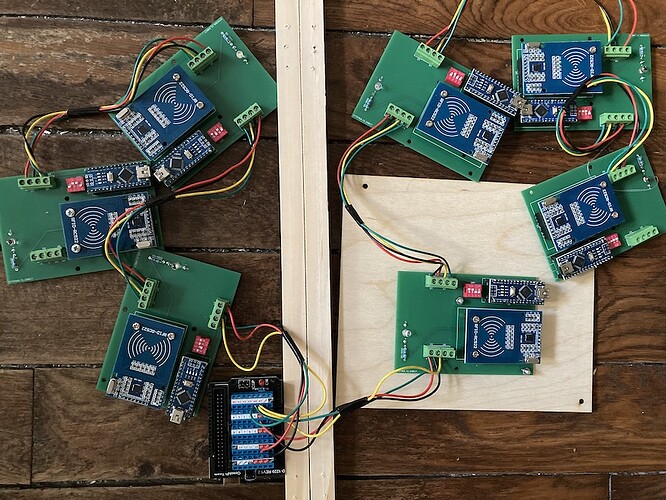
For my project, I would to connect 7 RFID readers (RC522) to a Arduino UNO. I know it's not easy to have more than 4 of these readers on the same SPI bus and managed by the same Arduino. So I decided to have one Arduino Nano per RC522 (probably a bit overkill but I wanted to stay modular) and then connect them via I2C to the Arduino Uno (controller).
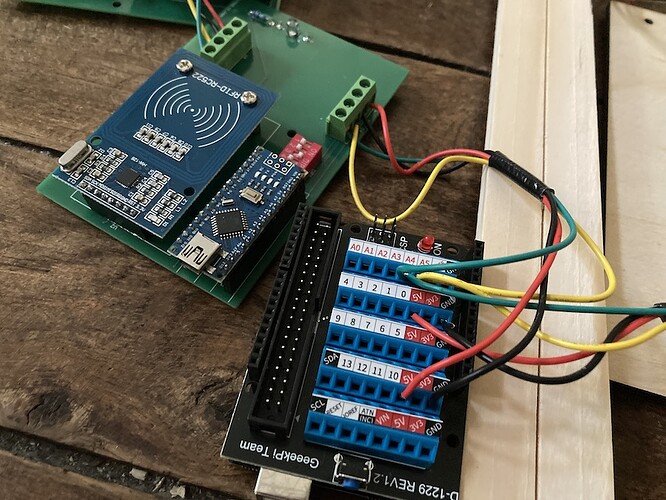
I created one PCB per « block », containing :
- 1 RC522 RFID reader
- 1 Arduino Nano (target)
- DIP switches to set the I2C address
- 1 LED
- Terminal blocks to connect the PCBs
A4, A5, 5V and Ground of all the Arduino are connected together. A button connected to the controller trigger the request to all the targets to get the last RFID UID scanned.
/*
* TARGET code (arduino Nano with RFID Reader)
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <arduino-timer.h>
#define SS_PIN 10
#define RST_PIN 9
#define PIN_LED 6
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN);
MFRC522::MIFARE_Key key;
// Init array that will store new NUID
byte currentNFC[4];
bool detect = false;
byte no_count = 0;
byte no_max = 6;
//DIP switches for I2C Address
byte dip_pin[4] = {2,3,4,5};
int address = 8;
auto timer = timer_create_default();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus
rfid.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522
pinMode(PIN_LED, OUTPUT);
//Address I2C
for (byte i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(dip_pin[i], INPUT_PULLUP);
address += (!digitalRead(dip_pin[i])) * (1<<i);
}
Serial.println(address);
Wire.begin(address); // join i2c bus with address based on DIP
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // register event
for (byte i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
key.keyByte[i] = 0xFF;
}
Serial.println(F("This code scan the MIFARE Classsic NUID."));
Serial.print(F("Using the following key:"));
printHex(key.keyByte, MFRC522::MF_KEY_SIZE);
}
void loop() {
if(detect){
rfid.PCD_Init(); //reinit to detect removing
}
if ( ! rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent()){
if(detect){
no_count++;
//Serial.print("?");
if(no_count >= no_max){
//NFC is removed
Serial.println("Removed");
digitalWrite(PIN_LED, LOW);
currentNFC[0] = 0;
currentNFC[1] = 0;
currentNFC[2] = 0;
currentNFC[3] = 0;
detect = false;
}
}
}else{
no_count = 0;
// Verify if the NUID has been readed
if ( ! rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial())
return;
Serial.print(F("PICC type: "));
MFRC522::PICC_Type piccType = rfid.PICC_GetType(rfid.uid.sak);
Serial.println(rfid.PICC_GetTypeName(piccType));
if (rfid.uid.uidByte[0] != currentNFC[0] ||
rfid.uid.uidByte[1] != currentNFC[1] ||
rfid.uid.uidByte[2] != currentNFC[2] ||
rfid.uid.uidByte[3] != currentNFC[3] ) {
Serial.println(F("A new card has been detected."));
digitalWrite(PIN_LED, HIGH); // Allumage de la LED : état haut = HIGH
detect = true;
// Store NUID into currentNFC array
for (byte i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
currentNFC[i] = rfid.uid.uidByte[i];
}
Serial.println(F("The NUID tag is:"));
Serial.print(F("In hex: "));
printHex(rfid.uid.uidByte, rfid.uid.size);
Serial.println();
Serial.print(F("In dec: "));
printDec(rfid.uid.uidByte, rfid.uid.size);
Serial.println();
}
else Serial.println(F("Card read previously."));
// Halt PICC
rfid.PICC_HaltA();
}
}
/**
* Helper routine to dump a byte array as hex values to Serial.
*/
void printHex(byte *buffer, byte bufferSize) {
for (byte i = 0; i < bufferSize; i++) {
Serial.print(buffer[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(buffer[i], HEX);
}
}
/**
* Helper routine to dump a byte array as dec values to Serial.
*/
void printDec(byte *buffer, byte bufferSize) {
for (byte i = 0; i < bufferSize; i++) {
Serial.print(buffer[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(buffer[i], DEC);
}
}
void requestEvent() {
if(detect){
Serial.println(rfid.uid.uidByte[1]);
Wire.write(currentNFC[0]);
Wire.write(currentNFC[1]);
Wire.write(currentNFC[2]);
}else{
Wire.write(0);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.write(0);
}
}
/*
* CONTROLER code (arduino Uno)
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#define DEVICES_NUM 7
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
for(byte i=0 ; i < DEVICES_NUM; i++){
Wire.requestFrom(i+8, 3); // request 6 bytes from peripheral device #8, 9, 10 etc.
while (Wire.available()) { // peripheral may send less than requested
byte c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
Serial.print(c); // print the character
}
Serial.print(" | ");
}
Serial.println("");
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
delay(250);
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
delay(250);
}
My issue: everything works well up to 6 blocks. When I add the 7th, the I2C signal seems to get jammed and quickly freezes the Arduino Uno. I tried to switch hardware, reduce wire length, add pull-up resistance (probably not correctly) etc. But the 7th block always causes the issue.
So I know that I2C is not easy to use on these kind of wire lengths. I read a lot about this and I’m a bit lost, sorry if I make you repeat yourself. I don’t really understand how to choose (and connect) a pull-up resistance in my case. I guess I could also have other type of wires? Or maybe there is something else that could help me?
Thank you in advance for your help ![]()