I was trying the fading example and experimenting with 2 LEDs and although it works but I couldn't get the required half cycle.
int ledPin = 5;
int ledPin2 = 3;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// fade in from min to max in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 0 ; fadeValue <= 255; fadeValue = fadeValue+5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
// fade out from max to min in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 255 ; fadeValue >= 0; fadeValue = fadeValue-5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
// fade in from min to max in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 0 ; fadeValue <= 255; fadeValue = fadeValue+5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin2, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
// fade out from max to min in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 255 ; fadeValue >= 0; fadeValue = fadeValue-5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin2, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
}
My code works like red LED glows and fades and then green LED glows and fades. When red LED is on the green will be off and vice-versa. What I want is to get the red LED to glow and when it reaches full bright on then the green must slowly start glowing and when the red is faded completely then the green must glow bright fully.
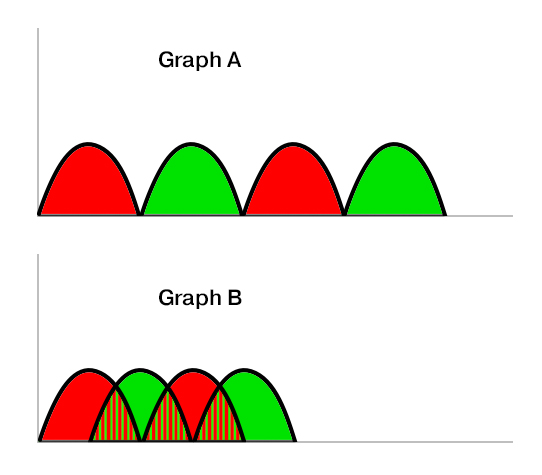
I'm explain it better with a graph.
Graph A shows how my code works
Graph B is what I want to do. Is it possible to do that?