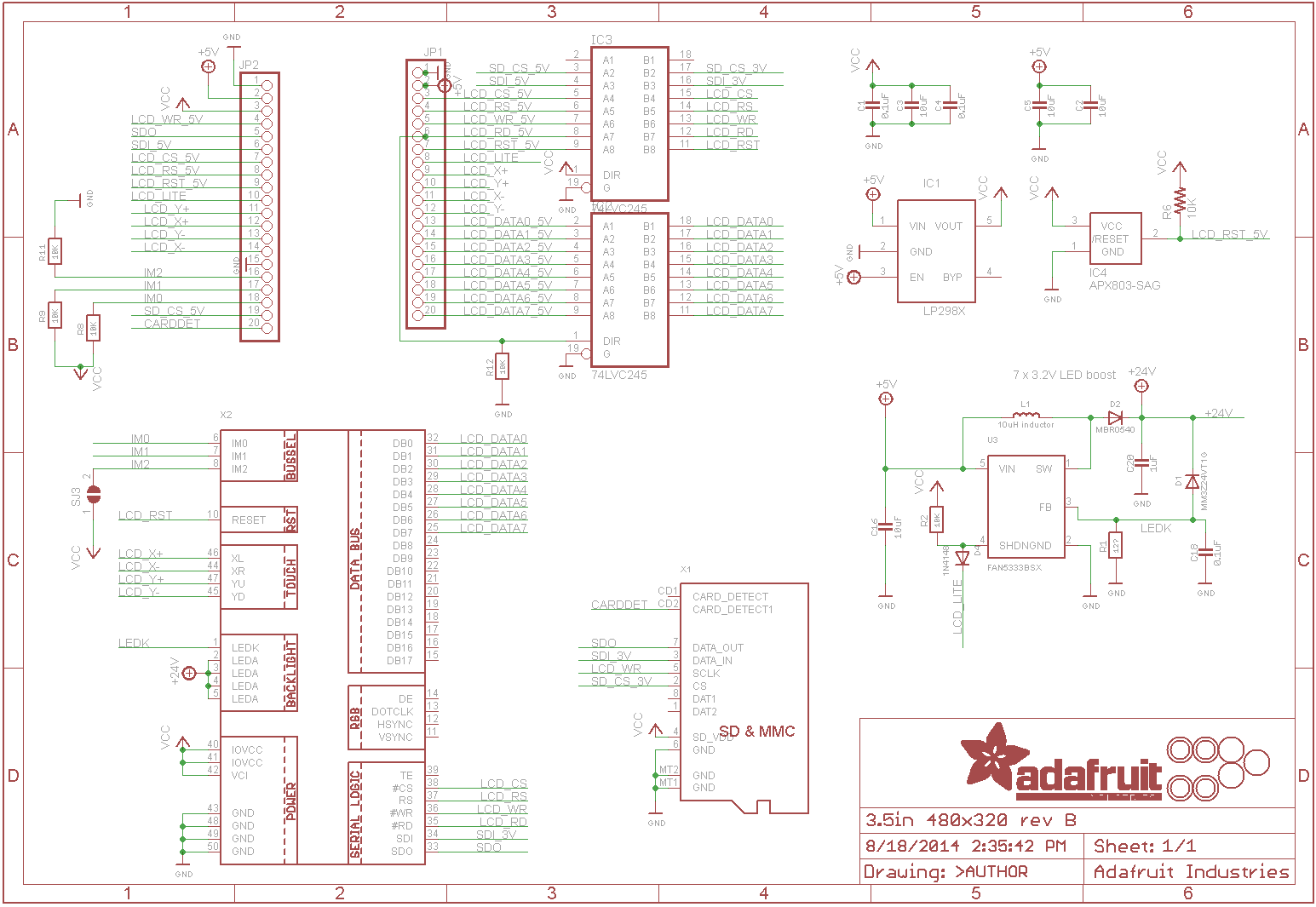
The code I am using is all example code from the arduino SD card library and the adafruit TFTLCD library but here it is. The code below is the tftbmp example with the CS pin changed. This does not work BTW.
// BMP-loading example specifically for the TFTLCD breakout board.
// If using the Arduino shield, use the tftbmp_shield.pde sketch instead!
// If using an Arduino Mega make sure to use its hardware SPI pins, OR make
// sure the SD library is configured for 'soft' SPI in the file Sd2Card.h.
