Try switching to FastAccelStepper, as its superior for ESP32 anyhow.
"This stepper driver uses mcpwm modules of the esp32: for the first three stepper motors mcpwm0, and mcpwm1 for the steppers four to six. "
As it knows how to use ESP32:s mcpwm modules and this makes it much lighter to run.
Here is my current test code using FastAccelStepper on a single motor, it has some extras but you can probably get what you need out of it. It reports actual mm/s speeds, currently its set to 4mm per revolution. So just change it in the serial reports and you get actual speeds.
Ok, now i realized that you were allready using FastAccelStepper 
I think your issues is probably about how and where you instruct the stepper to move. Are you using RTOS? If not, start using RTOS. In this example i also use RTOS to run the motor on a different core on its own loop, and serial reporting on another core on its own loop.
But this is just a really simple, move back & forth and set speeds & accelerations test code for my test jig.
/*
ESP32 ONLY! RUNS ON TWO CORES.
DOES NOT USE EN PIN, DIRECTLY SOLDERED TO GROUND TO KEEP IT SIMPLE.
SET SPEED, ACCELERATION & CURRENT IN SERIAL TERMINAL LIKE THIS
TO SET SPEED:
-------------
TO SET 1000, INPUT 1000
TO SET 2000, INPUT 2000
MAX 99999, INPUT 99999
ACCELERATION:
-------------
TO SET 1000, INPUT 101000
TO SET 2000, INPUT 102000
MAX 99999, INPUT 199999
CURRENT:
--------
TO SET 100mA, INPUT 200100
TO SET 1000mA, INPUT 201000;
MAX 2000mA, INPUT 202000;
*/
//LIBRARIES THAT YOU NEED
#include <TMCStepper.h> // https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/tmcstepper/
#include "FastAccelStepper.h" // https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/fastaccelstepper/
//DEFINE YOUR STARTING VALUES!
int AMPS = 2000; // SET STARTING CURRENT MAX 2000
int micro = 0; // SET MICROSTEPS
int Maccell = 1000; // SET STARTING ACCELERATION
int Mspeed = 1000; // SET STARTING STEPS/S
int MMperRev = 2; // SET MM PER REVOLUTION
int moveMM = 57; // SET MOVEMENT IN MM
float StepsPerRoation = 200; // PHYSICAL STEPS OF MOTOR, NO MICROSTEPS INCLUDED
//SET THESE 3 PER YOUR CONNECTIONS, AND YOU ARE GOOD TO GO!:
#define DIR_PIN 4 // Direction
#define STEP_PIN 0 // Step
#define SERIAL_PORT Serial2 // HardwareSerial port
#define STALL_VALUE 255 // [0..255]
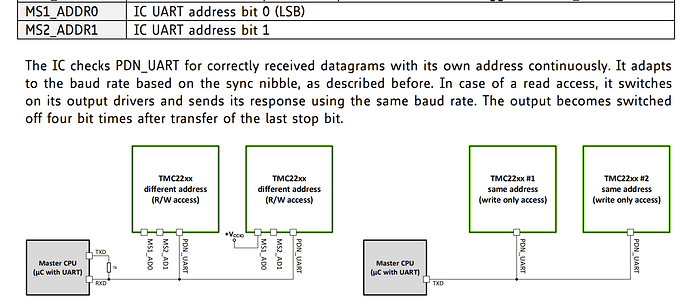
#define DRIVER_ADDRESS 0b00 // TMC2209 Driver address according to MS1 and MS2
#define R_SENSE 0.11f // 0.11 for MKS TMC2209
TMC2209Stepper driver(&SERIAL_PORT, R_SENSE, DRIVER_ADDRESS);
using namespace TMC2209_n;
FastAccelStepperEngine engine = FastAccelStepperEngine();
FastAccelStepper *stepper = NULL;
unsigned long howLong=0;
TaskHandle_t Motor;
TaskHandle_t Print;
TaskHandle_t Input;
void setup() {
// INTITIALIZE SERIAL0 ITERFACE
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(F("---------------------------------------------------"));
Serial.println(F("UART0 serial output interface intitialized @ 115200"));
// INITIALIZE SERIAL2 UART FOR TMC2209
SERIAL_PORT.begin(115200); //,SERIAL_8N1, 16, 17
Serial.println(F("UART2 interface for TMC2209 intitialized @ 115200"));
Serial.println(F("---------------------------------------------------"));
//TMCSTEPPER SETTINGS
driver.begin();
driver.toff(2); // [1..15] enable driver in software
driver.blank_time(24); // [16, 24, 36, 54]
driver.hysteresis_start(1); // [1..8]
driver.hysteresis_end(12); // [-3..12]
driver.rms_current(AMPS, 0.01); // motor RMS current "rms_current will by default set ihold to 50% of irun but you can set your own ratio with additional second argument; rms_current(1000, 0.3)."
driver.seimin(1); // minimum current for smart current control 0: 1/2 of IRUN 1: 1/4 of IRUN
driver.semin(15); // [0... 15] If the StallGuard4 result falls below SEMIN*32, the motor current becomes increased to reduce motor load angle.
driver.semax(15); // [0... 15] If the StallGuard4 result is equal to or above (SEMIN+SEMAX+1)*32, the motor current becomes decreased to save energy.
driver.sedn(4); // current down step speed 0-11%
driver.seup(2); // Current increment steps per measured StallGuard2 value 5 seup0 %00 … %11: 1, 2, 4, 8
driver.iholddelay(3); // 0 - 15 smooth current drop
driver.TPWMTHRS(0); // 0: Disabled, 0xFFFFF = 1048575 MAX TSTEP.
