Hello,
I am making a project where I have an Arduino Mega (Elegoo MEGA 2560 R3) reading data from sensors and then sending this data over UART to an ESP32. From the ESP, the data is then sent to Influxdb (an open-source time series database). I am following a tutorial that uses a BME280 with just the ESP (not arduino) to read and send the data. I am using an arduino to read the sensors because I will be using multiple sensors and there isnt much space left on the ESP for the rest of the code.
So, on the site, they read the data from the BME sensor and store it in a variable "temperature".
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BME280.h>
#if defined(ESP32)
#include <WiFiMulti.h>
WiFiMulti wifiMulti;
#define DEVICE "ESP32"
#elif defined(ESP8266)
#include <ESP8266WiFiMulti.h>
ESP8266WiFiMulti wifiMulti;
#define DEVICE "ESP8266"
#define WIFI_AUTH_OPEN ENC_TYPE_NONE
#endif
#include <InfluxDbClient.h>
#include <InfluxDbCloud.h>
// WiFi AP SSID
#define WIFI_SSID "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_SSID"
// WiFi password
#define WIFI_PASSWORD "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_PASSWORD"
// InfluxDB v2 server url, e.g. https://eu-central-1-1.aws.cloud2.influxdata.com (Use: InfluxDB UI -> Load Data -> Client Libraries)
#define INFLUXDB_URL "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_DATABASE_URL"
// InfluxDB v2 server or cloud API authentication token (Use: InfluxDB UI -> Load Data -> Tokens -> <select token>)
#define INFLUXDB_TOKEN "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_TOKEN"
// InfluxDB v2 organization id (Use: InfluxDB UI -> Settings -> Profile -> <name under tile> )
#define INFLUXDB_ORG "REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_ORG"
// InfluxDB v2 bucket name (Use: InfluxDB UI -> Load Data -> Buckets)
#define INFLUXDB_BUCKET "SENSOR"
// Set timezone string according to https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/TZ-Variable.html
// Examples:
// Pacific Time: "PST8PDT"
// Eastern: "EST5EDT"
// Japanesse: "JST-9"
// Central Europe: "CET-1CEST,M3.5.0,M10.5.0/3"
#define TZ_INFO "WET0WEST,M3.5.0/1,M10.5.0"
// InfluxDB client instance with preconfigured InfluxCloud certificate
InfluxDBClient client(INFLUXDB_URL, INFLUXDB_ORG, INFLUXDB_BUCKET, INFLUXDB_TOKEN, InfluxDbCloud2CACert);
// InfluxDB client instance without preconfigured InfluxCloud certificate for insecure connection
//InfluxDBClient client(INFLUXDB_URL, INFLUXDB_ORG, INFLUXDB_BUCKET, INFLUXDB_TOKEN);
// Data point
Point sensorReadings("measurements");
//BME280
Adafruit_BME280 bme; // I2C
float temperature;
float humidity;
float pressure;
// Initialize BME280
void initBME(){
if (!bme.begin(0x76)) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME280 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Setup wifi
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
wifiMulti.addAP(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
Serial.print("Connecting to wifi");
while (wifiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
Serial.println();
//Init BME280 sensor
initBME();
// Add tags
sensorReadings.addTag("device", DEVICE);
sensorReadings.addTag("location", "office");
sensorReadings.addTag("sensor", "bme280");
// Accurate time is necessary for certificate validation and writing in batches
// For the fastest time sync find NTP servers in your area: https://www.pool.ntp.org/zone/
// Syncing progress and the time will be printed to Serial.
timeSync(TZ_INFO, "pool.ntp.org", "time.nis.gov");
// Check server connection
if (client.validateConnection()) {
Serial.print("Connected to InfluxDB: ");
Serial.println(client.getServerUrl());
} else {
Serial.print("InfluxDB connection failed: ");
Serial.println(client.getLastErrorMessage());
}
}
void loop() {
// Get latest sensor readings
temperature = bme.readTemperature();
humidity = bme.readHumidity();
pressure = bme.readPressure()/100.0F;
// Add readings as fields to point
sensorReadings.addField("temperature", temperature);
sensorReadings.addField("humidity", humidity);
sensorReadings.addField("pressure", pressure);
// Print what are we exactly writing
Serial.print("Writing: ");
Serial.println(client.pointToLineProtocol(sensorReadings));
// Write point into buffer
client.writePoint(sensorReadings);
// Clear fields for next usage. Tags remain the same.
sensorReadings.clearFields();
// If no Wifi signal, try to reconnect it
if (wifiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.println("Wifi connection lost");
}
// Wait 10s
Serial.println("Wait 10s");
delay(10000);
}
This part in particular is what I am refering too:
void loop() {
// Get latest sensor readings
temperature = bme.readTemperature();
humidity = bme.readHumidity();
pressure = bme.readPressure()/100.0F;
// Add readings as fields to point
sensorReadings.addField("temperature", temperature);
sensorReadings.addField("humidity", humidity);
sensorReadings.addField("pressure", pressure);
And the code works fine but...
Since the data is coming over the serial port, I changed the code so that the serial data is being stored in the temperature variable (Using a GY-906 sensor btw).
void loop() {
// Get latest sensor readings
temperature = Serial2.read();
// Add readings as fields to point
sensorReadings.addField("TemperatureTwo", temperature);
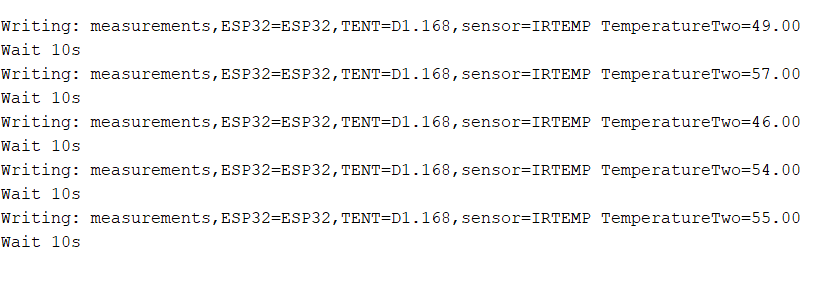
But when I do this, the serial monitor keeps showing me this
When the actual temperature readings are around 20C (I had the serial monitor from the arduino open to cross check the data going through).
Can someone please explain why this doesnt work? Thanks.
EDIT: Forgot to mention that when I printed Serial2.read(), the data shows up correctly on the ESP but its when I put it into a variable that it breaks.
EDIT2: Arduino Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_MLX90614.h>
Adafruit_MLX90614 mlx = Adafruit_MLX90614();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
mlx.begin();
}
void loop() {
Serial.println(mlx.readObjectTempC());
delay(10000);
}