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h> // Core graphics library
#include <Adafruit_TFTLCD.h> // Hardware-specific library
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>
// The control pins for the LCD can be assigned to any digital or
// analog pins...but we'll use the analog pins as this allows us to
// double up the pins with the touch screen (see the TFT paint example).
#define LCD_CS A3 // Chip Select goes to Analog 3
#define LCD_CD A2 // Command/Data goes to Analog 2
#define LCD_WR A1 // LCD Write goes to Analog 1
#define LCD_RD A0 // LCD Read goes to Analog 0
// When using the BREAKOUT BOARD only, use these 8 data lines to the LCD:
// For the Arduino Uno, Duemilanove, Diecimila, etc.:
// D0 connects to digital pin 8 (Notice these are
// D1 connects to digital pin 9 NOT in order!)
// D2 connects to digital pin 2
// D3 connects to digital pin 3
// D4 connects to digital pin 4
// D5 connects to digital pin 5
// D6 connects to digital pin 6
// D7 connects to digital pin 7
// For the Arduino Mega, use digital pins 22 through 29
// (on the 2-row header at the end of the board).
// For Arduino Uno/Duemilanove, etc
// connect the SD card with DI going to pin 11, DO going to pin 12 and SCK going to pin 13 (standard)
// Then pin 10 goes to CS (or whatever you have set up)
#define SD_CS 53 // Set the chip select line to whatever you use (10 doesnt conflict with the library)
// In the SD card, place 24 bit color BMP files (be sure they are 24-bit!)
// There are examples in the sketch folder
// our TFT wiring
Adafruit_TFTLCD tft(LCD_CS, LCD_CD, LCD_WR, LCD_RD, A4);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
tft.reset();
uint16_t identifier = tft.readID();
if(identifier == 0x9325) {
Serial.println(F("Found ILI9325 LCD driver"));
} else if(identifier == 0x9328) {
Serial.println(F("Found ILI9328 LCD driver"));
} else if(identifier == 0x7575) {
Serial.println(F("Found HX8347G LCD driver"));
} else if(identifier == 0x9341) {
Serial.println(F("Found ILI9341 LCD driver"));
} else if(identifier == 0x8357) {
Serial.println(F("Found HX8357D LCD driver"));
} else {
Serial.print(F("Unknown LCD driver chip: "));
Serial.println(identifier, HEX);
Serial.println(F("If using the Adafruit 2.8\" TFT Arduino shield, the line:"));
Serial.println(F(" #define USE_ADAFRUIT_SHIELD_PINOUT"));
Serial.println(F("should appear in the library header (Adafruit_TFT.h)."));
Serial.println(F("If using the breakout board, it should NOT be #defined!"));
Serial.println(F("Also if using the breakout, double-check that all wiring"));
Serial.println(F("matches the tutorial."));
return;
}
tft.begin(identifier);
Serial.print(F("Initializing SD card..."));
if (!SD.begin(SD_CS)) {
Serial.println(F("failed!"));
return;
}
Serial.println(F("OK!"));
bmpDraw("woof.bmp", 0, 0);
delay(1000);
}
void loop()
{
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++) {
tft.setRotation(i);
tft.fillScreen(0);
for(int j=0; j <= 200; j += 50) {
bmpDraw("miniwoof.bmp", j, j);
}
delay(1000);
}
}
// This function opens a Windows Bitmap (BMP) file and
// displays it at the given coordinates. It's sped up
// by reading many pixels worth of data at a time
// (rather than pixel by pixel). Increasing the buffer
// size takes more of the Arduino's precious RAM but
// makes loading a little faster. 20 pixels seems a
// good balance.