// StealthChop PWM mode is enabled, if configured. When the velocity exceeds
// the limit set by TPWMTHRS, the driver switches to SpreadCycle.
driver.TCOOLTHRS(0); // 0-7 TSTEP
// 0: TPWM_THRS= 0
// 1: TPWM_THRS= 200
// 2: TPWM_THRS= 300
// 3: TPWM_THRS= 400
// 4: TPWM_THRS= 500
// 5: TPWM_THRS= 800
// 6: TPWM_THRS= 1200
// 7: TPWM_THRS= 4000
driver.pwm_autoscale(true); // Needed for stealthChop
driver.en_spreadCycle(false); // false = StealthChop / true = SpreadCycle
driver.microsteps(micro); // microsteps
driver.shaft(false); // direction
driver.intpol(true); // interpolate to 256 microsteps
//driver.ihold(2); // hold current 0=1/32 … 31=32/32
//driver.irun(31);
driver.SGTHRS(STALL_VALUE);
//driver.I_scale_analog(0); // if 5v vdd
//ACCELL STEPPER SPEED & ACCELERATION
engine.init();
stepper = engine.stepperConnectToPin(STEP_PIN);
stepper->setDirectionPin(DIR_PIN);
stepper->setSpeedInHz(Mspeed); // STEPS PER SECOND
stepper->setAcceleration(Maccell);
if (micro!=0) {StepsPerRoation=StepsPerRoation*micro;};
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(PrintTask, "Print", 2000,NULL,tskIDLE_PRIORITY,&Print,1);
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(MotorTask, "Motor", 5000,NULL,5,&Motor,0);
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(InputTask, "Input", 5000,NULL,2,&Input,1);
}
void loop() {
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}
//PRINT SERIAL--------------------------------------------------
void PrintTask(void*) {
int SSpeed;
int steppes;
float ActualSpeed;
float MaxSpeed;
for(;;) {
steppes = driver.TSTEP();
SSpeed = 12000000./(steppes*256.);
ActualSpeed = (SSpeed/StepsPerRoation)*MMperRev;
if (ActualSpeed > MaxSpeed) {MaxSpeed = ActualSpeed;};
if (ActualSpeed == 0) {MaxSpeed = 0;};
Serial.print("ACTUAL");Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.print("MAX");Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.print("AVARAGE");Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.println("REQUESTED");
Serial.print(ActualSpeed,2);Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.print(MaxSpeed,2);Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.print((moveMM/(howLong/1000.)),2);Serial.print(F(" / "));Serial.print((Mspeed/StepsPerRoation)*MMperRev,2);Serial.println(F(" MM/S"));
Serial.print(SSpeed);Serial.print(" / ");Serial.print(MaxSpeed/(MMperRev/StepsPerRoation),0);Serial.print(" / ");Serial.print((moveMM/(MMperRev/StepsPerRoation))/(howLong/1000.),0);Serial.print(" / "); Serial.print(Mspeed);Serial.println(F(" STEPS/S"));
Serial.print(60.*(SSpeed/StepsPerRoation),0);Serial.print(" / "); Serial.print(60.*((MaxSpeed/(MMperRev/StepsPerRoation))/StepsPerRoation),0);Serial.print(" / "); Serial.print((((moveMM/(MMperRev/StepsPerRoation))/(howLong/1000.))/StepsPerRoation)*60.,0);Serial.print(" / "); Serial.print(60.*(Mspeed/StepsPerRoation),0);Serial.println(F(" RPM"));
Serial.print(Maccell);Serial.println(F(" ACCELERATION"));
Serial.println("----------------------------------");
Serial.print(driver.cs2rms(driver.cs_actual()),DEC);Serial.print(" / ");Serial.print(AMPS);Serial.println(" MA MOTOR CURRENT");
Serial.print(stepper->getCurrentPosition());Serial.print(" / ");Serial.print(stepper->targetPos());Serial.println(" STEP POSITION");
Serial.print(driver.SG_RESULT());Serial.println(" STALLGUARD");
Serial.print(steppes);Serial.println(" TSTEP");
Serial.print(float(howLong/1000.),2);Serial.println("S LAST MOVEMENT DURATION");
Serial.print(driver.microsteps());Serial.println(F(" MICROSTEPS"));
Serial.println("----------------------------------");
vTaskDelay(100);
}
}
//CHECK FOR SERIAL COMMANDS--------------------------------------------------------
void InputTask(void*) {
for(;;)
{
int dataIn=0;
if (Serial.available()) {
dataIn = Serial.parseInt();
if (dataIn>0 && dataIn<10000) {
Mspeed=dataIn;
stepper->setSpeedInHz(Mspeed);
};
if (dataIn>=100000 && dataIn<200000 ) {
Maccell=dataIn-10000;
stepper->setAcceleration(Maccell);
};
if (dataIn>=200000 && dataIn<=202001 ) {
AMPS=dataIn-200000;
driver.rms_current(AMPS, 0.01);
};
};
vTaskDelay(5);
}
}
//MOTOR--------------------------------------------------------
void MotorTask(void*) {
for(;;)
{
unsigned long timeIs = millis();
stepper->moveTo(moveMM/(MMperRev/StepsPerRoation),true); // TRUE makes this a blocking function. Remove it to use it as non blocking.
howLong = millis()-timeIs;
vTaskDelay(2000);
stepper->moveTo(0,true); //
vTaskDelay(2000);
}
}