Hi there,
My question is related to the thread "CYD: SD Issues, probably due to Touch pins?".
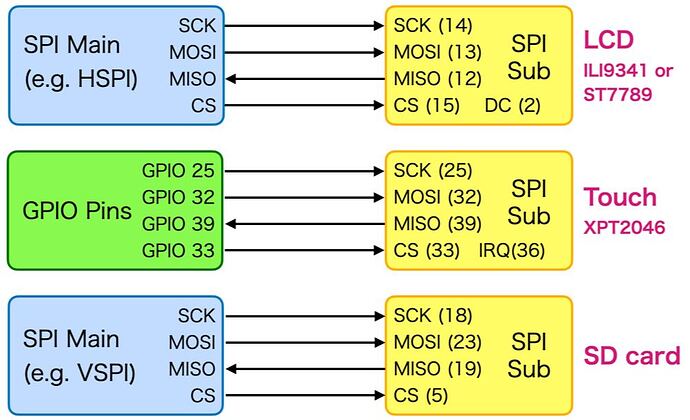
For 'Cheap Yellow Display', I was able to confirm that when I assign the TFT_eSPI and touch screen to HSPI, and the SD card to VSPI, everything seems to be working fine.
I assume that each peripheral library performs SPI transaction and chip select are performed correctly. Here are some partial code snippet of the configuration:
Piout using pins_arduino.h
#define TFT_DC CYD_TFT_DC // 2
#define TFT_MISO CYD_TFT_MISO // 12
#define TFT_MOSI CYD_TFT_MOSI // 13
#define TFT_SCLK CYD_TFT_SCK // 14
#define TFT_CS CYD_TFT_CS // 15
#define TFT_RST -1 // 2 (CYD_TFT_RS conflicts with CYD_TFT_DC)
#define TFT_BL CYD_TFT_BL // 21
#define TOUCH_IRQ CYD_TP_IRQ // 36
#define TOUCH_MOSI CYD_TP_MOSI // 32
#define TOUCH_MISO CYD_TP_MISO // 39
#define TOUCH_CLK CYD_TP_CLK // 25
#define TOUCH_CS CYD_TP_CS // 33
#define SD_CS CYD_SD_SS // 5
#define SD_MOSI CYD_SD_MOSI // 23
#define SD_MISO CYD_SD_MISO // 19
#define SD_SCK CYD_SD_SCK // 18
#define SPI_SD_FREQUENCY 50000000 // 50 MHz
Setup_User.h for TFT_eSPI
// The ESP32 has 2 free SPI ports i.e. VSPI and HSPI, the VSPI is the default.
// If the VSPI port is in use and pins are not accessible (e.g. TTGO T-Beam)
// then uncomment the following line:
#define USE_HSPI_PORT
For XPT2046_Touchscreen library
static SPIClass ts_spi = SPIClass(HSPI);
static XPT2046_Touchscreen ts(TOUCH_CS, TOUCH_IRQ);
...
bool touch_setup(void) {
ts_spi.begin(TOUCH_CLK, TOUCH_MISO, TOUCH_MOSI, TOUCH_CS);
ts.begin(ts_spi);
...
}
For SD card library
static SPIClass sd_spi = SPIClass(SD_SPI_BUS);
#define SD_CONFIG SD_CS, sd_spi, SPI_SD_FREQUENCY
...
bool sdcard_setup(void) {
sd_spi.begin(SD_SCK, SD_MISO, SD_MOSI, SD_CS);
if (!SD.begin(SD_CONFIG)) {
Serial.println("Initializing SD card failed.");
return false;
}
...