#define BUFFPIXEL 20
void bmpDraw(char *filename, int x, int y) {
File bmpFile;
int bmpWidth, bmpHeight; // W+H in pixels
uint8_t bmpDepth; // Bit depth (currently must be 24)
uint32_t bmpImageoffset; // Start of image data in file
uint32_t rowSize; // Not always = bmpWidth; may have padding
uint8_t sdbuffer[3*BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel in buffer (R+G+B per pixel)
uint16_t lcdbuffer[BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel out buffer (16-bit per pixel)
uint8_t buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Current position in sdbuffer
boolean goodBmp = false; // Set to true on valid header parse
boolean flip = true; // BMP is stored bottom-to-top
int w, h, row, col;
uint8_t r, g, b;
uint32_t pos = 0, startTime = millis();
uint8_t lcdidx = 0;
boolean first = true;
if((x >= tft.width()) || (y >= tft.height())) return;
Serial.println();
Serial.print(F("Loading image '"));
Serial.print(filename);
Serial.println('\'');
// Open requested file on SD card
if ((bmpFile = SD.open(filename)) == NULL) {
Serial.println(F("File not found"));
return;
}
// Parse BMP header
if(read16(bmpFile) == 0x4D42) { // BMP signature
Serial.println(F("File size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile));
(void)read32(bmpFile); // Read & ignore creator bytes
bmpImageoffset = read32(bmpFile); // Start of image data
Serial.print(F("Image Offset: ")); Serial.println(bmpImageoffset, DEC);
// Read DIB header
Serial.print(F("Header size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile));
bmpWidth = read32(bmpFile);
bmpHeight = read32(bmpFile);
if(read16(bmpFile) == 1) { // # planes -- must be '1'
bmpDepth = read16(bmpFile); // bits per pixel
Serial.print(F("Bit Depth: ")); Serial.println(bmpDepth);
if((bmpDepth == 24) && (read32(bmpFile) == 0)) { // 0 = uncompressed
goodBmp = true; // Supported BMP format -- proceed!
Serial.print(F("Image size: "));
Serial.print(bmpWidth);
Serial.print('x');
Serial.println(bmpHeight);
// BMP rows are padded (if needed) to 4-byte boundary
rowSize = (bmpWidth * 3 + 3) & ~3;
// If bmpHeight is negative, image is in top-down order.
// This is not canon but has been observed in the wild.
if(bmpHeight < 0) {
bmpHeight = -bmpHeight;
flip = false;
}
// Crop area to be loaded
w = bmpWidth;
h = bmpHeight;
if((x+w-1) >= tft.width()) w = tft.width() - x;
if((y+h-1) >= tft.height()) h = tft.height() - y;
// Set TFT address window to clipped image bounds
tft.setAddrWindow(x, y, x+w-1, y+h-1);
for (row=0; row<h; row++) { // For each scanline...
// Seek to start of scan line. It might seem labor-
// intensive to be doing this on every line, but this
// method covers a lot of gritty details like cropping
// and scanline padding. Also, the seek only takes
// place if the file position actually needs to change
// (avoids a lot of cluster math in SD library).
if(flip) // Bitmap is stored bottom-to-top order (normal BMP)
pos = bmpImageoffset + (bmpHeight - 1 - row) * rowSize;
else // Bitmap is stored top-to-bottom
pos = bmpImageoffset + row * rowSize;
if(bmpFile.position() != pos) { // Need seek?
bmpFile.seek(pos);
buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Force buffer reload
}
for (col=0; col<w; col++) { // For each column...
// Time to read more pixel data?
if (buffidx >= sizeof(sdbuffer)) { // Indeed
// Push LCD buffer to the display first
if(lcdidx > 0) {
tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first);
lcdidx = 0;
first = false;
}
bmpFile.read(sdbuffer, sizeof(sdbuffer));
buffidx = 0; // Set index to beginning
}
// Convert pixel from BMP to TFT format
b = sdbuffer[buffidx++];
g = sdbuffer[buffidx++];
r = sdbuffer[buffidx++];
lcdbuffer[lcdidx++] = tft.color565(r,g,b);
} // end pixel
} // end scanline
// Write any remaining data to LCD
if(lcdidx > 0) {
tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first);
}
Serial.print(F("Loaded in "));
Serial.print(millis() - startTime);
Serial.println(" ms");
} // end goodBmp
}
}
bmpFile.close();
if(!goodBmp) Serial.println(F("BMP format not recognized."));
}
// These read 16- and 32-bit types from the SD card file.
// BMP data is stored little-endian, Arduino is little-endian too.
// May need to reverse subscript order if porting elsewhere.
uint16_t read16(File f) {
uint16_t result;
((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB
((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); // MSB
return result;
}
uint32_t read32(File f) {
uint32_t result;
((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB
((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read();
((uint8_t *)&result)[2] = f.read();
((uint8_t *)&result)[3] = f.read(); // MSB
return result;
}