- Here is an example you should be able to learn from:
//
//================================================^================================================
// C a b l e T e s t e r S k e t c h
//
// URL
//
// LarryD
//
// Version YY/MM/DD Comments
// ======= ======== ========================================================================
// 1.00 22/03/01 Running code
// 1.10 22/04/01 Added resistance measurement
// 1.20 23/09/23 Added short/long press for testing, added class TIMER stuff
// 1.30 24/03/18 Changed to "go no go" cable testing
// 1.40 25/02/20 At powerup/reset time, switch adusts number of wires in the standard cable
//
//
//
// Notes:
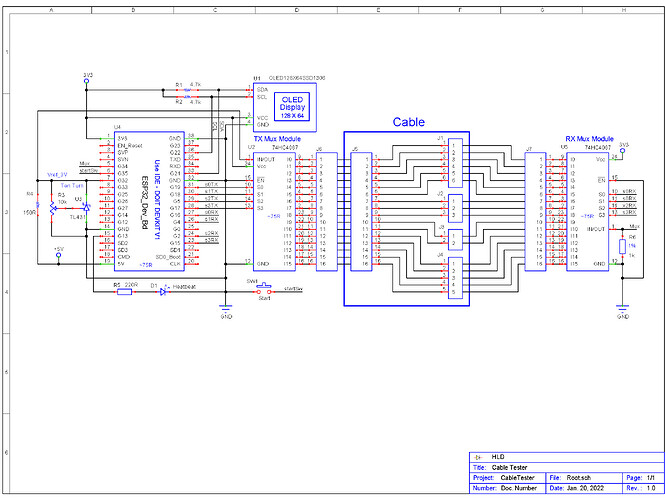
// - See "CableTester" schematic.
// - Arduino UNO, 2 X CD74HC4067 (16 channel analog mux), N.O. switch
// - Tests cables with up to 16 wires.
// - Connector resistance for each wire is checked.
// - Only one connection from one connector to the other connector is allowed,
// Ex: pin #1 on the left side of our cable is connected to pin #2
// on the right side of our cable
//
//
//=================================================================================================
#define LEDon HIGH //PIN---[220R]---A[LED]K---GND
#define LEDoff LOW
#define PRESSED LOW //+5V---[Internal 50k]---PIN---[Switch]---GND
#define RELEASED HIGH
#define CLOSED LOW //+5V---[Internal 50k]---PIN---[Switch]---GND
#define OPENED HIGH
#define ENABLED true
#define DISABLED false
#define RELAYon LOW
#define RELAYoff HIGH
#define NOconnection 255
// millis() / micros() B a s e d T I M E R S
//================================================^================================================
//
/*example
//========================
makeTIMER toggleLED =
{
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin
MILLIS/MICROS, 500ul, ENABLED/DISABLED, YES/NO, A0-A5
//.SpeedAdjustPin defaults to 0 i.e. no speed adjustment is used
//if .SpeedAdjustPin = A0-A5, a potentiometer on this pin adjusts the TIMER's speed (for diagnostics)
//class static flag "makeTIMER::normalFlag" can be used to ENABLE/DISABLE adjustable TIMER speed,
//ENABLE = normal speed, DISABLED = potentiometer controls TIMER speed
};
*/
//These TIMER objects are non-blocking
class makeTIMER
{
#define MILLIS 0
#define MICROS 1
#define ENABLED true
#define DISABLED false
#define YES true
#define NO false
#define STILLtiming 0
#define EXPIRED 1
#define TIMERdisabled 2
private:
public:
static bool s_normalFlag; //when ENABLED, adjustable TIMERs run at normal speed
unsigned long Time; //when the TIMER started
//these "members" are needed to define a TIMER
byte TimerType; //what kind of TIMER is this? MILLIS/MICROS
unsigned long Interval; //delay time which we are looking for
bool TimerFlag; //is the TIMER enabled ? ENABLED/DISABLED
bool Restart; //do we restart this TIMER ? YES/NO
byte SpeedAdjustPin; //a potentiometer on this pin, A0-A5, adjusts TIMER speed
//================================================
//constructor with no parameters
makeTIMER()
{
TimerType = MILLIS;
Interval = 1000ul;
TimerFlag = ENABLED;
Restart = YES;
SpeedAdjustPin = 0;
Time = 0;
}
//================================================
//constructor with parameters
makeTIMER(byte _TimerType, unsigned long _Interval,
bool _TimerFlag, bool _Restart, byte _SpeedAdjustPin = 0)
{
TimerType = _TimerType;
Interval = _Interval;
TimerFlag = _TimerFlag;
Restart = _Restart;
SpeedAdjustPin = _SpeedAdjustPin;
Time = 0;
}
//================================================
//condition returned: STILLtiming (0), EXPIRED (1) or TIMERdisabled (2)
//function to check the state of our TIMER ex: if(myTimer.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED);
byte checkTIMER()
{
//========================
//is this TIMER enabled ?