}
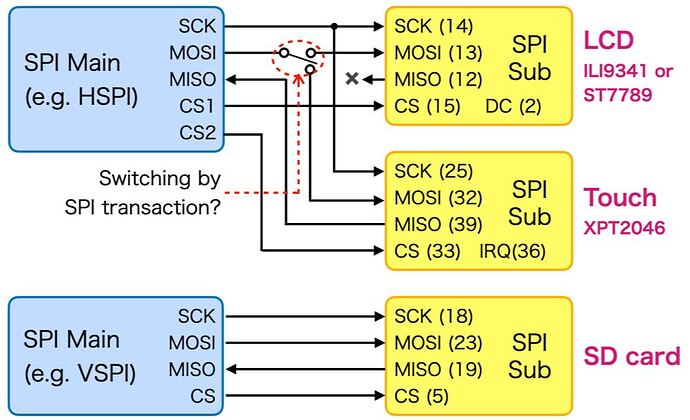
However, I would like to know if those just happen to work, or if those are correct according to the SPI library specifications.
To summarize my question simply, I'd explain using SPI_Multiple_Buses from the SPI example sketch. (I've removed ALTERNATE_PINS for simplicity.)
/* The ESP32 has four SPi buses, however as of right now only two of
* them are available to use, HSPI and VSPI. Simply using the SPI API
* as illustrated in Arduino examples will use VSPI, leaving HSPI unused.
*
* However if we simply initialize two instance of the SPI class for both
* of these buses both can be used. However when just using these the Arduino
* way only will actually be outputting at a time.
*
* Logic analyzer capture is in the same folder as this example as
* "multiple_bus_output.png"
*
* created 30/04/2018 by Alistair Symonds
*/
#include <SPI.h>
// Define ALTERNATE_PINS to use non-standard GPIO pins for SPI bus
#define VSPI_MISO 2
#define VSPI_MOSI 4
#define VSPI_SCLK 0
#define VSPI_SS 33
#define HSPI_MISO 26
#define HSPI_MOSI 27
#define HSPI_SCLK 25
#define HSPI_SS 32
#if !defined(CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32)
#define VSPI FSPI
#endif
static const int spiClk = 1000000; // 1 MHz
//uninitialized pointers to SPI objects
SPIClass *vspi = NULL;
SPIClass *hspi = NULL;
void setup() {
//initialize two instances of the SPIClass attached to VSPI and HSPI respectively
vspi = new SPIClass(VSPI);
hspi = new SPIClass(HSPI);
//clock miso mosi ss
//alternatively route through GPIO pins of your choice
vspi->begin(VSPI_SCLK, VSPI_MISO, VSPI_MOSI, VSPI_SS); //SCLK, MISO, MOSI, SS
//alternatively route through GPIO pins
hspi->begin(HSPI_SCLK, HSPI_MISO, HSPI_MOSI, HSPI_SS); //SCLK, MISO, MOSI, SS
//set up slave select pins as outputs as the Arduino API
//doesn't handle automatically pulling SS low
pinMode(vspi->pinSS(), OUTPUT); //VSPI SS
pinMode(hspi->pinSS(), OUTPUT); //HSPI SS
}
// the loop function runs over and over again until power down or reset
void loop() {
//use the SPI buses
spiCommand(vspi, 0b01010101); // junk data to illustrate usage
spiCommand(hspi, 0b11001100);
delay(100);
}
void spiCommand(SPIClass *spi, byte data) {
//use it as you would the regular arduino SPI API
spi->beginTransaction(SPISettings(spiClk, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(spi->pinSS(), LOW); //pull SS slow to prep other end for transfer
spi->transfer(data);
digitalWrite(spi->pinSS(), HIGH); //pull ss high to signify end of data transfer
spi->endTransaction();
}
My question: If I rewrite the above sketch as shown below and the clocks for each SPI bus instance are different (i.e. different SPISettings), will it still work correctly?
void setup() {
//initialize two instances of the SPIClass attached to VSPI and HSPI respectively
vspi = new SPIClass(HSPI);
hspi = new SPIClass(HSPI);
...
}
Unfortunately, I cannot analyze with a logic analyzer.
Thanks in advance.