if (TimerFlag == ENABLED)
{
//============
//is this an adjustable TIMER OR is the "normalSpeed" switch closed ?
if (SpeedAdjustPin == 0 || s_normalFlag == ENABLED)
{
//============
//this TIMER "is not" speed adjustable,
//has this TIMER expired ?
if (getTime() - Time >= Interval)
{
//============
//should this TIMER restart again?
if (Restart == YES)
{
//restart this TIMER
Time = getTime();
}
//this TIMER has expired
return EXPIRED;
}
}
//============
//this TIMER is speed adjustable
else
{
//============
//for diagnostics, we use a potentiometer to adjust TIMER speed,
//has this TIMER expired ?
if (getTime() - Time >= Interval / adjustInterval())
{
//============
//should this TIMER restart again?
if (Restart == YES)
{
//restart this TIMER
Time = getTime();
}
//this TIMER has expired
return EXPIRED;
}
}
return STILLtiming;
} //END of if (TimerFlag == ENABLED)
//========================
else
{
//this TIMER is disabled
return TIMERdisabled;
}
} //END of checkTime()
//================================================
//function to enable and restart this TIMER ex: myTimer.enableRestartTIMER();
void enableRestartTIMER()
{
TimerFlag = ENABLED;
//restart this TIMER
Time = getTime();
} //END of enableRestartTIMER()
//================================================
//function to disable this TIMER ex: myTimer.disableTIMER();
void disableTIMER()
{
TimerFlag = DISABLED;
} //END of disableTIMER()
//================================================
//function to restart this TIMER ex: myTimer.restartTIMER();
void restartTIMER()
{
Time = getTime();
} //END of restartTIMER()
//================================================
//function to force this TIMER to expire ex: myTimer.expireTimer();
void expireTimer()
{
//force this TIMER to expire
Time = getTime() - Interval;
} //END of expireTimer()
//================================================
//function to set the Interval for this TIMER ex: myTimer.setInterval(100);
void setInterval(unsigned long value)
{
//set the Interval
Interval = value;
} //END of setInterval()
//================================================
//function to return the current time
unsigned long getTime()
{
//return the time i.e. millis() or micros()
//========================
if (TimerType == MILLIS)
{
return millis();
}
//========================
else
{
return micros();
}
} //END of getTime()
//================================================
//for diagnostics, a potentiometer on an analog pin is used to adjust TIMER speed, thanks alto777
unsigned int adjustInterval()
{
unsigned int Speed = analogRead(SpeedAdjustPin);
//using integer math to save on memory
Speed = 1 + (Speed * 14) / 1023; //Speed will have a range from 1 to 15
return Speed;
} //END of adjustInterval()
}; //END of class makeTIMER
//================================================
//initialize the static "s_normalFlag" variable,
//when ENABLED, adjustable TIMERs run at normal speed
bool makeTIMER::s_normalFlag = DISABLED;
// T I M E R D e f i n i t i o n s
//================================================^================================================
//
//========================
//example: uses default library values
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin
// MILLIS, 1000ul, ENABLED, YES, 0
//makeTIMER testTIMER{};
//======================== 500ms
makeTIMER heartbeatTIMER =
{
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin (A5 is the potentiometer pin)
MILLIS, 500ul, ENABLED, YES, 0
};
//======================== 5ms
makeTIMER switchesTIMER =
{
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin
MILLIS, 5ul, ENABLED, YES, 0
};
//======================== 1ms
makeTIMER machineTIMER =
{
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin
MICROS, 1 * 1000ul, ENABLED, YES, 0
};
//======================== 5ms
makeTIMER commonTIMER =
{
//.TimerType, .Interval, .TimerFlag, .Restart, .SpeedAdjustPin
MICROS, 5 * 1000ul * 1000ul, ENABLED, YES, 0
};
// c l a s s m a k e I n p u t
//================================================^================================================
//
//a class to define "Input" objects, switches or sensors
//================================================
class makeInput
{
#define NOTvalidated 0
#define VALIDATED 1
#define NOchange 2
private:
public:
static byte s_filter;
//say the above validating "s_filter" variable is set to 10
//if we scan "inputs" every 5ms
//i.e. we sample our inputs every 5ms looking for a change in state.
//5ms * 10 = 50ms is needed to validate a switch change in state.
//i.e. a switch change in state is valid "only after" 10 identical changes are detected.
//This technique is used to filter out EMI (spikes), noise, etc.
//i.e. we ignore switch changes in state that are less than 50ms.
unsigned long switchTime; //the time the switch was closed
byte counter; //a counter used for validating a switch change in state
//these "members" are needed to define an "Input"
byte pin; //the digital input pin number
byte lastState; //the state the input was last in
//================================================
//constructor with parameters
makeInput(byte _pin, byte _lastState)
{
pin = _pin;
lastState = _lastState;
switchTime = 0;
counter = 0;
pinMode(pin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
//================================================
//condition returned: NOTvalidated (0), VALIDATED (1) or NOchange (2)
//check to see if the input object has had a valid state change
byte validChange()
{
byte currentState = digitalRead(pin);
//===================================
//has there been an input change in state ?
if (lastState != currentState)
{
//we have had another similar change in state
counter++;
//============
//is the "change in state" stable ?
if (counter >= s_filter)
{
//an input change has been validated
//get ready for the next scanning sequence
counter = 0;
//update to this new state
lastState = currentState;
//============
if (currentState == CLOSED)
{
//capture the time when the switch closed
switchTime = millis();
}
return VALIDATED;
}
return NOTvalidated;
}
//===================================
//there has not been an input change in state
counter = 0;
return NOchange;
} //END of validChange()
}; //END of class makeInput
//================================================
//a change in state is confirmed/validated when 10 identical state changes in a row is seen
byte makeInput::s_filter = 10;
// S t a t e M a c h i n e
//================================================^================================================
//
//the states in our machine
enum STATES : byte
{
STARTUP, POWERUP_WAITING, WAITING, TEST_STANDARD, READ_STANDARD, DISPLAY_STANDARD, TEST_TARGET,
READ_TARGET, DISPLAY_TARGET, COMPARE_CABLES, UPDATE_LCD, FINISHED
};
//========================
STATES mState = STARTUP;
// G P I O s A n d V a r i a b l e s
//================================================^================================================
//
//which controller is being used ?
//# define ESP32
//========================
# ifdef ESP32
//Analogs
//================================================
//
const byte muxPin = 34;
const byte referencePin = 32;
//OUTPUTS
//================================================
//
const byte s0TXpin = 19;
const byte s1TXpin = 18;
const byte s2TXpin = 5;
const byte s3TXpin = 17;
const byte s0RXpin = 16;
const byte s1RXpin = 4;
const byte s2RXpin = 2;
const byte s3RXpin = 15;
const byte heartbeatLED = 13;
const byte outputArray[] = {19, 18, 5, 17, 16, 4, 2, 15, 13};
const byte outputSize = sizeof(outputArray) / sizeof(outputArray[0]);
//========================
# else
const byte muxPin = A0;
const byte referencePin = A1;
const byte s0TXpin = 4;
const byte s1TXpin = 5;
const byte s2TXpin = 6;
const byte s3TXpin = 7;
const byte s0RXpin = 8;
const byte s1RXpin = 9;
const byte s2RXpin = 10;
const byte s3RXpin = 11;
const byte heartbeatLED = 13;
const byte outputArray[] = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13};
const byte outputSize = sizeof(outputArray) / sizeof(outputArray[0]);
# endif
//INPUTS
//================================================
//
# ifdef ESP32
const byte startSw = 35;
# else
const byte startSw = 2;
# endif
//========================
makeInput startSwitch =
{
//.pin, .lastState
startSw, OPENED
};
//VARIABLES
//================================================
//
const byte numberOfPins = 16; //number of pins in our cable connector
const int loadResistance = 973; //973 ohms, 1% tolerance
const int muxResistance = 74 * 2; //resistance for each mux
byte standardCableWireCount = numberOfPins;
byte numWires = numberOfPins;
byte txCounter = 0;
byte rxCounter = 0;
long Vref;
long Vmux;
unsigned long shortPushTime = 1 * 1000ul; //less than 1 second
unsigned long longPushTime = 3 * 1000ul; //greater than 3 second
// c l a s s C a b l e
//================================================^================================================
//
//a Class to define Cable Objects
//
//cables are made up of a maximum of 16 wires, there can only be a 1:1 connection
//i.e. TX pin #1 pin can only be connected to one RX pin
//Example: zero indexed
// ~~~~~^~~~~~~
// ??[ 0].rxPin = 1, .connection = 0 (ohms) i.e. Tx pin 1 goes to RX pin 2
// ??[ 1].rxPin = 0, .connection = 0 (ohms) i.e. TX pin 2 goes to RX pin 1
// ??[ 2].rxPin = 2, .connection = 0 (ohms) i.e. TX pin 3 goes to RX pin 3
// . . .
// ??[15].rxPin = 15, .connection = 0 (ohms) i.e. TX pin 16 goes to RX pin 16
//================================================
class Cable
{
private:
public:
//Object members
byte rxPin;
byte resistance; //255 is open circuit, otherwise 0-254 ohms
//========================
//overload the comparison == operator so we can compare two Cable Objects
bool operator == (const Cable &_target) const
//bool operator == (Cable _target) //this works too
{
//============
//do the members agree ?
if (rxPin == _target.rxPin && resistance == _target.resistance)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
}; //END of class Cable
// C a b l e D e f i n i t i o n s
//================================================^================================================
//
//make our cable Objects
//========================
Cable standardCable[numberOfPins] = {};
//========================
Cable targetCable[numberOfPins] = {};
// D e b u g
//================================================^================================================
//
unsigned long startTime;
//Serial.println(micros() - startTime);
//startTime = micros();
// s e t u p ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
//========================
//set pinModes
for (byte x = 0; x < outputSize; x++)
{
digitalWrite(outputArray[x], LOW);
pinMode(outputArray[x], OUTPUT);
}
mState = STARTUP;
} //END of setup()
// l o o p ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void loop()
{
//========================================================================
//Print the time it takes to return to this same spot.
//Comment the next 3 lines when no longer needed
//static unsigned long startTime;
//Serial.println(micros() - startTime);
//startTime = micros();
//======================================================================== T I M E R heartbeatLED
//condition returned: STILLtiming, EXPIRED or TIMERdisabled
//is it time to toggle the heartbeat LED ?
if (heartbeatTIMER.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED)
{
//toggle the heartbeat LED
digitalWrite(heartbeatLED, digitalRead(heartbeatLED) == HIGH ? LOW : HIGH);
}
//======================================================================== T I M E R switches
//condition returned: STILLtiming, EXPIRED or TIMERdisabled
//is it time to check our switches ?
if (switchesTIMER.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED)
{
checkSwitches();
}
//======================================================================== T I M E R machine
//condition returned: STILLtiming, EXPIRED or TIMERdisabled
//is it time to service our State Machine ?
if (machineTIMER.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED)
{
checkMachine();
}
//================================================
// Other non blocking code goes here
//================================================
} //END of loop()
// c h e c k M a c h i n e ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void checkMachine()
{
//================================================
//service the current "state"
switch (mState)
{
//========================
case STARTUP:
{
txCounter = 0;
rxCounter = 0;
updateMuxes();
clearCableStruture(standardCable);
clearCableStruture(targetCable);
Serial.println("Tester Ready\n");
Serial.println("Long press reads the cable as our standard");
Serial.print("Adjust wire count in the Standard Cable: 2-16 = ");
Serial.println(numWires);
mState = POWERUP_WAITING;
}
break;
//========================
case POWERUP_WAITING:
{
//============
//was the counter adjusted ?
if (numWires != standardCableWireCount )
{
Serial.print("Wires in the Standard cable = ");
Serial.println(standardCableWireCount);
//update to the new value
numWires = standardCableWireCount;
}
}
break;
//========================
case WAITING:
{
//do nothing
}
break;
//========================
case TEST_STANDARD:
{
Serial.println("\nReading Standard Cable");
//we assume there is no connection
clearCableStruture(standardCable);
txCounter = 0;
rxCounter = 0;
updateMuxes();
//this is a micro second TIMER
//TIMER set to 5ms
commonTIMER.setInterval(5 * 1000ul);
//start this TIMER
commonTIMER.enableRestartTIMER();
mState = READ_STANDARD;
}
break;
//========================
case READ_STANDARD:
{
//condition returned: STILLtiming, EXPIRED or TIMERdisabled
//is it time to test the next cable wire ?
if (commonTIMER.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED)
{
//unsigned long startTime;
//startTime = micros();
//a 16 wire cable takes 256(tests) * 5ms(TIMER interval) = 1.28 seconds to test
//
//a call takes about 550us(per wire)* 256(tests) = ~140ms per 16 wire cable (worst case)
checkConnection(standardCable);
//Serial.println(micros() - startTime);
//============
//are we finished testing this cable ?
if (txCounter == 0 && rxCounter == 0)
{
//we are finished with the TIMER
commonTIMER.disableTIMER();
Serial.println("\nStandard cable is read");
mState = DISPLAY_STANDARD;
}
}
}
break;
//========================
case DISPLAY_STANDARD:
{
displayObject(standardCable);
Serial.println("\nShort press compares a target cable to the standard");
mState = WAITING;
}
break;
//========================
case TEST_TARGET:
{
txCounter = 0;
rxCounter = 0;
updateMuxes();
//this is a micro second TIMER
//TIMER set to 5ms
commonTIMER.setInterval(5 * 1000ul);
//start this TIMER
commonTIMER.enableRestartTIMER();
mState = READ_TARGET;
}
break;
//========================
case READ_TARGET:
{
//============
//condition returned: STILLtiming, EXPIRED or TIMERdisabled
//is it time to test the next cable wire ?
if (commonTIMER.checkTIMER() == EXPIRED)
{
//a "call" takes about 500us per wire, 16 wire cable takes 1.28 seconds to test
checkConnection(targetCable);
//============
//are we finished testing this cable ?
if (txCounter == 0 && rxCounter == 0)
{
//we are finished with the TIMER
commonTIMER.disableTIMER();
Serial.println("\nTarget cable is read");
mState = DISPLAY_TARGET;
}
}
}
break;
//========================
case DISPLAY_TARGET:
{
displayObject(targetCable);
mState = COMPARE_CABLES;
}
break;
//========================
case COMPARE_CABLES:
{
Serial.println("\nComparing a Standard Cable to a Target Cable");
//============
//check the two cables
for (byte x = 0; x < standardCableWireCount; x++)
{
Serial.print("Wire #");
//============
//add a space if the number is < 10
if (x + 1 < 10)
{
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.print(x + 1);
//============
//is this wire the same ?
if (standardCable[x] == targetCable[x])
{
Serial.println(" is Good");
}
//============
else
{
Serial.println(" is Bad");
}
}
Serial.println("Comparison Finished\n");
Serial.println("Short press compares a target cable to the standard");
//we are finished with the comparison
mState = WAITING;
}
break;
//========================
case UPDATE_LCD:
{
}
break;
//========================
case FINISHED:
{
//Do something
}
break;
} //END of switch/case
} //END of checkMachine()
// c h e c k S w i t c h e s ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
//we have access to:
//object.validChange() - checks to see if there was a valid state change
//object.pin - input hardware pin number
//object.lastState - the state the input was/is in
//object.switchTime - unsigned long variable where we can save millis()
void checkSwitches()
{
//======================================================================== startSwitch
//was there a valid input change ?
//condition returned: NOTvalidated (0), VALIDATED (1) or NOchange (2)
if (startSwitch.validChange() == VALIDATED)
{
//========================
//was this switch closed ?
if (startSwitch.lastState == CLOSED)
{
}
//========================
//this switch was opened
else
{
//================================================ Short Push
//was this a short push ?
if (millis() - startSwitch.switchTime <= shortPushTime)
{
//============
if (mState == POWERUP_WAITING)
{
standardCableWireCount++;
//============
//have we reached the maximum ?
if (standardCableWireCount > numberOfPins)
{
standardCableWireCount = 2;
}
}
//============
else
{
//initialize the target structure
clearCableStruture(targetCable);
mState = TEST_TARGET;
}
}
//================================================ Long Push
//was this a long push ?
else if (millis() - startSwitch.switchTime >= longPushTime)
{
mState = TEST_STANDARD;
}
}
} //END of startSwitch
} //END of checkSwitches()
// c h e c k C o n n e c t i o n ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void checkConnection(Cable Object[])
{
//================================================
// {-------------- R1 ---------------}
// Vref ---[muxResistance]---[crimpResistance]---.--- Vmux
// |
// |
// [loadResistance] R2 1% tolerance
// |
// GND
//
// Note: crimpResistance is actually the sum of two crimps,
// one on TX side and one on RX side
//
//voltage divider math:
//R1 = ((R2 * Vref) / Vmux) - R2
Vref = analogRead(referencePin); //read twice for settling time
Vref = analogRead(referencePin);
Vmux = analogRead(muxPin); //read twice for settling time
Vmux = analogRead(muxPin);
//we need an unsigned variable to detect a negative result
long R1 = ((loadResistance * Vref) / Vmux) - loadResistance;
//remove the mux resistance
long crimpResistance = R1 - muxResistance;
//========================
//update the target structure
Object[txCounter].rxPin = rxCounter;
//========================
if (crimpResistance < 15 )
{
//save a resistance of 0 ohms
Object[txCounter].resistance = 0;
//back to the first RX pin
rxCounter = 0;
//next wire to test
txCounter++;
//============
//are we finished with this cable ?
if (txCounter >= standardCableWireCount)
{
txCounter = 0;
}
updateMuxes();
return;
}
//========================
//resistance is between 0 and 255
else if (crimpResistance < NOconnection)
{
//update resistance
Object[txCounter].resistance = crimpResistance;
//back to the first RX pin
rxCounter = 0;
//next wire to test
txCounter++;
//============
//are we finished with this cable ?
if (txCounter >= standardCableWireCount)
{
txCounter = 0;
}
updateMuxes();
return;
}
//========================
//next RX pin
rxCounter++;
//============
//have we finished all the RX pins ?
if (rxCounter >= standardCableWireCount)
{
//back to the first RX pin
rxCounter = 0;
//next TX pin
txCounter++;
//============
//are we finished with this cable ?
if (txCounter >= standardCableWireCount)
{
//back to the first TX pin
txCounter = 0;
}
}
updateMuxes();
} //END of checkConnection()
// u p d a t e M u x e s ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void updateMuxes()
{
//TX mux
digitalWrite(s0TXpin, bitRead(txCounter, 0));
digitalWrite(s1TXpin, bitRead(txCounter, 1));
digitalWrite(s2TXpin, bitRead(txCounter, 2));
digitalWrite(s3TXpin, bitRead(txCounter, 3));
//RX mux
digitalWrite(s0RXpin, bitRead(rxCounter, 0));
digitalWrite(s1RXpin, bitRead(rxCounter, 1));
digitalWrite(s2RXpin, bitRead(rxCounter, 2));
digitalWrite(s3RXpin, bitRead(rxCounter, 3));
} // END of updateMuxes()
// c l e a r C a b l e S t r u t u r e ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void clearCableStruture(Cable Object[])
{
//========================
//update target structure with defaults
for (byte x = 0; x < numberOfPins; x++)
{
//defaults to no connection
Object[x].rxPin = x;
Object[x].resistance = NOconnection;
}
} //END of clearCableStruture()
// d i s p l a y O b j e c t ( )
//================================================^================================================
//
void displayObject(Cable Object[])
{
Serial.println("TX RX");
//========================
//summarize what was read from the target cable
for (byte x = 0; x < standardCableWireCount; x++)
{
Serial.print(x + 1);
//============
//should we add a space ?
if (x + 1 < 10)
{
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.print(" ");
//============
//is this wire connected ?
if (Object[x].resistance == NOconnection)
{
Serial.println("Not connected");
}
//============
//this wire is connected
else
{
Serial.print("Connected to ---> ");
//============
//should we add a space ?
if (Object[x].rxPin + 1 < 10)
{
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.print(Object[x].rxPin + 1);
Serial.print(" Resistance ");
Serial.println(Object[x].resistance);
}
}
} //END of displayObject()
//
//================================================^================================================
//